Kit, database establishment method, and method and system for detecting area target variation
A target region and kit technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problem of inability to distinguish low-frequency mutations in tumor specimens with sequencing errors, and achieve low false positive rate, high cost performance, pertinence, and high specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
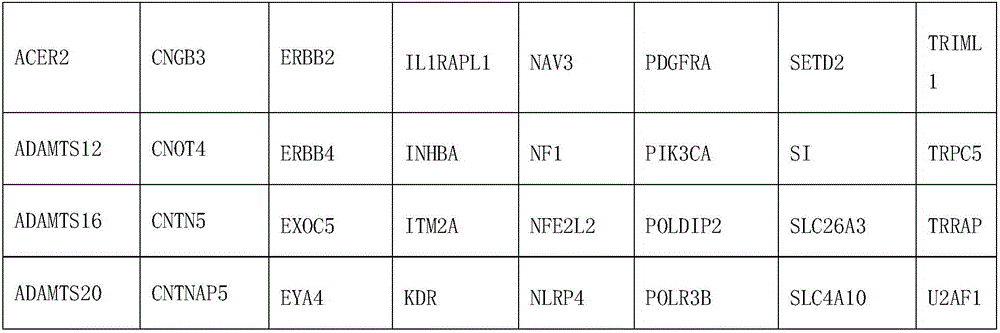
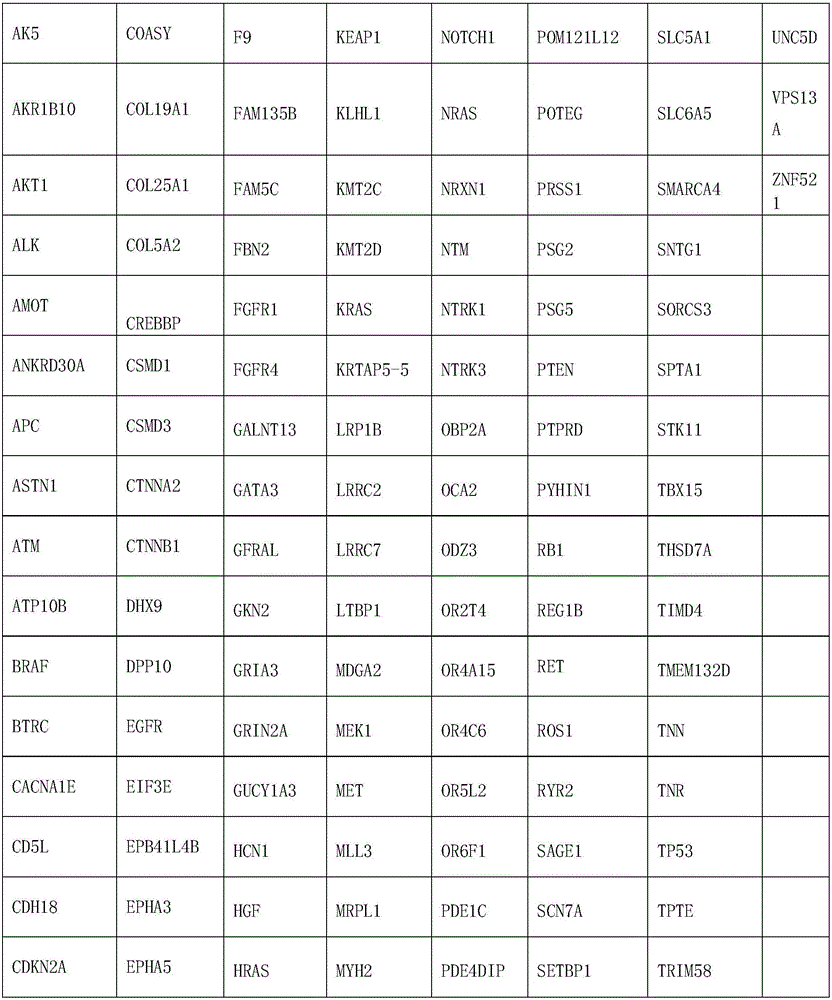
[0069] Embodiment one design chip
[0070] 1. Count the number of mutation samples in each exon region of the driver gene related to lung cancer caused by a single gene in the OMIM data and related literature, the number of mutation samples, the number of samples where the hottest mutation is located, and the PI value (to evaluate the frequency of patient response in The level of each exon, PI=the cumulative number of patients carrying mutations in each exon / exon length), and arranged in descending order according to the PI value. Then, take the sample of the first exon region mutation as the sample database, count the number of different samples in all other intervals and sample databases, and list the sample interval with the largest number of different samples as the second screening interval to the chip. At the same time, the mutation samples of the two intervals screened are used as the sample database, and the third interval is screened in the same way until the sample d...
Embodiment 2
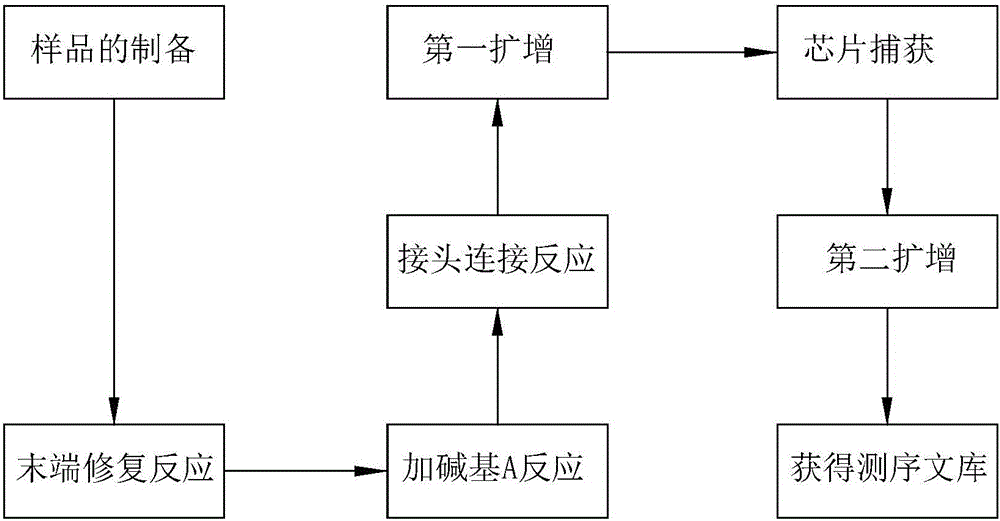
[0075] Example 2 Construction of the target region sequencing library, the specific process see figure 1 .
[0076] (1) Sample preparation
[0077] 1. Take 5-10mL of peripheral blood from the subject, store it in an EDTA anticoagulant tube, and separate the peripheral blood within 4-6 hours;
[0078] 2. Plasma cell-free DNA extraction (refer to the QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit extraction reagent manual for plasma cell-free DNA extraction); obtain plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA), which may contain DNA fragments (ctDNA) from tumor cells. (2) Library construction
[0079] 1. End repair
[0080]
[0081] After the reaction, add 120 μL of Agencourt AMPure XPreagent, after the magnetic beads are purified, finally redissolve 42 μL ddH2O, and carry out the next reaction with magnetic beads;
[0082] 2. Add A at the end
[0083]
[0084] After the reaction, add 90 μL of PEG / NaCl SPRI solution, mix well and perform magnetic bead purification, and finally redissolve (35-li...
Embodiment 3
[0098] Example 3 On-machine sequencing
[0099] The sequencing library obtained in Example 2 was sequenced on the computer using the Nextseq CN 500PE75 program, and the sequencing experiment was performed in accordance with the operating instructions provided by the manufacturer (see the cBot officially announced by Hangzhou Berry Hekang Gene Diagnostics Co., Ltd.).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com