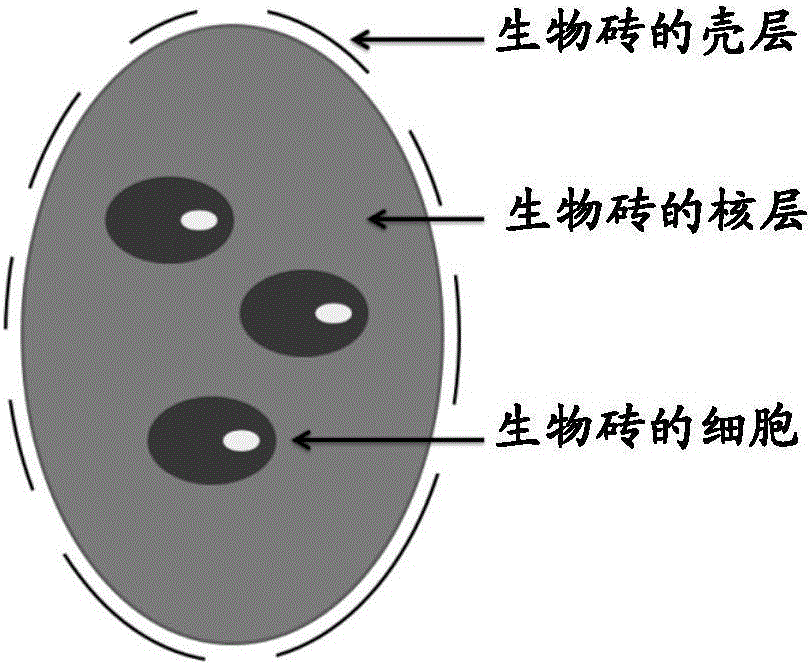
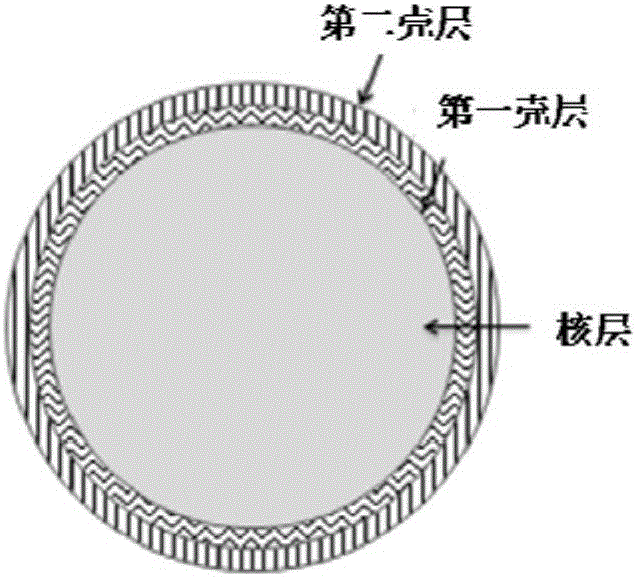
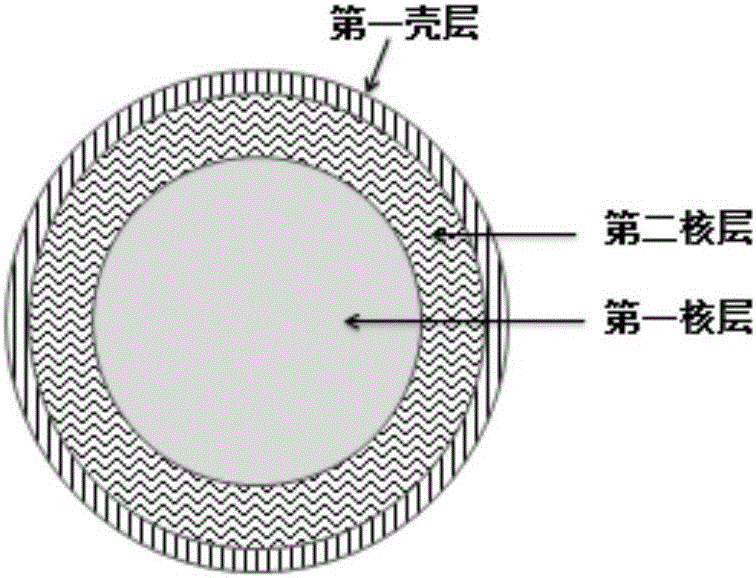
Biobrick including endothelial cells and application thereof
A technology of endothelial cells and bio-bricks, applied in the field of biology, can solve the problems of size limitation, limited application of bioprinting technology, low survival rate of three-dimensional construct body cells, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0276] The methods of the present invention for making constructs are compatible with other bioprinting methods known in the art. For example, the method of the present invention can be used in bioprinters developed by Cyfuse, Organovo and EnvisionTEC. Three main types of bioprinters have been developed, namely, inkjet bioprinters, extrusion bioprinters and laser-assisted bioprinters (see MurphSV and Atala A. (2014) Nature Biotechnology, 32(8): 773- 785). Alternatively, the methods of the present invention for making constructs can be used in bioprinting methods using automated or non-automated mechanical processes (rather than printers), or in bioprinting using manual placement or manual deposition methods (e.g. using pipettes) method. In certain preferred embodiments, bioprinting is performed by inkjet. In certain preferred embodiments, bioprinting is performed by extrusion. In certain preferred embodiments, bioprinting is performed by manual placement or manual depositi...
specific Embodiment approach
[0322] The invention will now be described with reference to the following examples, which are intended to illustrate the invention, but not to limit it.
[0323] Reagents, kits or instruments whose sources are not specified in the examples are all conventional products commercially available on the market. Those skilled in the art understand that the examples describe the present invention by way of example and are not intended to limit the scope of the claimed invention.
Embodiment 1
[0324] Embodiment 1. The preparation of biological brick
[0325] This example provides an exemplary method of making a biobrick. The preparation method of the bio-brick should be carried out under sterile conditions. In addition, if the bio-brick is intended to be applied to the human body, the biosafety level of its preparation method should reach the GMP workshop level.
[0326] The instrument used in this method is a granulator (BUCHI, Encapsulator, B-395Pro), and the diameters of the concentric nozzles it is equipped with are as follows: the inner layer nozzle, 200 μm; the outer layer nozzle, 300 μm.
[0327] The materials used in this method are as follows:
[0328] (1) Materials used to prepare the nuclear layer
[0329] Type I collagen: 4mg / ml, neutralized with sterile 1M NaOH;
[0330] Sodium alginate: Dissolve and dilute with deionized water;
[0331] Vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF;
[0332] Type I collagen was mixed with 2% (w / v) (ie, 2 g / 100 ml, the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com