A Realization Method of Wireless Ad Hoc Network
A wireless ad hoc network and implementation method technology, applied in wireless communication, network topology, network planning and other directions, can solve the problems of affecting system throughput, lack of good scheduling mechanism for different types of services, low transmission efficiency, etc. The effect of resource reservation and preemption, improving time slot utilization, and increasing the number of terminals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
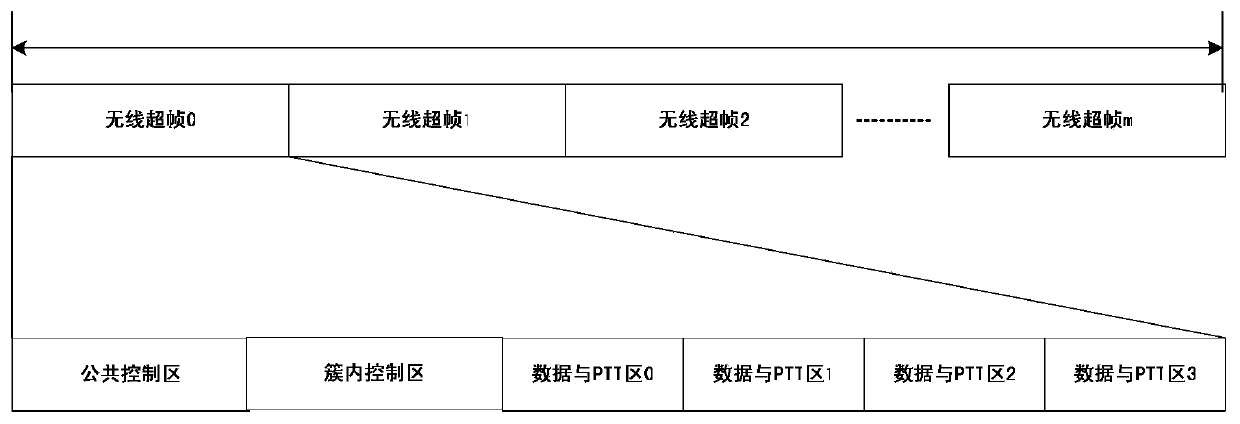
[0052] This embodiment will describe in detail the special wireless frame structure adopted by the wireless ad hoc network. The wireless superframe for inter-node communication consists of a common control area, an intra-cluster control area, and several data and PTT areas, such as figure 2 shown.
[0053] The common control area consists of synchronization area, cluster broadcast area, cross-cluster PTT service instruction area, cross-cluster routing and control message area, such as image 3 shown. This embodiment uses the public frequency hopping mode in the public control area, that is, the nodes of the entire network use the same frequency hopping mode (the public frequency hopping mode selects a narrowband frequency band used by the nodes of the entire network, rather than the specific use of the frequency domain subcarrier position ).
[0054] Nodes send and receive synchronization signals and synchronization channels in the synchronization area of the common cont...
Embodiment 2
[0078] The cross-cluster PTT service indication area in the common control area in the frame structure and the intra-cluster PTT service indication area in the intra-cluster control area are divided into several cross-cluster PTT indication time slots, cross-cluster data broadcast indication time slots, and intra-cluster PTT indication time slots. slots and intra-cluster data broadcast indication slots. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is:
[0079] The node can randomly select the indicated time slot to use for resource preemption of cross-cluster PTT service, cross-cluster data broadcast service, intra-cluster PTT service and intra-cluster data broadcast service;
[0080] Nodes can also use statically configured indicated time slots according to node IDs to preempt resources for cross-cluster PTT services, cross-cluster data broadcast services, intra-cluster PTT services, and intra-cluster data broadcast services.
Embodiment 3
[0082] The wireless ad hoc network of the present embodiment is a TDMA system, and a section of Guard (guard interval) can be reserved between each time slot in the TDMA system, such as Figure 10 As shown, the purpose is to prevent users at different locations from transmitting on adjacent time slots to avoid time slot collisions. If a single user occupies consecutive time slots, time slot collisions will not occur, so the guard interval in the middle can be As an available symbol, make full use of it, so as to achieve the purpose of improving system efficiency. Based on this idea, this embodiment defines two states of time slot transmission: continuous transmission state and discontinuous transmission state, wherein the continuous transmission state means that when a node occupies a continuous time slot, it can transmit on a given time slot, or Data can be sent on the Guard between the two time slots before and after; the discontinuous transmission state means that the node ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com