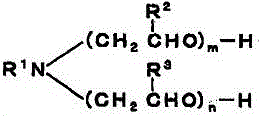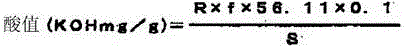Polyester synthetic fiber textile treatment agent, polyester synthetic fiber treatment method and polyester-based synthetic fiber
A synthetic fiber and treatment agent technology, which is applied to the polyester-based synthetic fiber textile treatment agent, the polyester-based synthetic fiber treatment and the polyester-based synthetic fiber field, can solve the problem of inability to cope, insufficient uniformity of the fiber web, and resistance to winding. Rolling resistance, scum build-up resistance and insufficient loop formation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] Hereinafter, examples and the like are given to clarify the configuration and effect of the present invention, but the present invention is not limited to these examples. It should be noted that in the following examples and comparative examples, parts mean parts by mass, and % means % by mass.
[0040] Test Category 1 (Preparation of Aqueous Liquid Treatment Agent for Polyester Synthetic Fiber Textile)
[0041] ・Preparation of an aqueous solution of a treatment agent for polyester-based synthetic fiber textiles (Example 1)
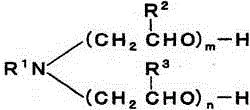
[0042] 60 parts of octadecyl phosphate potassium salt (acid value 10KOHmg / g) (A-1), α-nonylphenyl-ω-hydroxyl (polyoxyethylene) (10 moles) and α-dodecyl Amino-ω-hydroxyl (polyoxyethylene) (10 moles) 70:30 (mass ratio) mixture (B-1) 20 parts, and octadecyl phosphate and polyoxyethylene (m+n=4) dodecane 20 parts of the salt (C-1) of aminoether was added under stirring to half the amount of ion-exchanged water heated to 80° C., and dissolved complete...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Acid value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com