Blue-green algae harmless disposal and recycling treatment method
A treatment method and technology for recycling, applied in the field of harmless disposal and recycling of cyanobacteria, which can solve the problems of unreported and unreported tertiary degradation, and achieve harmless disposal and recycling and processing speed. High, low algal toxin residue effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
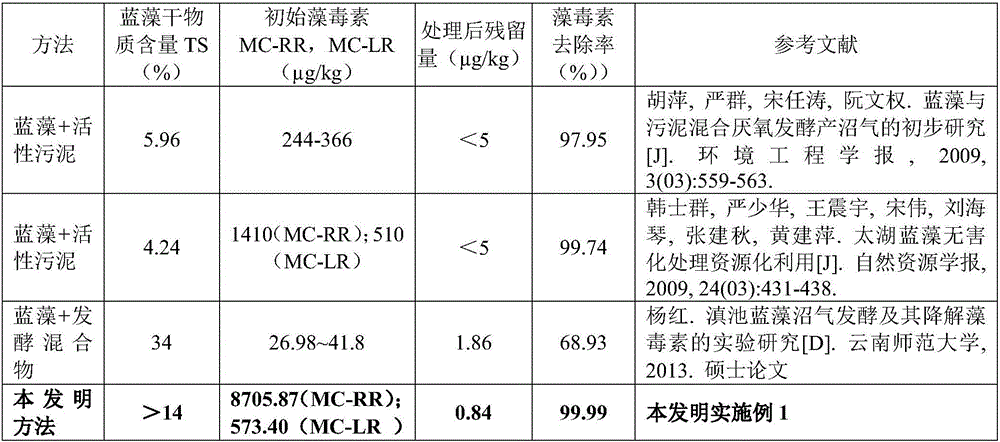
[0067] Example 1 Algae toxin efficient degradation
[0068] Algal toxins have a strong carcinogenic effect, and algal toxins in cyanobacteria are the bottleneck of their resource utilization. The technical solution of the present invention adopting the three-stage algae toxin degradation step can effectively reduce the algae toxin residue in biogas residue and biogas slurry.
[0069] The target cyanobacteria material used in this embodiment has a high dry matter content (TS%), greater than 14%, and its algal toxin content is particularly high. The algal toxin MC-RR concentration is 8705.87 μg / kg, and the MC-LR concentration is 573.40 μg / kg kg, much higher than the target cyanobacterial toxin content reported in the existing literature.
[0070] In this embodiment, after the target cyanobacteria material is treated with the technical solution of the present invention, the removal rate of algae toxins is over 99.99%, and the content of algae toxins in biogas residue and biogas ...
Embodiment 2
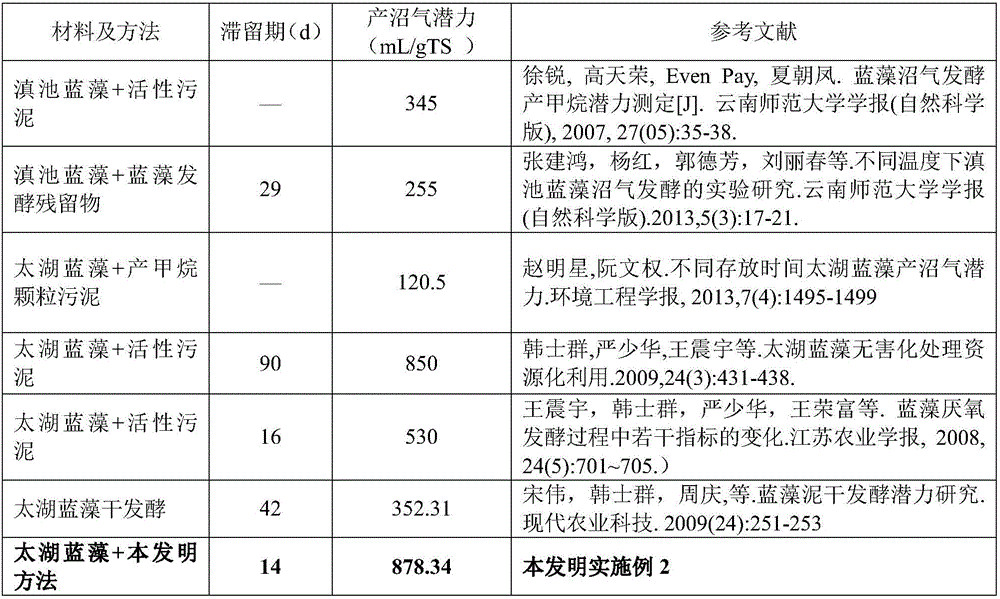
[0074] Example 2 Biogas production potential
[0075] The key factors that determine the fermentation efficiency and economic benefits of cyanobacteria are the fermentation residence period and the biogas production potential (gas production per unit dry matter). The retention period refers to the processing cycle. If the method of the present invention is completely executed once from the first step to the fourth step, it is a processing cycle, and its length is the length of the retention period. The shorter the retention period, the shorter the time the equipment is occupied, and the higher the production efficiency. Biogas production potential determines the biogas production efficiency of fermented materials, and the higher the biogas production potential, the higher the efficiency.
[0076] The residence period of this example is about 14 days on average, which is shorter than other treatment methods reported in the existing literature, can make full use of fermentation e...
Embodiment 3
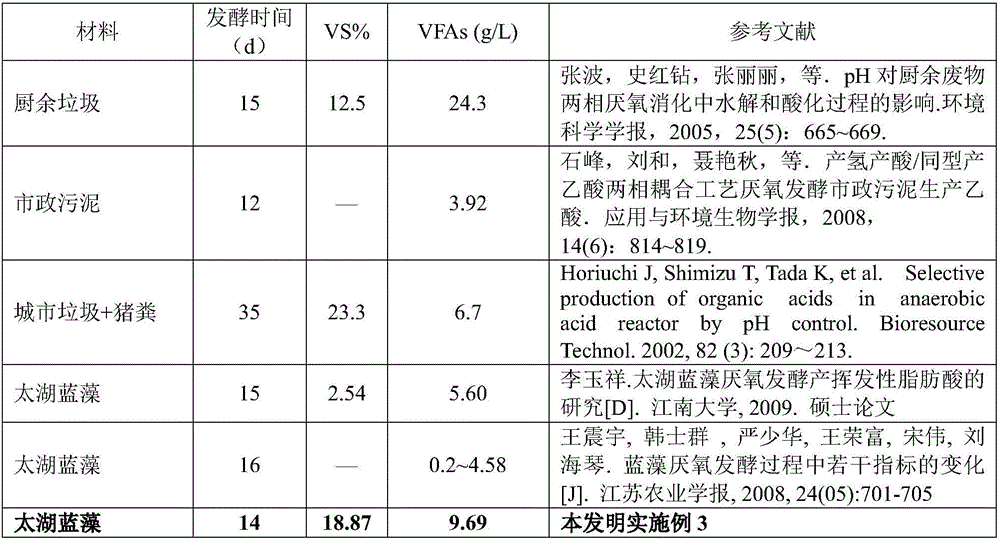
[0079] Embodiment 3 produces volatile fatty acid VFAs
[0080] During microbial anaerobic fermentation, volatile fatty acids (VFAs) are not only an indispensable nutrient but also a raw material for methanogenesis. The content of VFAs in anaerobic fermentation research is a symbolic parameter of the quality of organic matter degradation process conditions, and its content is positively correlated with methane production.
[0081] In this example, before the biogas production by dry fermentation is about to enter the gas production stage, the material contains more VFAs. Although its content is lower than that of kitchen waste that contains fat itself, it is much higher than other Taihu cyanobacteria fermentation processes reported in existing literature. (as shown in Table 3). It can be seen that the technical scheme of the present invention can make Taihu Lake cyanobacteria contain more volatile fatty acids (VFAs) when dry fermentation produces biogas and is about to enter t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com