Fgf-18 formulation in xyloglucan gels
A technology of FGF-18 and xyloglucan, applied in the field of pharmaceutical preparations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0135] Example 1: Temperature-responsive gelling system based on DEG-XG
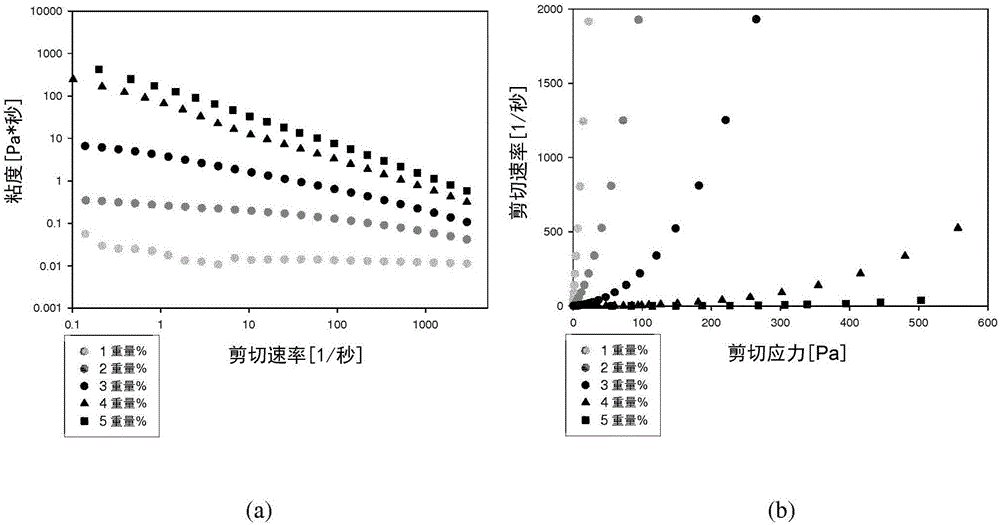
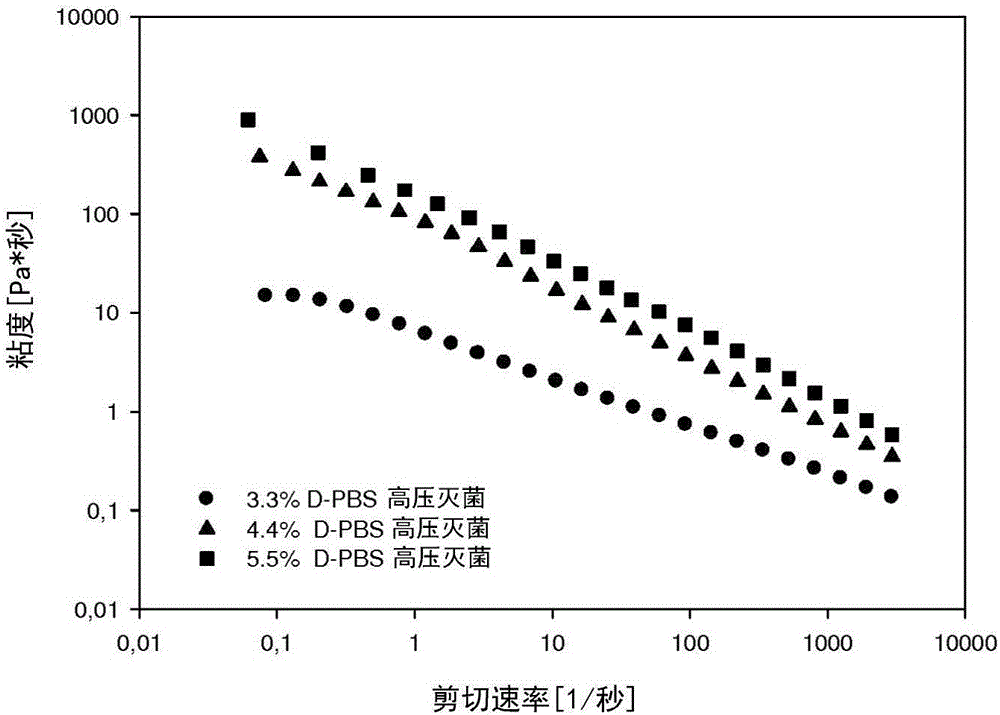
[0136] Deg-XG solutions were prepared at 1, 2, 3, 4, 5% by weight in water. Deg-XG was prepared at 3.3 wt% and 4.4 wt% in D-PBS, and it was also loaded with 54 μg / ml of FGF-18. All systems were tested for injectability after overnight storage at 5°C (time=0) and after further incubation at 37°C for 1, 2 and 3 hours.
[0137] Injectability (Tables 1 and 2). The time to inject a given volume (1 ml) of polymer solution increased with increasing polymer concentration. The amount remaining in the syringe was between 5-8% at concentrations up to 4% by weight, although it increased significantly to about 15% at 5% by weight. The presence of FGF-18 did not significantly affect the performance of the two systems characterized (3 and 4 wt%). After storage at 25°C, for the 3 wt% system, the amount remaining in the syringe increased only after 4 h, while for the 4 wt% system, the amount remaining in the syringe ...
Embodiment 2
[0144] Example 2: Dynamic mechanical properties of DEG-XG based temperature-responsive gelling systems.
[0145] The dynamic mechanical properties of the gels incubated at 37°C for different times were investigated by stress and frequency sweep tests.
[0146] For the water-based gel system, the G’ curves of the strain sweep at a frequency of 1 Hz after incubation at 37 °C for 5 and 30 min are shown in Figure 7 . G' increases dramatically with increasing concentration, although the more elastic-like the material becomes, the lower the strain it can withstand before losing integrity (a condition detected by a sudden decrease in G'). Strain sweep testing after 30 minutes at 37°C showed a general further increase in storage modulus and showed a difference between the 4 and 5 wt% Deg-XG / water systems. Similar tests were performed on D-PBS gels loaded with 540 and 54 μg / ml GF and a "placebo" system (D-PBS gel without GF) ( Figure 8 a-c).
[0147] The combined effect of diluti...
Embodiment 3
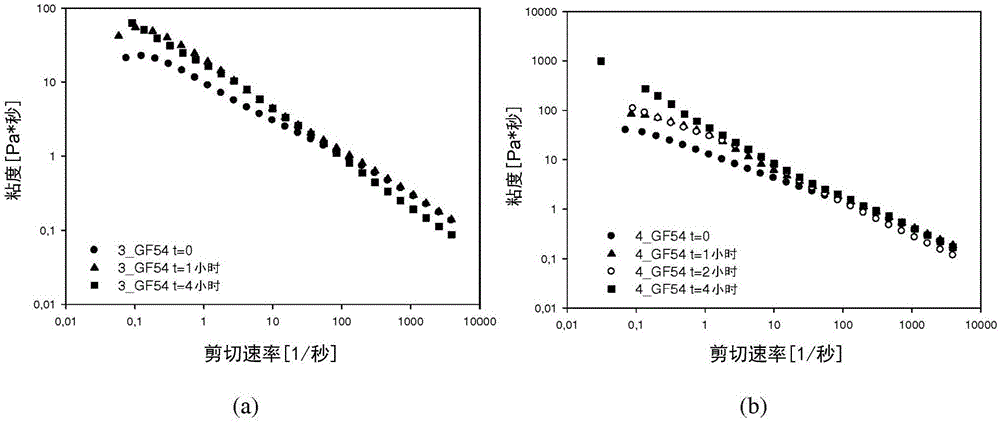
[0151] Embodiment 3: Study on gelation kinetics
[0152] Gelation kinetic studies were performed by repeating frequency sweeps of the Deg-XG / water system at 37°C at given time intervals. Plot storage modulus and loss modulus values versus time at 1 Hz ( Figure 11 ).
[0153] While the 1 wt% Deg-XG system shows a steady increase over time of G' and G", which first increase and then decrease, all other systems show nearly constant values for the two components of the complex modulus over the time range studied .These results are in agreement with qualitative preliminary studies of flow behavior using tilt tests.
[0154] Given the observed similarities between D-PBS and aqueous systems, we can assume that these two types of gels have the same qualitative properties.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com