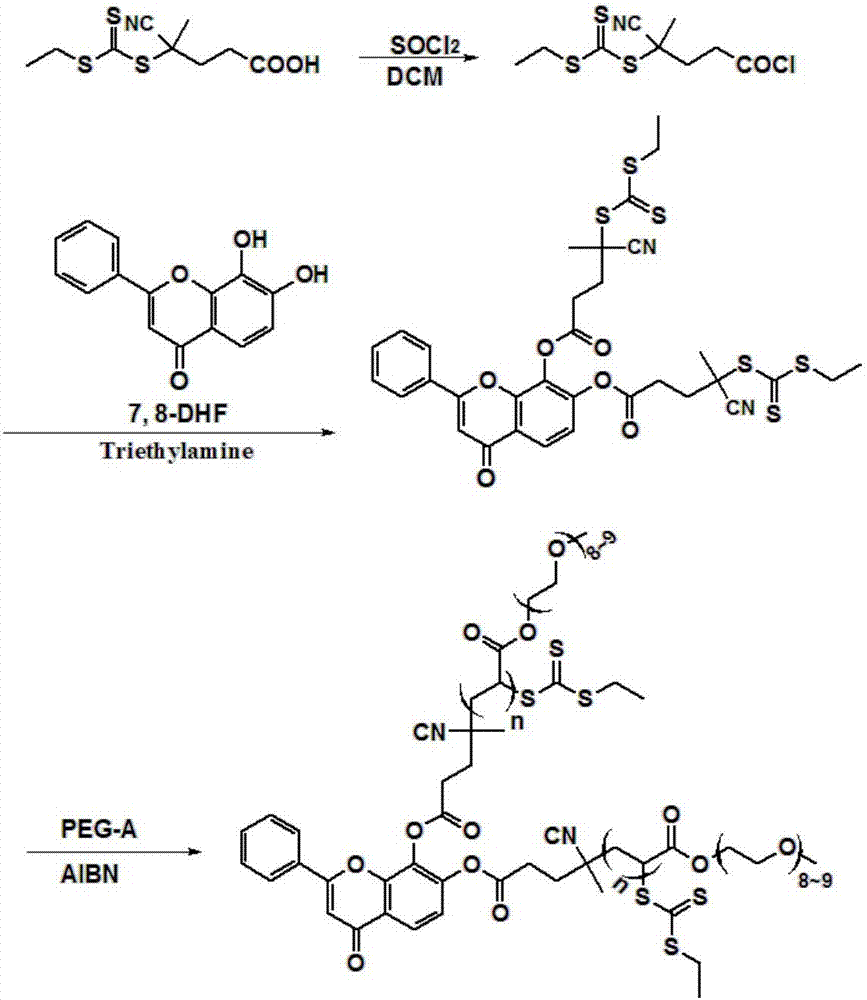
A method for improving the water solubility of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone based on raft polymerization
A dihydroxyflavone and water-soluble technology, which is applied in the field of improving the water solubility of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone based on RAFT polymerization method, can solve the complex and changeable reaction mechanism of anti-Parkinson (PD) drugs, fluctuating symptoms, and aggravation Symptoms and other problems of patients, to achieve the effect of easy molecular weight, obvious effect, and improved water solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1: The mensuration of 7,8-DHF solubility
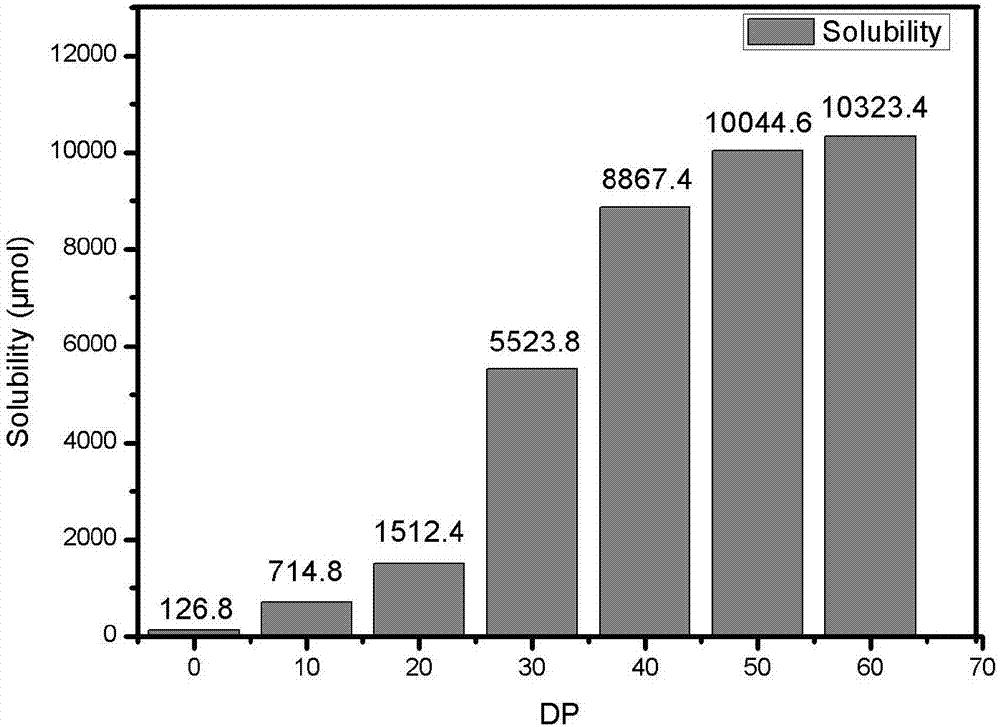
[0034] In this embodiment, 7 after modification, 8-DHF (7 samples are obtained by controlling the ratio of RAFT reagent and monomer respectively, sample 1 is pure 7, 8-DHF; sample 2 ratio is 1:10; sample 3 ratio is 1:20; the ratio of sample 4 is 1:30; the ratio of sample 5 is 1:40; the ratio of sample 6 is 1:50; the ratio of sample 7 is 1:60). figure 2 shown, from figure 2 It can be seen that the solubility of 7,8-DHF is about 10044 μmol / L. Compared with the 7,8-DHF with a solubility of 126.8 μmol / L before modification, the modified 7,8-DHF (when the degree of polymerization is 60 ) Solubility increased by 78 times.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2: the mensuration of drug efficacy after modification
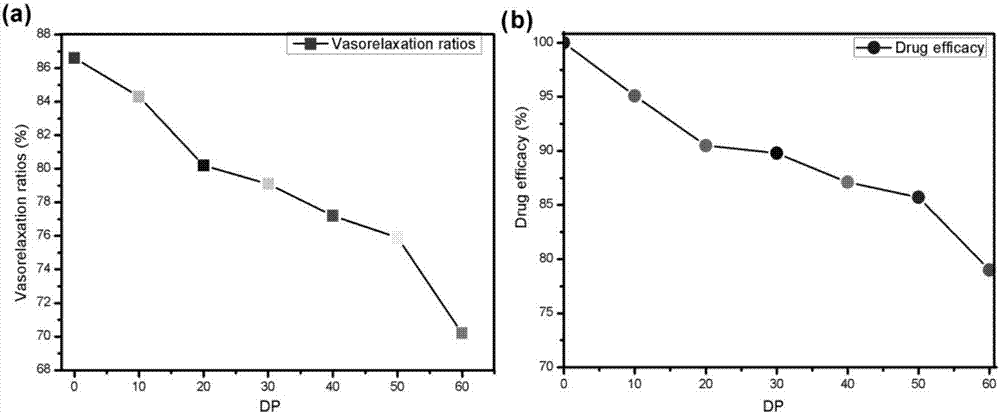
[0036] In this embodiment, the modified 7,8-DHF drug efficacy is measured, and the results are as follows: image 3 shown, from image 3 (a) It can be seen that the vasodilation of the samples of these 7 degrees of polymerization are 88.6±6.2%, 84.3±4.3%, 80.2±6.2%, 79.6±3.3%, 77.2±4.9%, 75.9±3.8% and 70.2±1.8%; image 3 (b) shows that the drug effect of modified 7,8-DHF decreases with the increase of degree of polymerization. When the degree of polymerization is 60, the drug effect of modified 7,8-DHF is the original drug level 79.2%.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: Determination of cytotoxicity after modification (DT is the cytotoxicity grade)
[0038] The present embodiment measures the toxicity of 7,8-DHF drug to cells after the modification, and the results are shown in Table 1. From Table 1, it can be obtained that the drug after modification has a toxicity level of one to cells, which is equal to the toxicity of the original drug. At the same level, the drug efficacy is only slightly reduced, and the toxicity of the drug is at the same level as before.
[0039] Table 1:
[0040]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com