Wavelength conversion device, light emitting device and projecting device
A wavelength conversion device and light-emitting layer technology, which is applied in the field of laser display technology and lighting, can solve the problems of heat accumulation in the light-emitting layer, long heat propagation path, and reduced conversion efficiency, so as to reduce heat, shorten heat propagation distance, and avoid heat. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
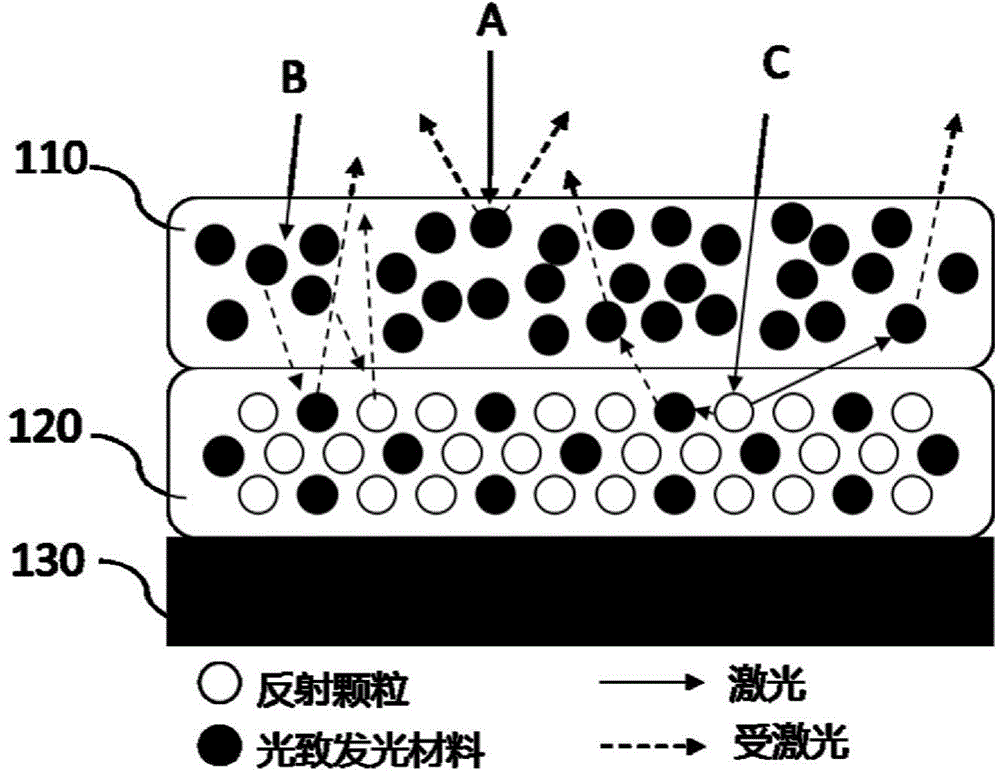
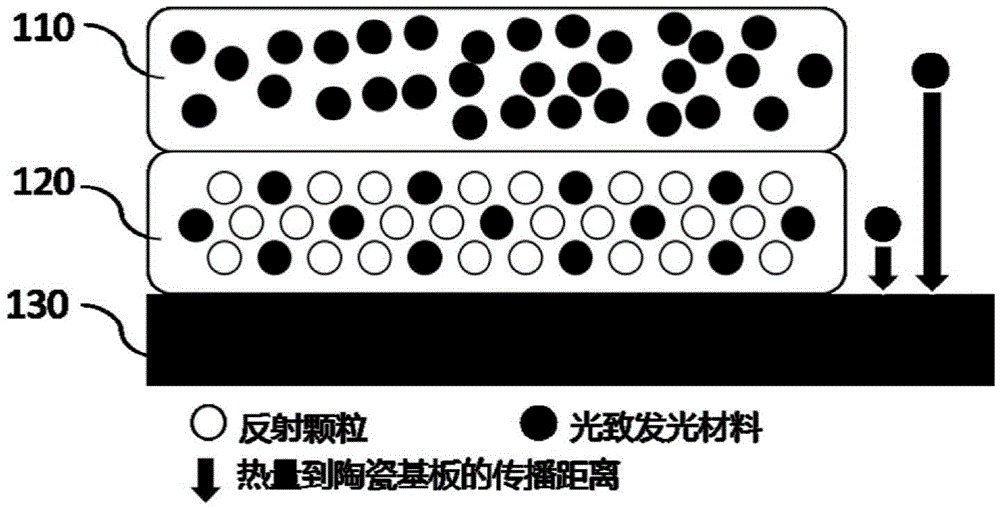
[0032] See figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic structural diagram of a wavelength conversion device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The wavelength conversion device includes a light emitting layer 110 , a reflective layer 120 and a thermally conductive substrate 130 .
[0033] The light emitting layer 110 includes a first photoluminescent material and a first adhesive. The black solid balls in the luminescent layer 110 in the figure represent phosphor particles of the first photoluminescent material, which may be any one of yellow phosphor, green phosphor, orange phosphor, and red phosphor. The first photoluminescent material is encapsulated into a layer by the first adhesive, and distributed uniformly or substantially uniformly in the continuum formed by the first adhesive. The first binder in the present invention is an inorganic binder, specifically, the inorganic binder is a first glass frit. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the ...
Embodiment 2
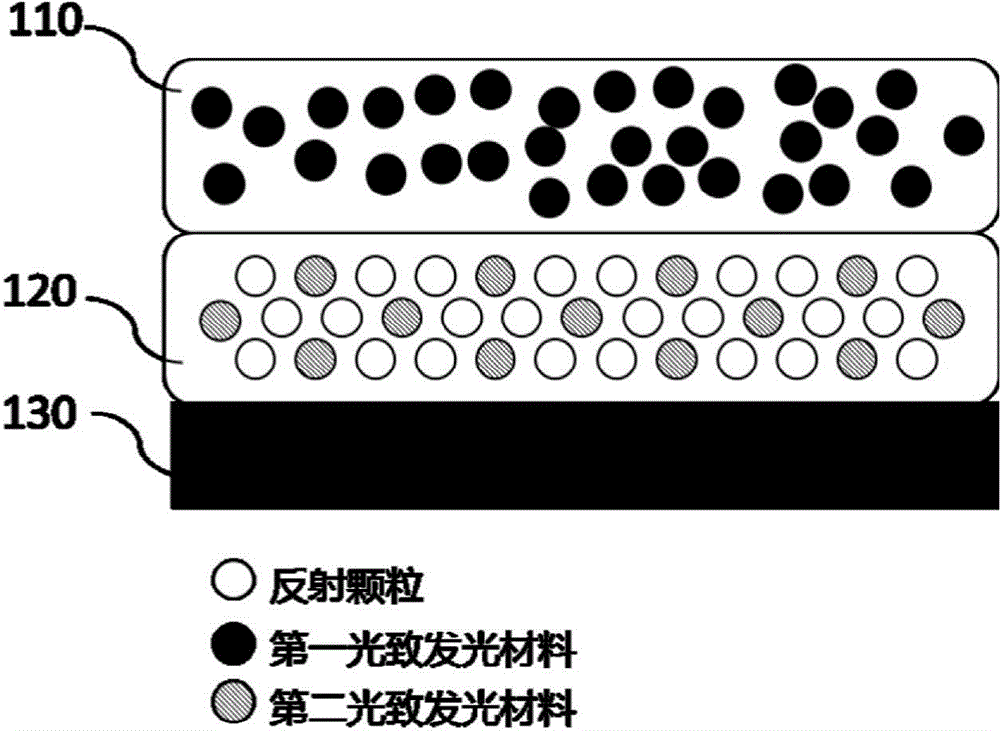
[0049] See image 3 , image 3 It is a schematic structural diagram of the wavelength conversion device of Embodiment 2 of the present invention. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is only that the second photoluminescent material in the reflective layer 120 (shown by the hatched ball in the figure) is in contact with the light emitting material. The first photoluminescent material in the layer 110 (the black solid ball in the figure) is different, and the light emitted by the first photoluminescent material can excite the second photoluminescent material and emit light with a longer wavelength.
[0050] After the first photoluminescent material is excited by the excitation light, the energy of the emitted light is reduced and the wavelength becomes longer. The heat generated by the second photoluminescent material excited by the light is much larger than that of the second photoluminescent material directly excited by the excitation light. reduce. Among...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Such as Figure 4 Shown is a schematic structural view of the color wheel in Embodiment 3 of the present invention, 4a is a cross-sectional view of the color wheel, and 4b is a top view of the color wheel. The color wheel is a circular color wheel, including a light emitting layer 110 , a reflective layer 120 and a ceramic substrate 130 . The structural composition of the light emitting layer 110 , the reflective layer 120 and the ceramic substrate 130 can refer to the description of the wavelength conversion device in the first and second embodiments above.
[0055] In this embodiment, the luminous layer 110, the reflective layer 120 and the ceramic substrate 130 are all annular structures, and in a modified embodiment of the present invention, the luminescent layer 110, the reflective layer 120 and the ceramic substrate 130 can be solid circular layer structure. The light-emitting layer 110 and the reflective layer 120 may each have a fan-ring structure, for example...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com