Methods for treatment of muscular dystrophies
A technology for muscular dystrophy and malnutrition, which is applied in the fields of medical formula, muscular system diseases, neuromuscular system diseases, etc., and can solve problems such as side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
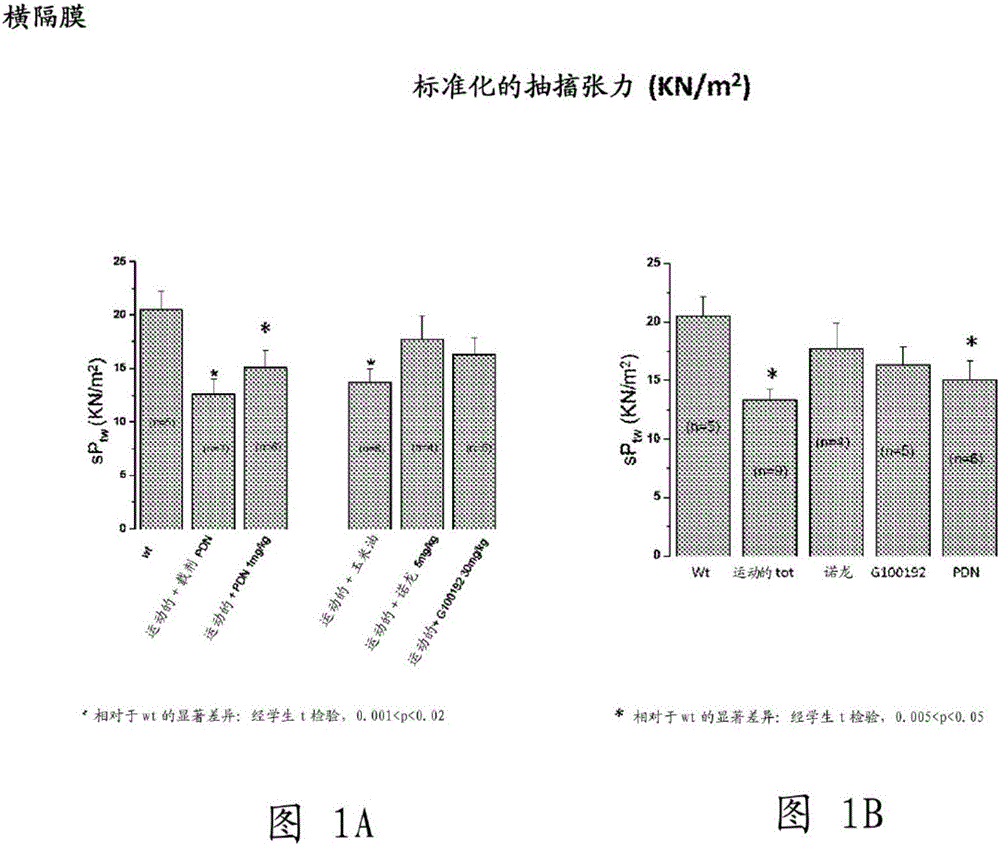
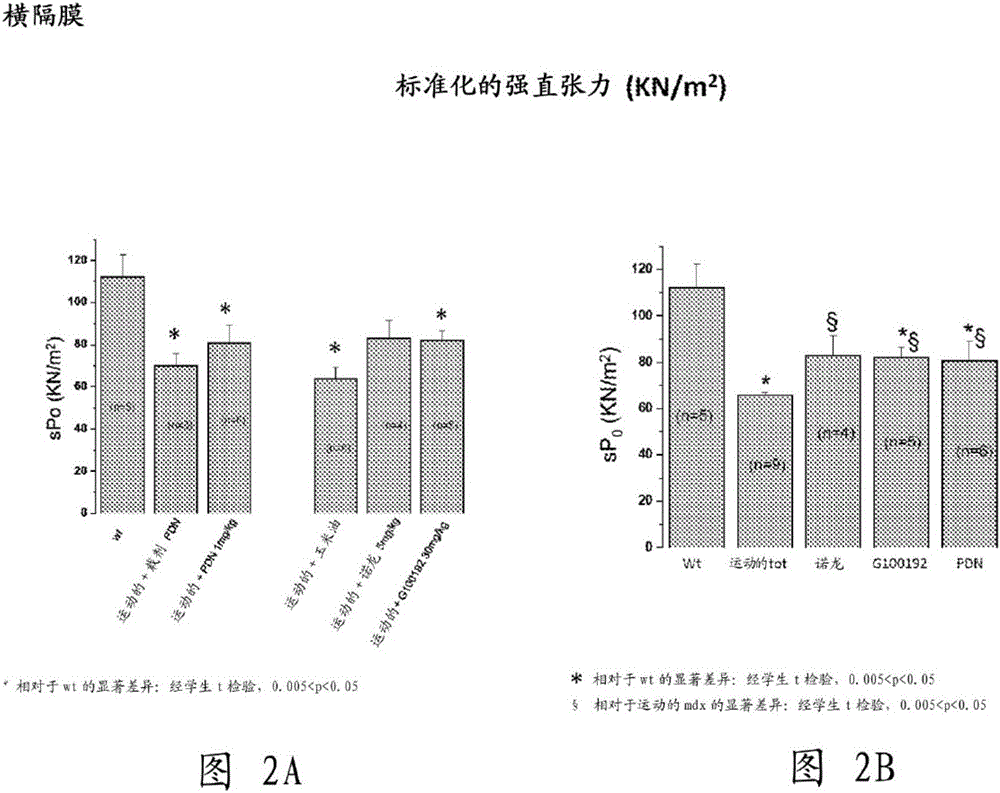
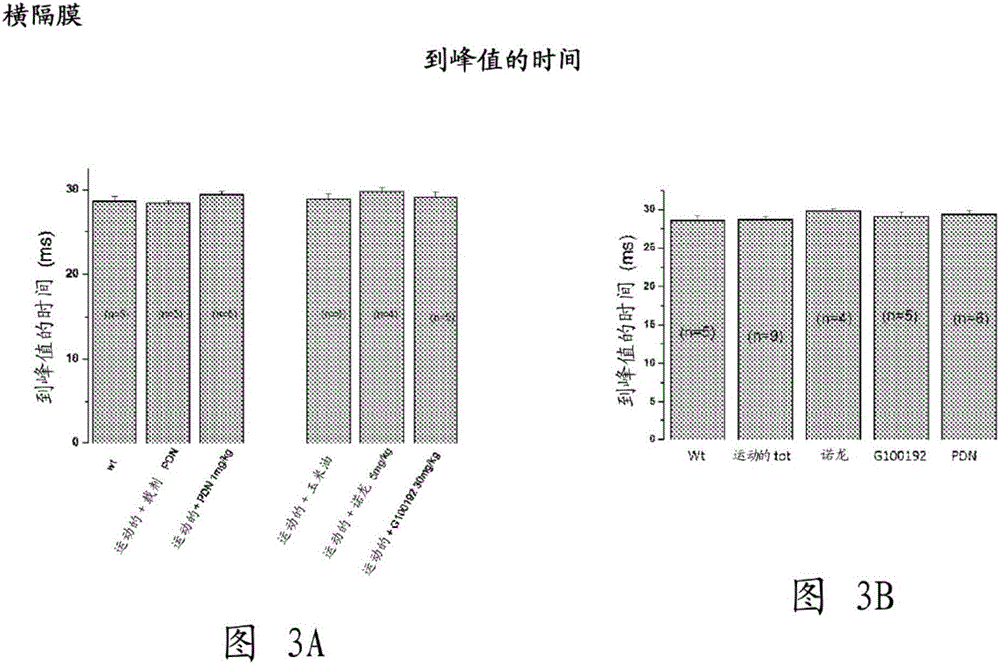
[0229] Example 1. Multidisciplinary Evaluation of Compound (I) Compared to Nandrolone and α-Methylprednisolone (PDN) in mdx of Exercise Effects of in vivo treatment on a mouse model of muscular dystrophy
[0230] introduce
[0231] The aim of this study was to test compound (I), a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) with muscle-specific effects, on chronic exercise in the mdx mouse model by a multidisciplinary approach of in vivo and ex vivo methods Impact. get duchener muscular dystrophy After the patients agreed to clinical use of glucocorticoids, the effect on compound (I) (30mk / kg, subcutaneous injection 6 days / week) was similar to that of those treated with α-methylprednisolone (PDN) (1mg / kg intraperitoneal injection 6 days / week) and compared with those of the anabolic nandrolone (5 mg / kg, subcutaneously 6 days / week).
[0232] Experiments describe results from ex vivo assays of key functional and morphological endpoints, corrected for methodological approac...
Embodiment 2
[0282] Example 2. Comparison of mdx mice treated with compound (I), nandrolone and α-methylprednisolone
[0283] Compound (I), nandrolone and α-methylprednisolone were administered 6 days per week to wild-type (Wt) and mdx mice. Figure 24 In vivo parameters of wild-type (Wt) and treated mdx mice treated with corn oil (Mdx+V1) or treated with compounds containing (I) (Mdx+compound (I)), or containing 5mg / kg nandrolone (Mdx+NAND), or containing water (Mdx+V2) or containing 1mg / kg α-methylprednisolone (Mdx+PDN) Composition treatment at 30 mg / kg. In each panel, vertical bars represent the mean ± S.E.M. of 5 to 7 animals. Significant differences between groups were assessed by correction for multiple comparisons using the ANOVA test and post-hoc Bonferroni t-test.
[0284] In (A), the vertical bar shows the body weight value (body weight) in g. No significant differences in values for mdx mice (treated or untreated) were observed using the ANOVA test. In (B), vertical bar...
Embodiment 3
[0285] Example 3. Treatment of mdx mice with different amounts of compound (I)
[0286] Compound (I) was administered to wild-type (Wt) and mdx mice 6 days a week. Figure 25 In vivo parameters of wild-type (Wt) and treated mdx mice treated with corn oil (Mdx+ V1) Treatment or treatment with Compound (I) (Mdx+Compound (I)) in amounts of 0.3 mg / kg, 3 mg / kg and 30 mg / kg. In each panel, values represent the mean±S.E.M. of 5 to 8 animals. Significant differences between groups were assessed by correction for multiple comparisons using the ANOVA test and post-hoc Bonferroni t-test.
[0287] In (A), the vertical bar shows the body weight value (body weight) in g. ANOVA test did not observe significant differences in BW at time 0, time 4 and time 6. Significant differences in BW were found at time 8 (F>3.9; p3.8; p最大 T0), week 4 (F 最大 T4), week 8 (F 最大 T8), week 12 (F 最大 T12), the vertical bar shows the maximum forelimb strength (forelimb force) in kg. ANOVA test showed s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com