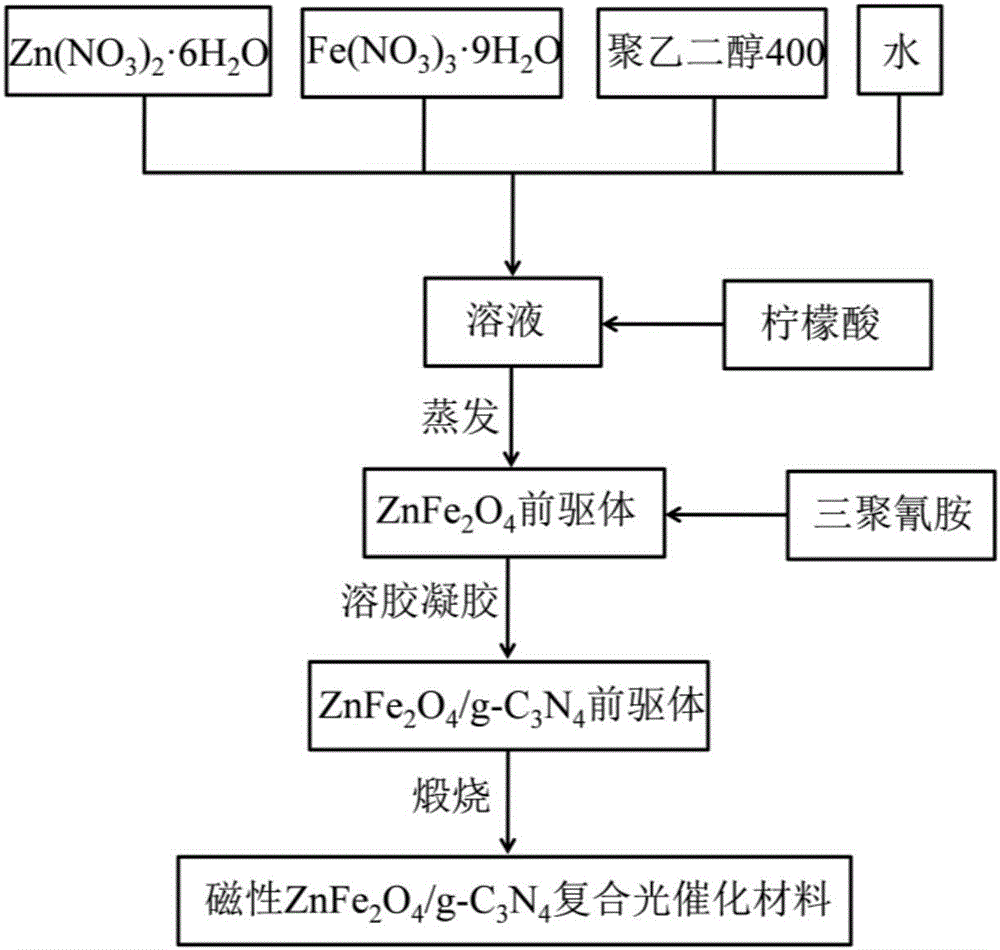
A method of preparing a magnetic ZnFe<2>O4/g-C3N4 composite photocatalytic material
A composite photocatalysis and znfe2o4 technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical/physical processes, etc., can solve the problem of high photogenerated electron-hole recombination rate, single function, and low recyclability and other problems, to achieve the effect of increasing recyclability, easy operation, and increasing composite catalytic activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] (1) Weigh 2.97g Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O and 8.08g Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O, add 2g of polyethylene glycol 400 (Xilong Chemical Industry, CP 500ml) and 20g of water into the mixed solution and stir to mix, place in a 30°C water bath and stir for 1h to form a mixed solution;
[0025] (2) Weigh 5.8g of citric acid and add it to the mixed solution obtained in step (1), place it in a water bath at 80°C and stir for 1.5h to obtain viscous ZnFe 2 o 4 Precursor;
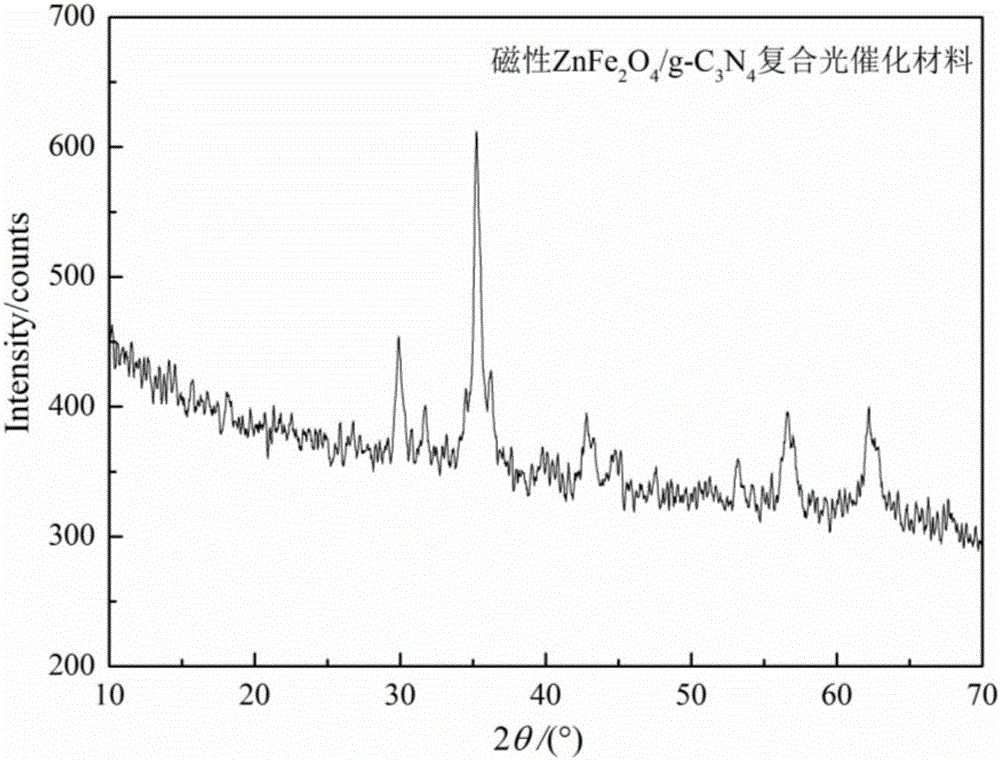
[0026] (3) Weigh 4.8g of melamine and add it to the viscous ZnFe2O4 precursor obtained in step (2), place it in a water bath at 85°C and continue stirring for 1h to obtain a porous solid, and then dry the porous solid in an oven at 120°C After 12 hours, calcine in a muffle furnace at 550°C for 3 hours to obtain magnetic ZnFe 2 o 4 / g -C 3 N 4 Composite photocatalytic material 2.31g. figure 1 The ZnFe with magnetic and photocatalytic activity prepared for this example 2 o 4 / g -C 3 N 4 XRD patterns of composite p...
Embodiment 2
[0028] (1) Weigh 1.49g Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O and 4.04g Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O, add 1.5g Polyethylene Glycol 400 (Xilong Chemical Industry, CP 500ml) and 12g water mixed solution and stir to mix, place in 40 ℃ water bath and stir for 0.5h to form mixed solution;
[0029] (2) Weigh 2.88g of citric acid and add it to the mixed solution obtained in step (1), place it in a water bath at 85°C and stir for 1h to obtain viscous ZnFe 2 o 4 Precursor;
[0030] (3) take by weighing 2.5g melamine and join the viscous shape ZnFe that step (2) obtains 2 o 4 Put the precursor in a 90°C water bath and continue to stir for 0.5h to obtain a porous solid, then dry the porous solid in an oven at 110°C for 8h, and then calcinate it in a muffle furnace at 560°C for 3h to obtain magnetic ZnFe 2 o 4 / g -C 3 N 4 Composite photocatalytic material 1.3g.
Embodiment 3
[0032] (1) Weigh 2.97g Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O and 8.08g Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O, add 2.5g Polyethylene Glycol 400 (Xilong Chemical Industry, CP 500ml) and 22g water mixed solution and stir to mix, place in 35 ℃ water bath and stir for 1h to form mixed solution;
[0033] (2) Weigh 5.8g of citric acid and add it to the mixed solution obtained in step (1), place it in a water bath at 80°C and stir for 1.5h to obtain viscous ZnFe 2 o 4 Precursor;
[0034] (3) take by weighing 5.0g melamine and join the viscous shape ZnFe that step (2) obtains 2 o 4 Put the precursor in a water bath at 90°C and continue to stir for 1 hour to obtain a porous solid, then dry the porous solid in an oven at 130°C for 12 hours, and then calcinate it in a muffle furnace at 600°C for 3 hours to obtain magnetic ZnFe 2 o 4 / g -C 3 N 4 Composite photocatalytic material 2.38g.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com