Method for culturing red algae with high-yield phycocyanin
A cultivation method and phycocyanin technology, applied in the field of efficient red algae cultivation, can solve the problems of unregulated, long doubling time, low efficiency, etc., and achieve the reduction of the number of devices and equipment, high metabolite yield, and improved cultivation. effect of speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0170] Example 1: Research on algae cell growth during heterotrophic and photoautotrophic culture of red algae
[0171] This example is used to compare the culture results of heterotrophic, polytrophic and photoautotrophic red algal cells. The red algae cells used in this example are red algae Galdieria sulphuraria 074G.
[0172] Heterotrophic and polyculture shake flask medium composition: (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 5 g / L, Glucose 35 g / L, KH 2 PO 4 0.2 g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.3 g / L, CaCl 2 2H 2 O 0.01 g / L, NaCl 0.01 g / L, Fe-EDTA 0.1 g / L, abscisic acid 0.1 mg / L, gibberellin 0.1 mg / L, brassin 1 mg / L, trace elements 2ml and water, of which The composition of trace elements is H 3 BO3 5 mg / L, MnCl 2 4H 2 O 5 mg / L, ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 1 mg / L, (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 O 1 mg / L, CuSO 4 ·5H 2 O 0.5 mg / L, NaVO 3 4H 2 O 0.1 mg / L, CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O 0.1 mg / l.
[0173] Photoautotrophic shake flask medium composition: (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 5 g / L, KH 2 PO 4 0.2 g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O...
Embodiment 2
[0177] Embodiment 2: Red algae is compared in the heterotrophic culture process in the bioreactor of different levels
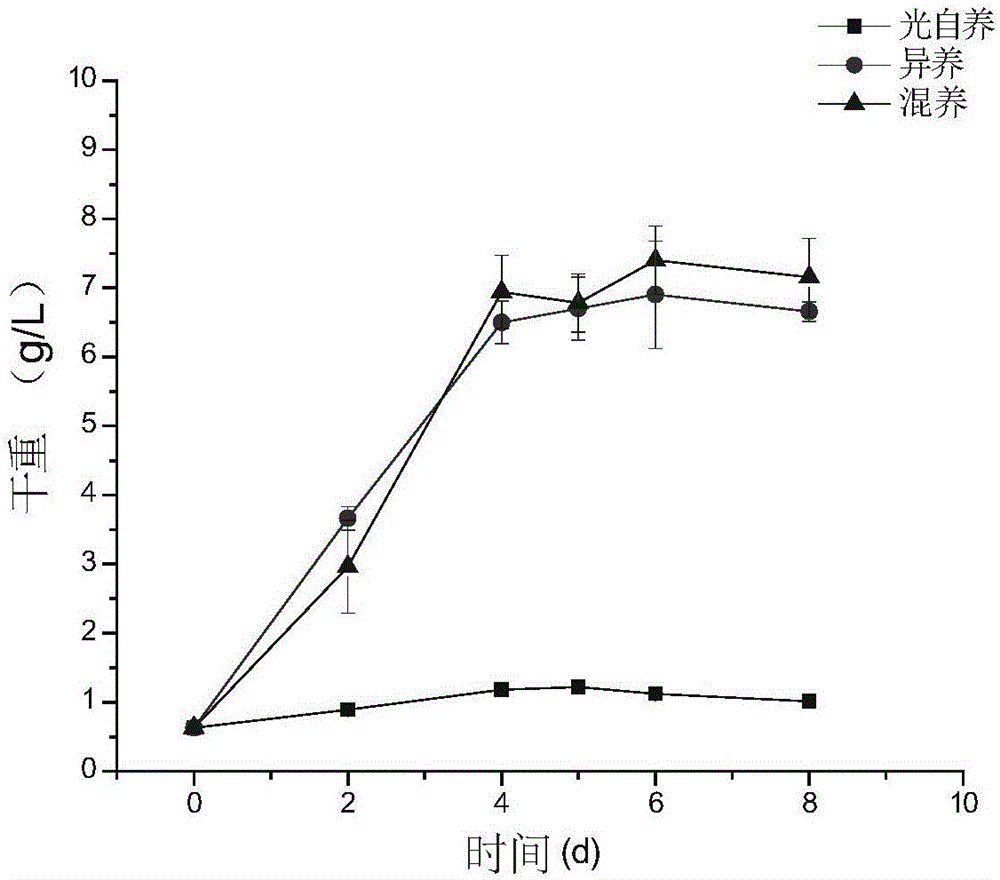
[0178] This example is used to compare the results of heterotrophic culture of red algae cells in different levels of bioreactors. The bioreactors in this example are 1L and 5L shake flasks, and the red algae cells used in this example are red algae Galdieriasulphuraria 074G.
[0179] The inoculum density of red algae 1L and 5L shake flask heterotrophic culture is 0.52g / l, the temperature is 40°C, and the rotation speed is 150rmp. After 8 days of heterotrophic culture of red algae, the glucose in the culture medium was exhausted, and the final algal cell densities of 1L and 5L shake flasks were 8.23g / l and 8.40g / L, respectively, which could be used as seeds for the next photoautotrophic culture. The results are shown in figure 2 , the standard deviation in the figure is the result of 3 independent separate experiments.
[0180] Add the heterotrophic med...
Embodiment 3
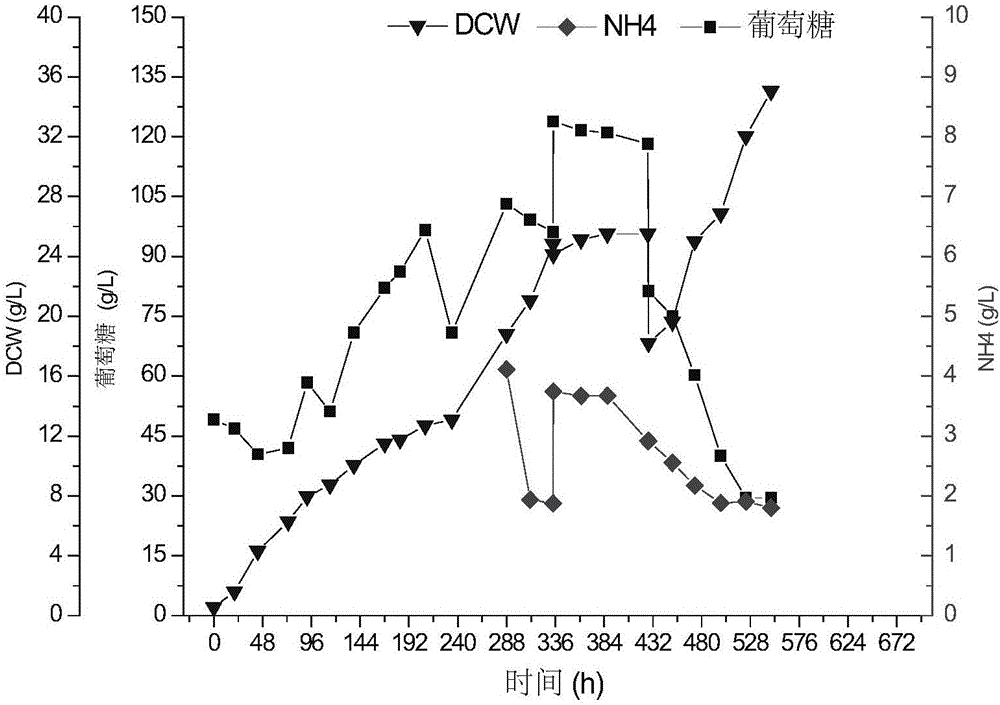
[0183] Embodiment 3: red algae heterotrophic seeds and photoautotrophic seeds are carried out photobioreactor in indoor 1L glass column photobioreactor Research on Autotrophic Culture
[0184] This example was carried out in an indoor 1L cylindrical airlift photobioreactor, and algae cells obtained under heterotrophic and photoautotrophic culture conditions were used as seeds respectively, wherein the heterotrophic algal cells were the cells obtained in Example 2. In this example, the dry weight and phycocyanin content of heterotrophic and photoautotrophic seeds were measured respectively during the photoautotrophic process.
[0185] The inoculation density of heterotrophic and photoautotrophic seeds is 0.5g / l, the temperature of photoautotrophic culture is 40℃, and 5% CO 2 , The ventilation volume is 0.25vvm. In photoautotrophic culture, the light intensity was 250 μmolm -2 the s -1 , continuous light. After photoautotrophic culture to 8 days, the dry weight of hetero...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Cell density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Inoculation density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com