Method for producing succulent plant culture medium from waste mushroom residue in industrial edible mushroom cultivation
A technology for succulent plants and cultivation substrates, which is applied in the field of manufacturing succulent plant cultivation substrates from discarded mushroom chaff in industrialized edible fungus cultivation, which can solve problems such as waste of resources, waste of apricot abalone fungus chaff, environmental pollution, etc., achieve good absorption capacity, and improve survival rate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
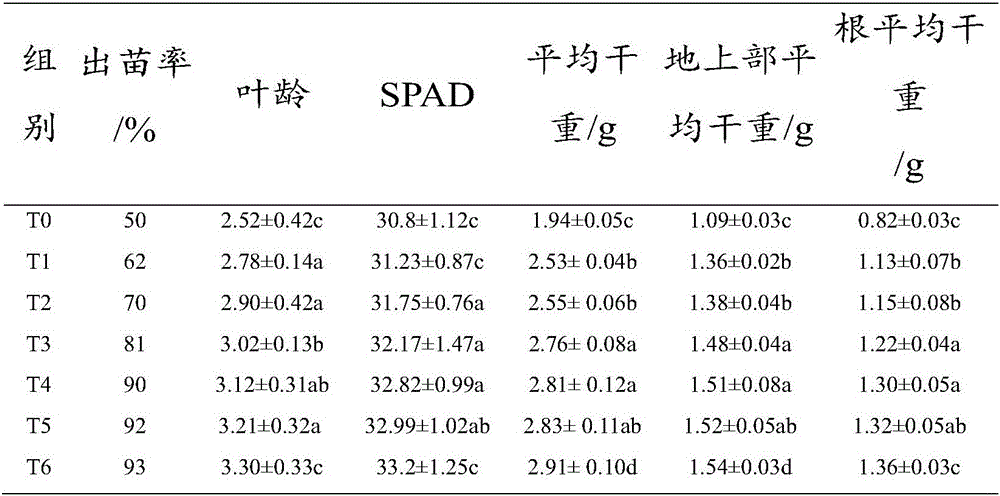
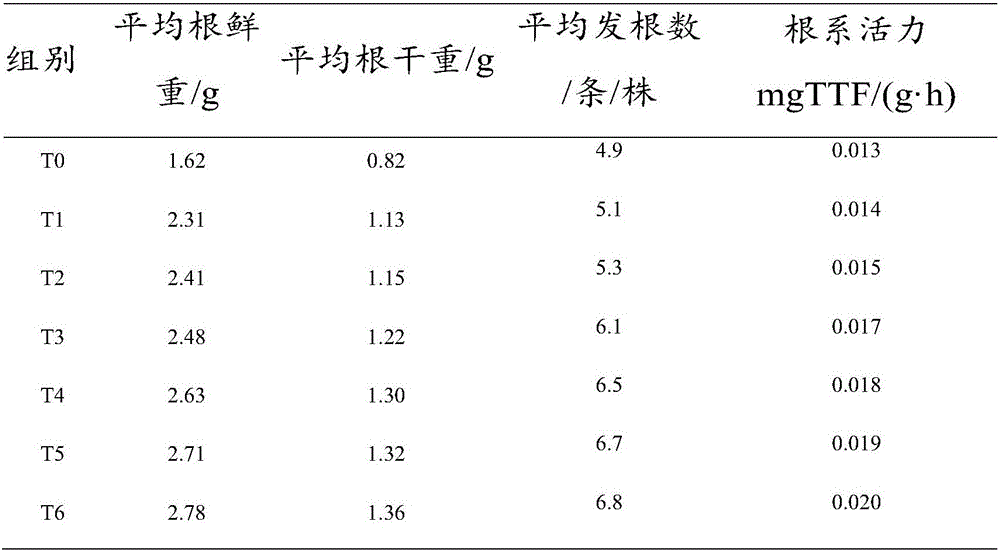
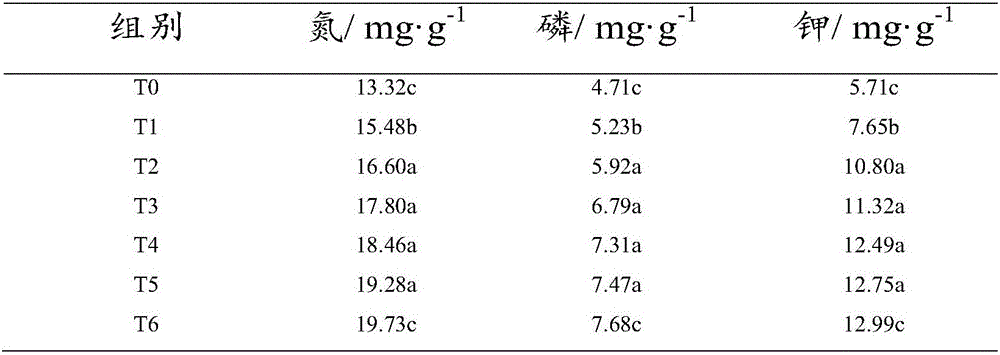
[0040]In this embodiment, the method of making the succulent plant cultivation substrate from the discarded chaff of edible fungus cultivation in this factory: first, remove the impurities (such as the plastic packaging used during cultivation) from the fresh Pleurotus eryngii chaff consigned by the factory, and then Put the chaff of fresh Pleurotus eryngii into a pulverizer and pulverize until the particle size is 0.5-1mm. Secondly, weigh according to the weight of 95 parts of fresh Pleurotus eryngii fungus chaff and 0.7 part of the fungus chaff pyrolysis composite bacterial agent. Then, fresh Pleurotus eryngii fungus chaff is piled up in the fermenter, the fungus chaff pyrolysis composite bacterial agent is added, mixed, and piled up again to form a heap, the height of the heap is 95cm. And adjust the initial moisture mass percentage of the heap to be 55% and the initial carbon-nitrogen ratio (that is, the value of C / N) to be 32.8. Wherein, the mass percentage of moisture i...
Embodiment 2
[0045] In this embodiment, the method for making the succulent plant cultivation substrate from the discarded chaff of edible fungus cultivation in this factory: first, remove the impurities (such as the plastic packaging used during cultivation) from the fresh Flammulina velutipes consigned by the factory, and then put the fresh Flammulina velutipes into The fungus chaff is put into a grinder and crushed until the particle size is 0.5-1mm. Secondly, according to the parts by weight of 99 parts of fresh Flammulina velutipes mushroom chaff and 1 part of bacterial chaff pyrolysis compound bacterial agent, the parts are weighed and prepared. Then, stack the chaff of the fresh Flammulina velutipes in the fermentation tank, add the pyrolysis compound bacterial agent of the chaff, mix, and stack to form a pile, the height of which is 100cm. And adjust the initial moisture mass percentage of the heap to be 60% and the initial carbon-to-nitrogen ratio (that is, the value of C / N) to be...
Embodiment 3
[0050] In this embodiment, the method of making the succulent plant cultivation substrate from the discarded chaff of edible fungus cultivation in this factory: first, remove the impurities (such as the plastic packaging used during cultivation) from the fresh mushroom chaff consigned by the factory, and then put the fresh mushroom chaff The fungus chaff is put into a grinder and crushed until the particle size is 0.5-1mm. Secondly, according to the parts by weight of 97 parts of fresh mushroom chaff and 0.8 part of the pyrolysis composite bacterial agent of fungus chaff, the raw materials are weighed and prepared. Then, fresh mushroom chaff is stacked in the fermenter, and the fungus chaff pyrolysis compound bacteria agent is added, mixed, and then stacked to form a pile with a height of 105 cm. And adjust the initial moisture mass percentage of the heap to be 65% and the initial carbon-to-nitrogen ratio (that is, the value of C / N) to be 35. Wherein, the mass percentage of m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com