A method for group division of Chinese giant salamander based on mitochondrial DNA sequence
A DNA sequence and group division technology, applied in the field of biological identification, can solve the problems of no group markers, difficult group division standards, unstable body surface patterns, etc., and achieve the effect of low experimental operation cost, easy operation and easy mastery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0041] (1) Sample collection and DNA extraction
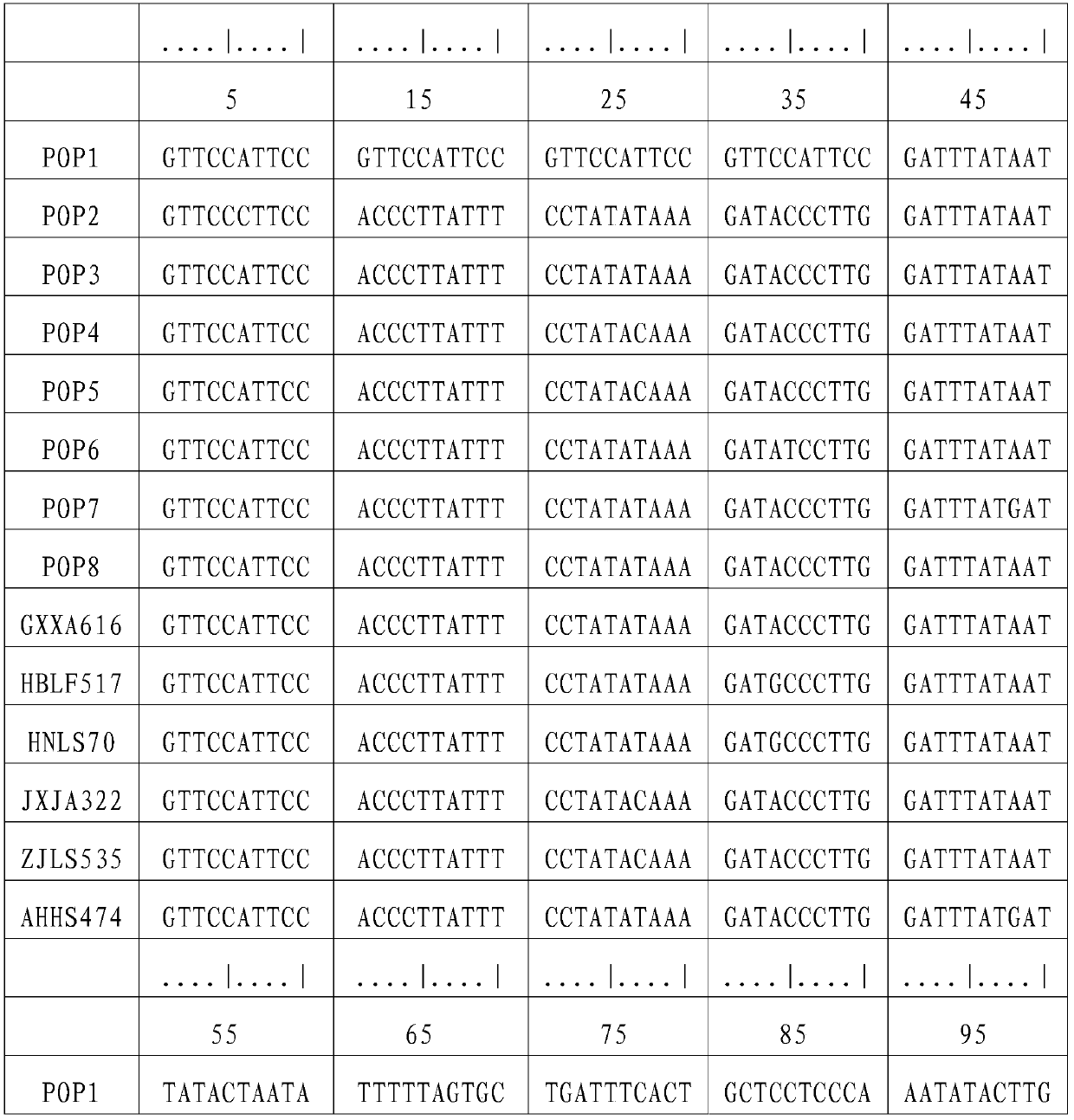
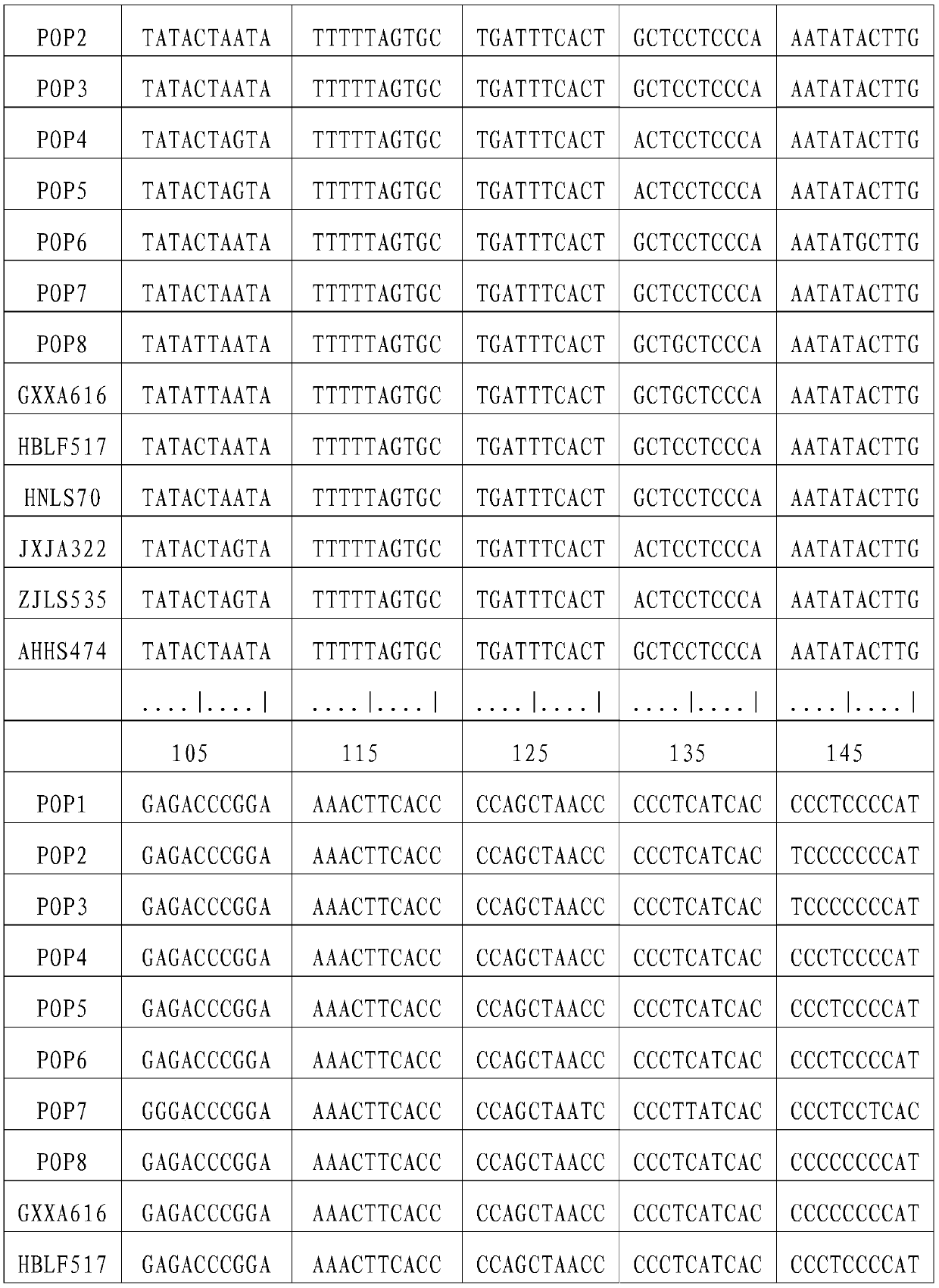
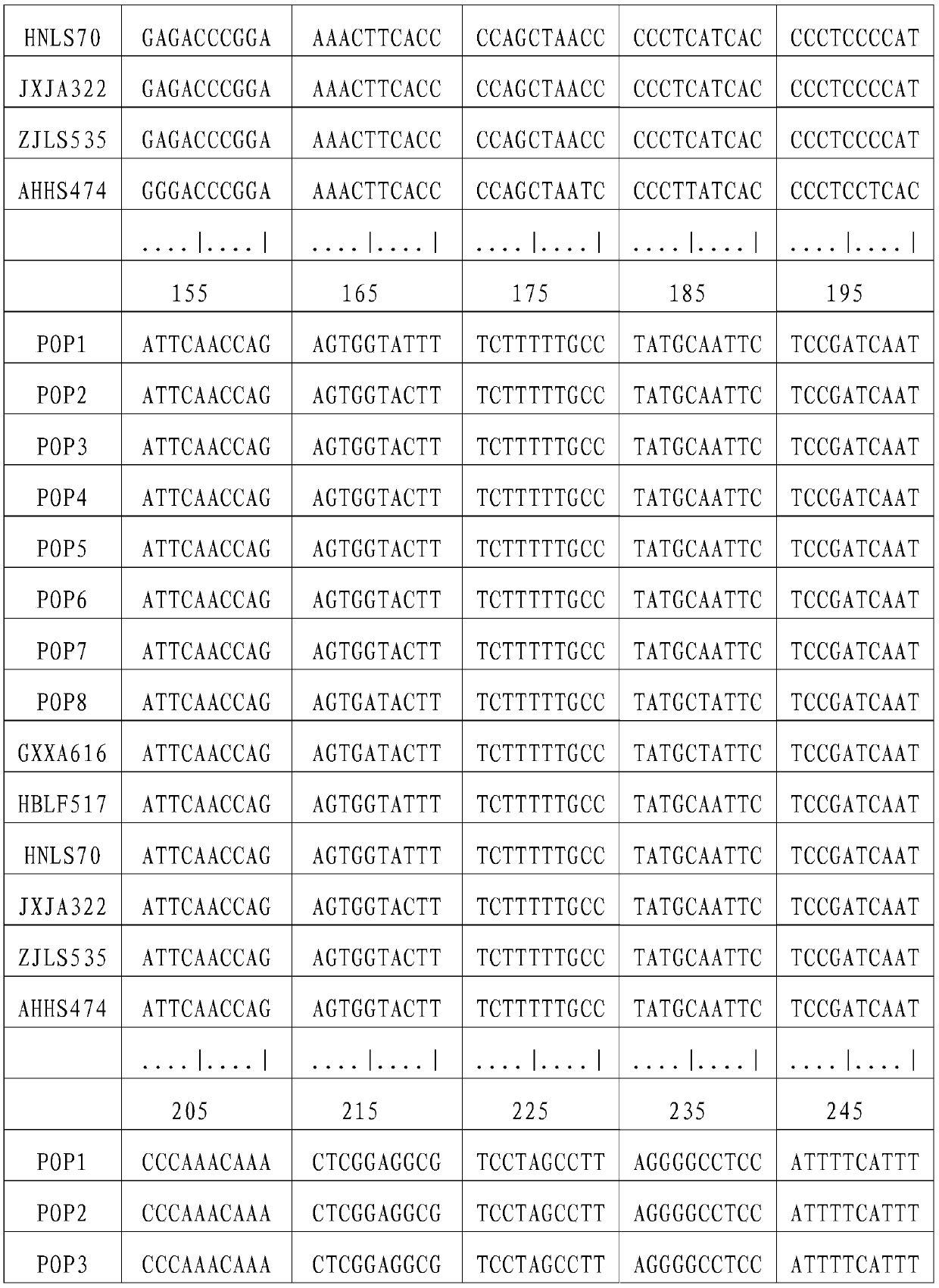
[0042] Chinese giant salamander individuals were collected from Xing'an in Guangxi (GXXA), Longshan in Hunan (HNLS), Jing'an in Jiangxi (JXJA), Huangshan in Anhui (AHHS), Laifeng in Hubei (HBLF), and Lishui in Zhejiang (ZJLS). The part or tissue collected can be a small amount of fin rays, blood, muscle, fresh molted skin, or oral epithelial cells scraped with a sterilized cotton swab, etc. Genomic DNA was extracted using DNA extraction kit or phenol-chloroform method. Use a spectrophotometer to measure the purity and content of the DNA, and store it at -20°C for future use. The DNA concentration was adjusted to 10-100ng / μL when used.
[0043] (2) Primer synthesis
[0044] The following primers were synthesized at Shanghai Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd.:
[0045] L14764: 5′-ATGAAACAGGGTCAAAGCAATCCAAC-3′
[0046] H16062: 5'-AGATGAGGGCAGACTCAGTTATG-3'.
[0047]Dissolve and dilute the primers to a concentration of 10 μmo / L w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com