Electro-optical modulator using ribbed waveguides
A silicon waveguide, conductive type technology, applied in the field of light modulation, can solve the problem of reducing the effectiveness of electro-optical devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] overview
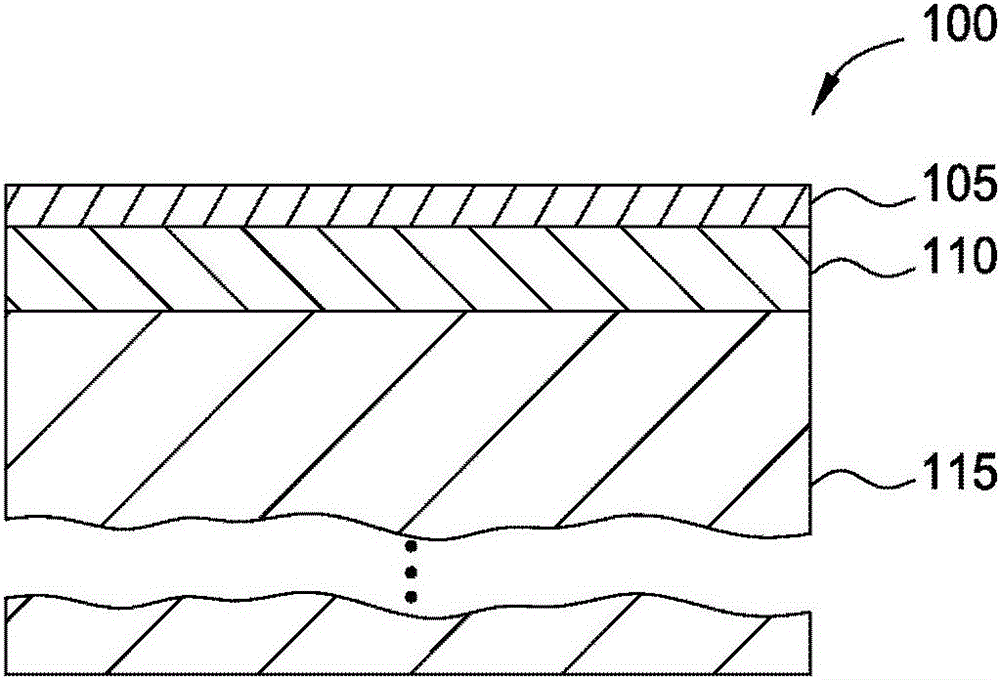
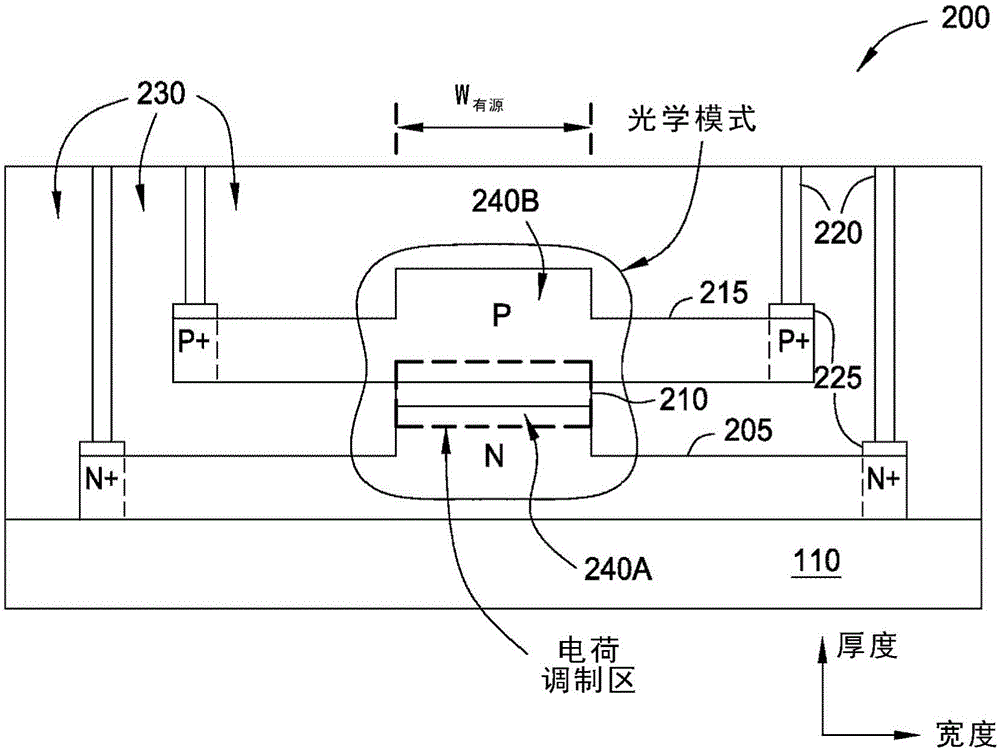
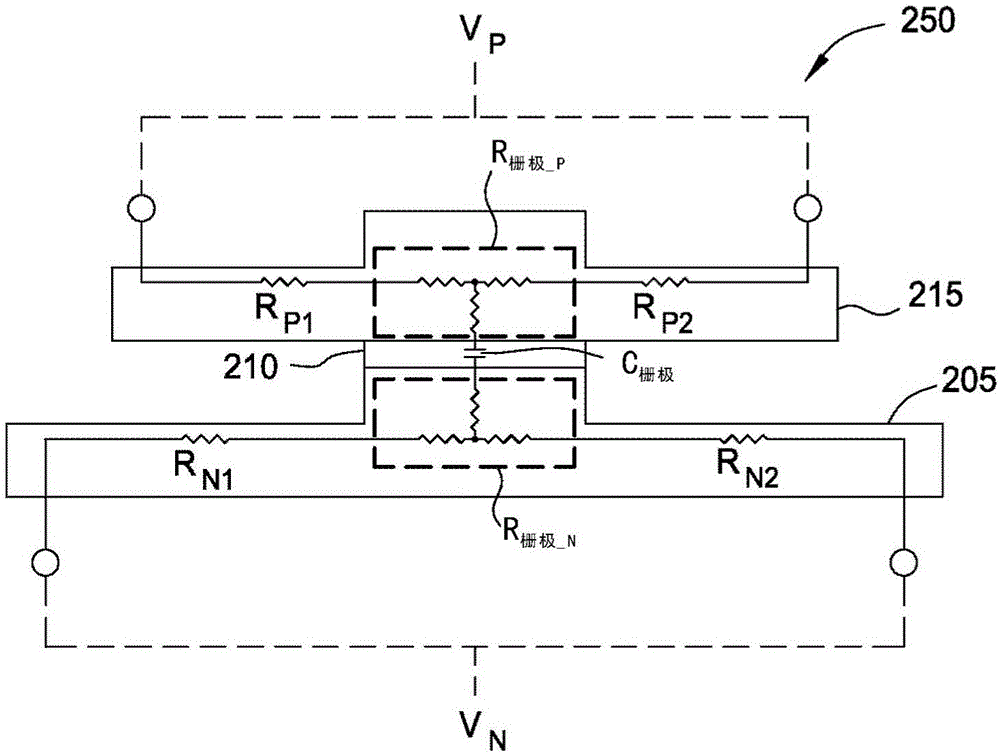
[0021] One embodiment presented by the present disclosure is an optical device comprising a first silicon waveguide disposed on a dielectric base layer, wherein the first silicon waveguide comprises a first ridge extending in the direction of the optical path. The optical device includes a dielectric layer having a lower surface disposed on the upper surface of the first ridge; and a second silicon waveguide disposed on the dielectric layer opposite to the lower surface of the dielectric layer. on the upper surface. The second silicon waveguide includes a second ridge extending in the direction of the light path and overlapping both the dielectric layer and the first ridge. Furthermore, the first silicon waveguide is doped with a first conductivity type and the second silicon waveguide is doped with a second different conductivity type. The optical device also includes a first electrical contact coupled to the first silicon waveguide and a second electric...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com