Method for quickly making models of diabetic mice
A technology of mouse model and diabetes, which is applied in the fields of pharmaceutical formula and drug delivery, can solve the problems of low molding rate, difficult to control dosage, and low molding rate of mice
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0007] 1 experimental equipment
[0008] Blood glucose tester (China Sinocare Biosensing Co., Ltd., blood glucose test strips, batch number: 2610NK), precision electronic balance (Mettler-Toledo Instruments (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.), 1ml syringe (Guangxi Beilunhe Medical Industry Group) Ltd.) etc.
[0009] 2 Experimental animals and materials
[0010] Animals: male KM mice, clean grade, weighing 24±2g, provided by the Experimental Animal Center of Guangxi Medical University, license number: SCXK Gui 2014-0002.
[0011] Materials: Alloxan (US Sigma Company, batch number: BCBN9150V), normal saline, etc.
[0012] 3 Experimental methods
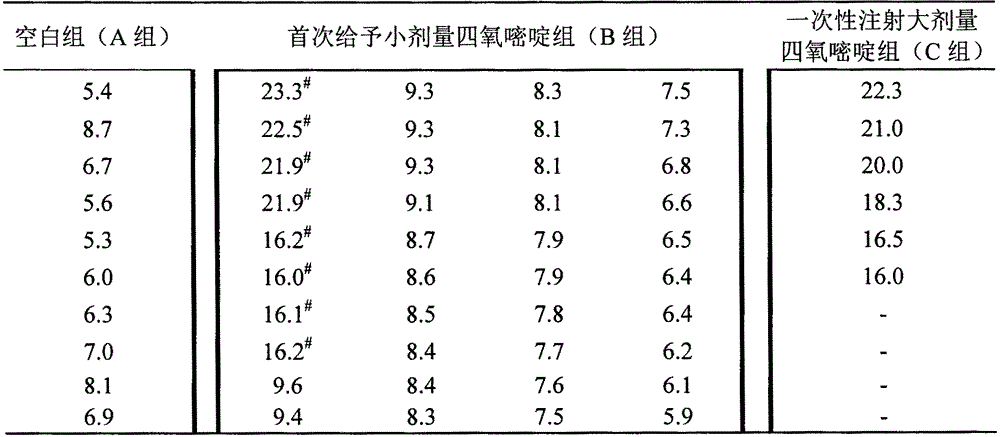
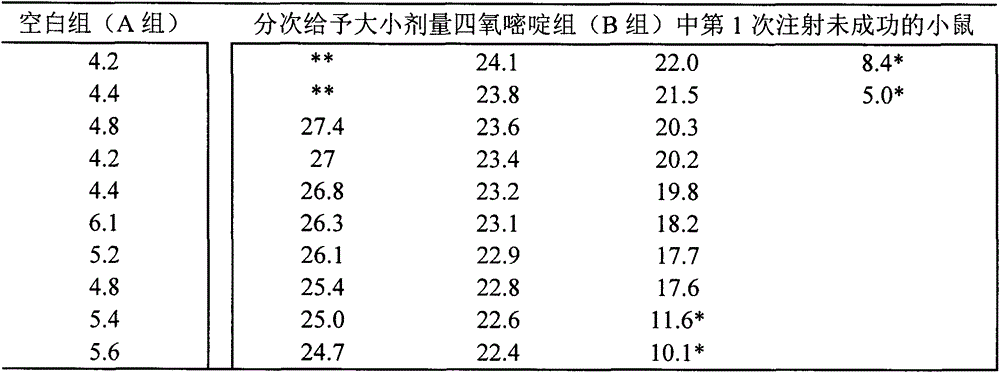
[0013] Purchase 60 male KM mice with a body weight of 24±2g. The temperature of the feeding environment is 26±3°C and the humidity is about 50-60%. hours (must be replaced with new bedding every time fasting and water, the same below), were randomly divided into 3 groups according to body weight: A group, B group, and C group, A group was 10 norm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com