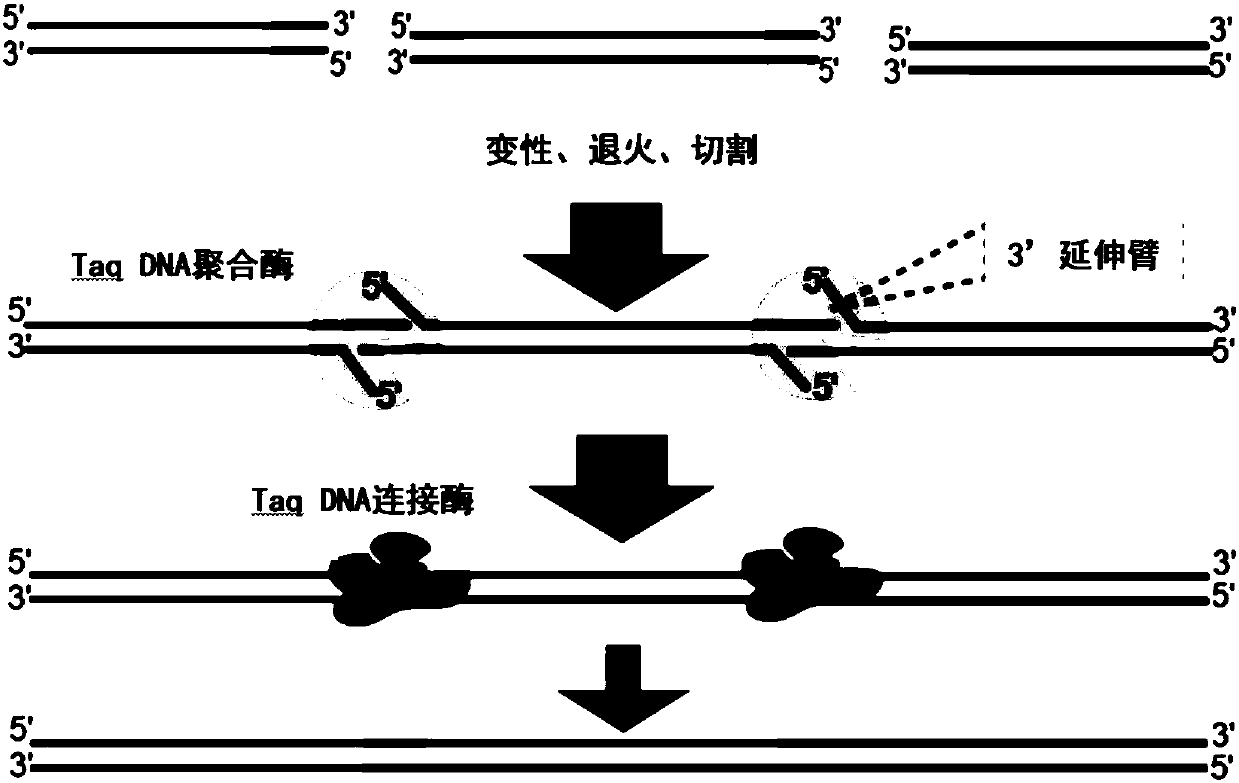
Method for rapidly assembling non-phosphorylated DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments in vitro
A non-phosphorylated, fragmented technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of increasing the reaction rate, increasing the reaction time, and increasing steps, so as to achieve high-throughput operations and enrich the diversity of combinatorial mutations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
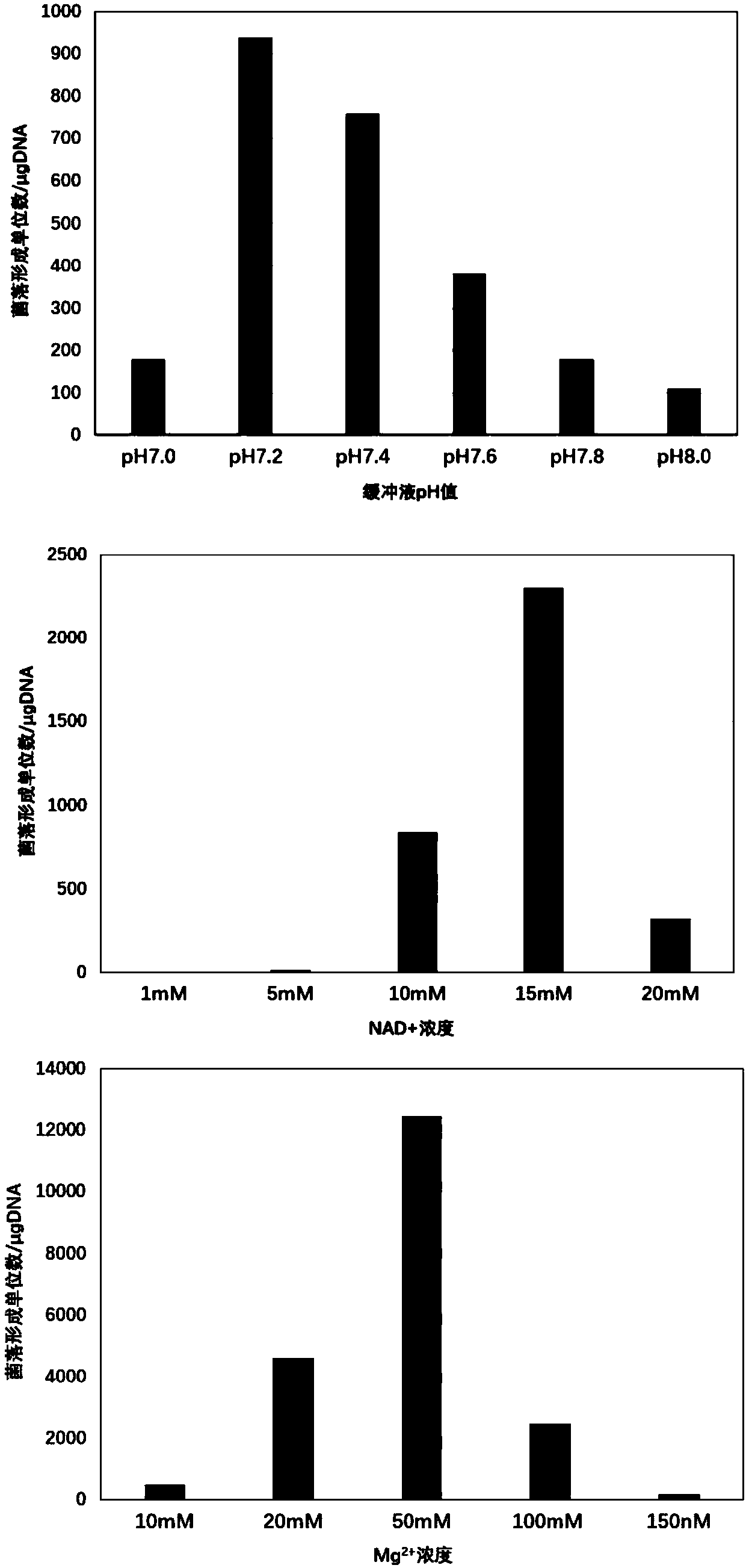
[0032] Embodiment 1 is optimized to the reaction system of assembly technology
[0033] Taking the green fluorescent protein gene gfp (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1) and the pUC19 vector as examples, the assembly reaction buffer was optimized. First, the pH of the assembly reaction, Mg 2+ and NAD+, these three components were optimized, and a gfp amplification primer with a 30bp homology arm and a pair of vector pUC19 amplification primers were designed according to the gfp fragment and the vector sequence. Primers are as follows:
[0034] puc19-F: TTCTTCTCCCTTACCCATGGCGTAATCATGGTCATAGCTGTTTCCT
[0035] puc19-R: TGGATGAACTATACAAATAACTGGCCGTCGTTTTACAACGTCG
[0036] gfp-P30F:CATGATTACGCCATGGGTAAGGGAGAAGAA
[0037] gfp-P30R:CGACGGCCAGTTATTTGTATAGTTCATCCA
[0038] With primer puc19-F (sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 6) and puc19-R PCR (sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 7) amplified to prepare the vector fragment pUC19 for assembly reaction; using primer gfp-P30F (sequence As ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Embodiment 2 uses the assembly technology of the present invention to quickly assemble 3 fragments
[0042] In order to verify the efficiency and accuracy of assembling multiple fragments, the green fluorescent protein gene gfp, the kanamycin gene kan (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2) and the pUC19 vector were used as examples to assemble three fragments ( Figure 4 ). The primer information is as follows:
[0043] GK / pUC19-F:ATGAGTTCTTCTAAGTCATAGCTGTTTCCT
[0044] GK / pUC19-R:TGGATGAACTATACAAATAACTGGCCGTCGTTTTACAACGTCG
[0045] GK / gfp-F:CATGATTACGCCATGGGTAAGGGAGAAGAA
[0046] GK / gfp-R:TTGAATATGGCTCATTTATTTGTATAGTTCATCCA
[0047] GK / kan-F:AATAACTGGCCGTCGATGAGCCATATTCAACGGGAAAC
[0048] GK / kan-R:AGGAAACAGCTATGACTTAGAAGAACTCATCGAGCATC
[0049] Use primers GK / pUC19-F (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 10) and GK / pUC19-R (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 11) PCR amplification to prepare the vector fragment pUC19 for the assembly reaction; use primer GK / gfp-F (sequence shown in...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3 Application of this assembly technology to quickly assemble 4 fragments
[0052] In order to verify the assembly ability of multiple fragments of this assembly method, the coenzyme A pathway gene derived from Escherichia coli was used to assemble four fragments. The three genes coaA (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 3), dfp (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 4), and coaD (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 5) of the pathway are expressed in tandem, and the expression vector for (eg Figure 5 shown), and designed and assembled into the vector pUC19 according to this sequence. The primer information of this embodiment is as follows:
[0053] COA / puc19-F: TGATGGCGAAGTTAGCGTAGGTCATAGCTGTTTCCT
[0054] COA / puc19-R: CTCTTTTATACTCATTACGAGCCGGAAGCATAAAG
[0055] COA / coaA-F:TGCTTCCGGCTCGTAATGAGTATAAAAAGAGCAAACGTTAAT
[0056] COA / coaA-R:ACCGGCCAGGCTCATTTATTTGCGTAGTCTGACCTCTTCT
[0057] COA / dfp-F:AGACTACGCAAATAAATGAGCCTGGCCGGTAAAAAAATCG
[0058]COA / dfp-R:CGCCCGTTTTTGCATTTAACGTCG...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com