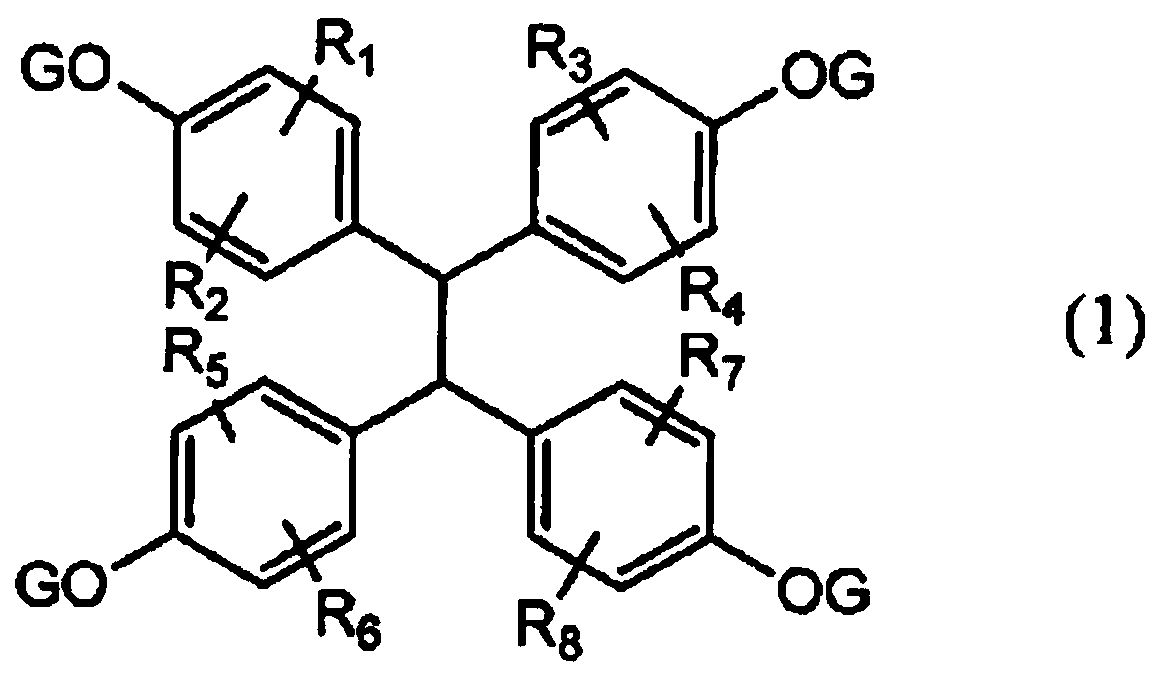
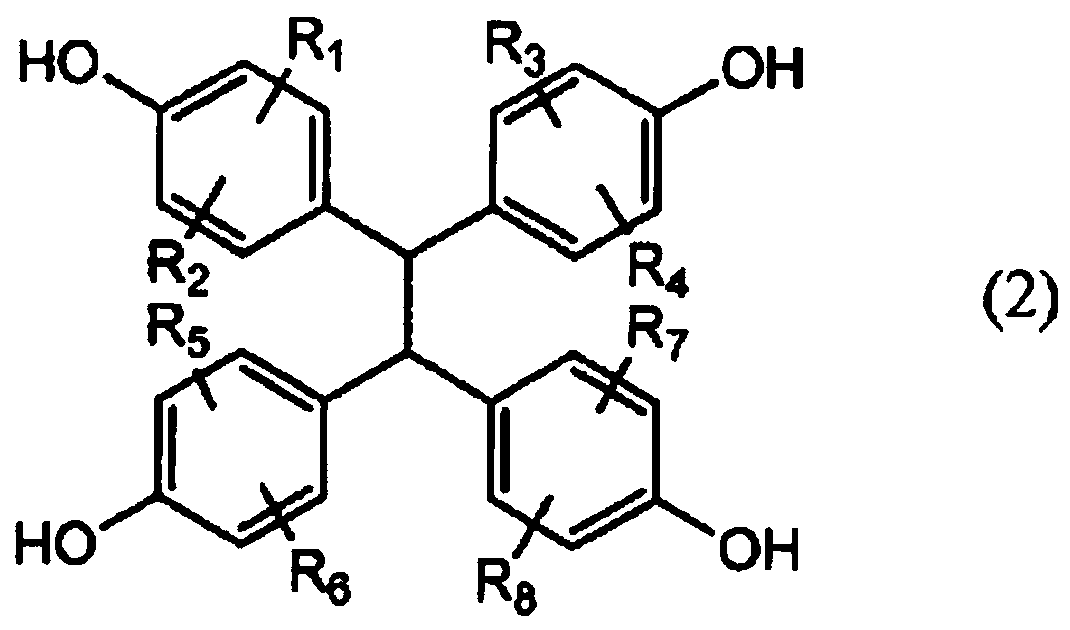
Active energy ray curable resin composition and spacer for display element and/or color filter protective film using same
A technology of active energy rays and curable resins, which is applied in the direction of optical filters, nonlinear optics, and photolithography on patterned surfaces, etc. It can solve the problem of poor elastic recovery rate and no record of spacers or color filters for display elements. Protective film and other problems, to achieve the effect of excellent toughness, excellent developability, high radiation sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-1~1-3
[0158] [Preparation of reactive polycarboxylic acid compound (A)]
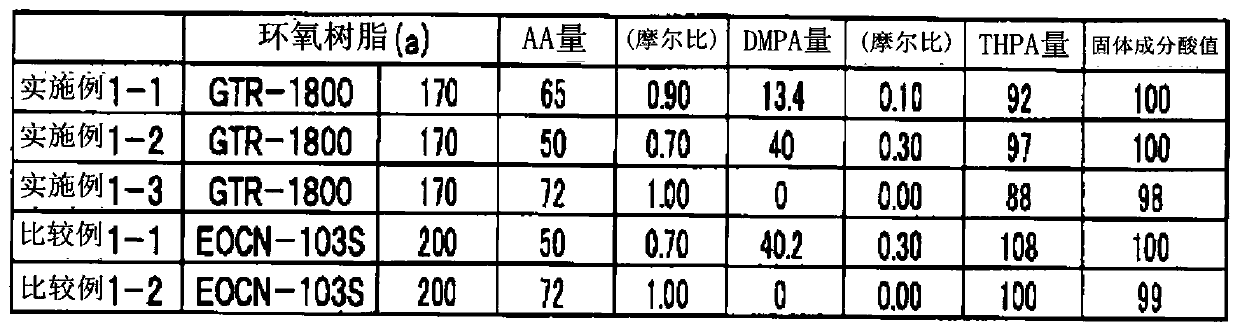
[0159] GTR-1800 (manufactured by Nippon Kayaku; epoxy equivalent 170g / eq) was added as epoxy resin (a) in the amount listed in Table 1, and acrylic acid (abbreviated as AA, Mw=72), and dimethylolpropionic acid (abbreviated as DMPA, Mw=134) was added as the compound (c) in the amount described in Table 1. 3 g of triphenylphosphine was added as a catalyst, and propylene glycol monomethyl ether monoacetate was added as a solvent so that the solid content would be 80% by weight of the reaction liquid. Reaction was carried out at 100° C. for 24 hours to obtain a reactive epoxy carboxylate compound (E) solution. The next reaction was performed with a solid content acid value (AV: mgKOH / g) of 5 or less as the reaction end point. In acid value measurement, it measures with a reaction solution, and converts it into the acid value by solid content.
[0160] Then, in the reactive epoxy carboxylate compound (E) solutio...
Embodiment 2-1
[0184] In the solution containing the reaction product obtained in the amount equivalent to 100 parts by weight (solid content) of Example 1-1 as a reactive polycarboxylic acid compound (A), add (B- 1) 100 parts by weight, 10 parts by weight of (C-1) as a photopolymerization initiator (C), and adding PGMEA and DEGDM as an organic solvent to obtain a desired solid content concentration, mixed as a surfactant (H) The composition (S-1) was prepared by filtering 0.3 parts by weight of (H-1) through a membrane filter with a pore diameter of 0.2 μm. It should be noted that the values of the organic solvents in Table 2 are the mass ratios of PGMEA and DEGDM.
Embodiment 2-2~2-3 and comparative example 2-1~2-3
[0186] Except that the types and compounding amounts of each component were set as shown in Table 2, the same operation as in Example 2-1 was carried out to prepare samples of Examples 2-2 to 2-3 and Comparative Examples 2-1 to 2-3. combination. It should be noted that the values of the organic solvents in Table 2 are the mass ratios of PGMEA and DEGDM.
[0187] Table 2
[0188]
[0189]
[0190] The following evaluations were performed about the compositions of Examples 2-1 to 2-3 and Comparative Examples 2-1 to 2-3, and spacers formed of coating films thereof. The evaluation results are summarized in Table 3.
[0191] (viscosity)
[0192] The viscosity (mPa·s) of each composition in 25 degreeC was measured using the E-type viscometer (Toki Sangyo Co., Ltd. make, TV-200).
[0193] (solid content concentration)
[0194] Accurately weigh 0.3 g of the composition in an aluminum dish, add about 1 g of diethylene glycol dimethyl ether, and then dry it on a hot plate at...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| epoxy equivalent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| epoxy equivalent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com