Method of repairing human articular cartilage based on 3D bioprinting
A bioprinting, articular cartilage technology, applied in tissue regeneration, medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of cartilage degeneration tissue transplantation, cartilage necrosis, failure and other problems, achieve low cytotoxicity, simple and fast operation, and accurate operation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
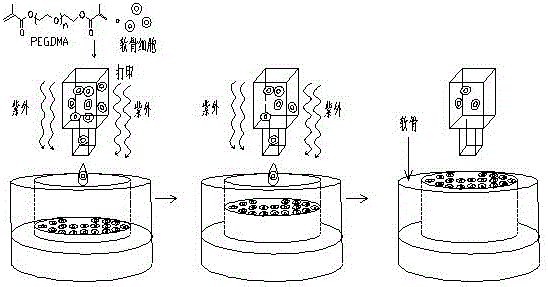
[0025] like figure 1 As shown, the present invention discloses a method for repairing human articular cartilage based on 3D bioprinting, comprising the following steps:
[0026] Preparation of PEGDMA
[0027] 3 kDa PEG (polyethylene glycol) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran and PEG was reacted with methacryloyl chloride overnight under nitrogen. The synthesized PEGDMA (polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate) macromonomer was purified by ether precipitation and overnight freeze-drying, and detected by proton nuclear magnetic resonance to ensure that the purity of the synthesized PEGDMA macromonomer was greater than 95%.
[0028] Human mesenchymal stem cell isolation
[0029] Take the healthy adult bone marrow fluid under sterile conditions, add an equal volume of PBS, and disperse the cells by pipetting. The cells were collected by centrifuging 300 g of bone marrow PBS mixture for 5 min at room temperature. Cells were resuspended in PBS and counted. Take 300 g of bone marrow PB...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com