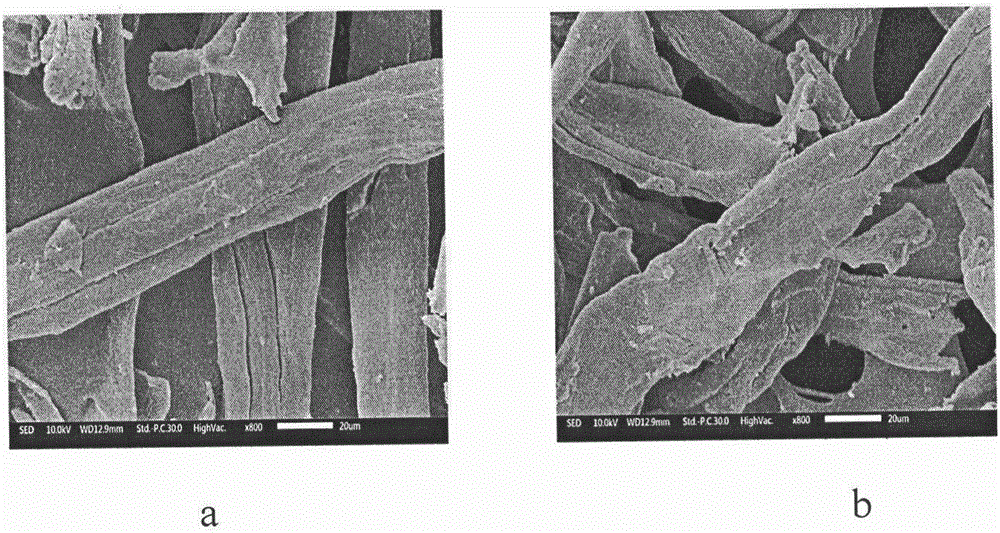
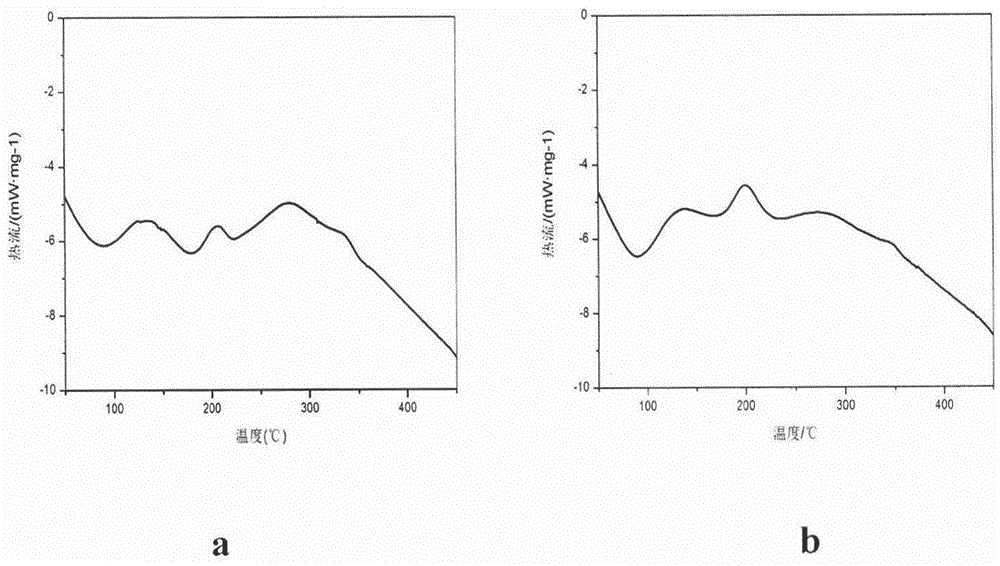
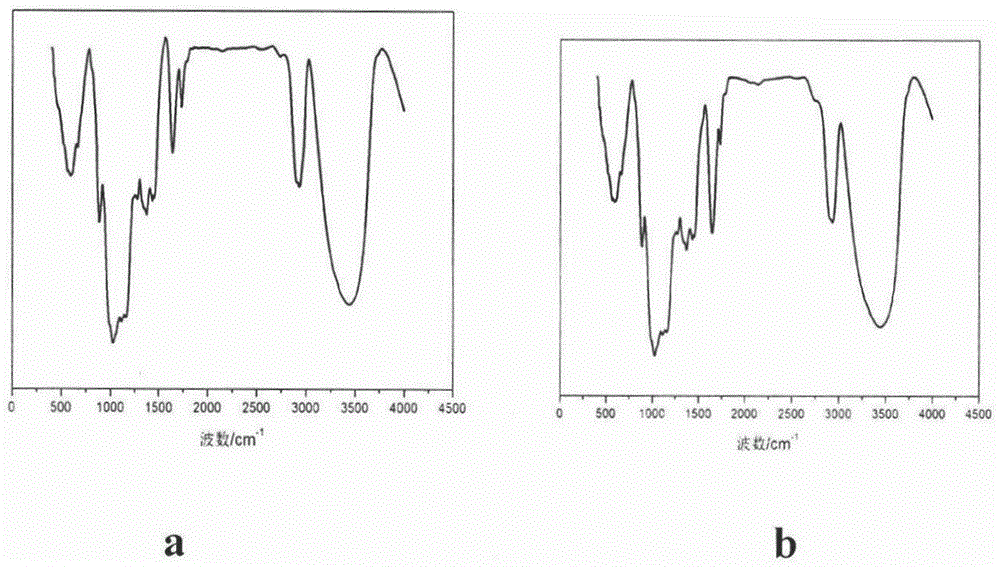
Method for removing protein in polysaccharide extraction liquid by dialdehyde cellulose
A dialdehyde cellulose and protein technology, applied in the innovative field of deproteinization method, can solve the problems of affecting efficacy, destroying the structure of proteoglycan complex, and weakening the resolubility of polysaccharides, so as to avoid waste and residue, improve deproteinization rate, The effect of low degradability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0026] (1) Preparation of dialdehyde cellulose: Weigh coniferous wood or broad-leaved wood cellulose powder, add sodium periodate and deionized water, adjust pH=3, and react in a water bath at 30°C for a certain period of time in the dark, and the degree of oxidation is different The dialdehyde cellulose is dried and ground into powder for later use.
[0027] (2) According to the procedures of hot water extraction, concentration, alcohol precipitation, filtration and drying, the crude polysaccharides of yam, ganoderma lucidum and astragalus are obtained;
[0028] (3) All three polysaccharides were deproteinized by Sevage method, and compared with dialdehyde cellulose method. Sevage method: Add 10 mL of Sevage reagent (chloroform:n-butanol=4:1) to the crude polysaccharide solution at a volume ratio of 5:1, shake for 20 min, and centrifuge to remove denatured protein at the junction of the water layer and the reagent layer. This step was repeated 7 times.
Embodiment 1
[0031] 1) Move the yam crude polysaccharide into a reaction tank, add purified water to prepare a polysaccharide solution with a mass fraction of 1%, and prepare dialdehyde cellulose prepared from coniferous wood for use;
[0032] 2) Add 20g of dialdehyde cellulose with an oxidation degree of 78% to 1L of yam polysaccharide solution, control the range of solid-liquid ratio to 4:200 (g / mL), adjust the pH value to 8, mix well, and react at a constant temperature of 40°C for 4 hours, after the reaction was completed, the supernatant was obtained by cooling and centrifugation; the above operation was repeated 3 times to obtain the polysaccharide solution after deproteinization. Taking the deproteinization rate as an index, compared with the Sevage method, the deproteinization rate reached 88.35% after the dialdehyde cellulose deproteinization for 4 times; and the deproteinization rate reached 74.38% after the Sevage method 4 times.
Embodiment 2
[0034] 1) Move the crude polysaccharide of yam into a reaction tank, add purified water to prepare a polysaccharide solution with a mass fraction of 2%, and prepare dialdehyde cellulose prepared from hardwood as a raw material for use;
[0035] 2) Add 5g of dialdehyde cellulose with an oxidation degree of 23% to 1L of yam polysaccharide solution, control the range of solid-liquid ratio to 1:200 (g / mL), adjust the pH value to 7, mix well, and react at a constant temperature of 20°C for 8 Hours, after the reaction is completed, the polysaccharide solution after deproteinization is obtained by cooling and centrifuging. Taking the deproteinization rate as an index, compared with the Sevage method, the deproteinization rate reached 49.87% after one deproteinization by the dialdehyde cellulose method; and 47.93% after one deproteinization by the Sevage method.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com