Method for mass producing human blood coagulation factor vii derivative
A technology for mass production of human blood coagulation factors, applied in blood coagulation/fibrinolytic factors, biochemical equipment and methods, botany equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of low expression and low productivity, and achieve large-scale and high-efficiency effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
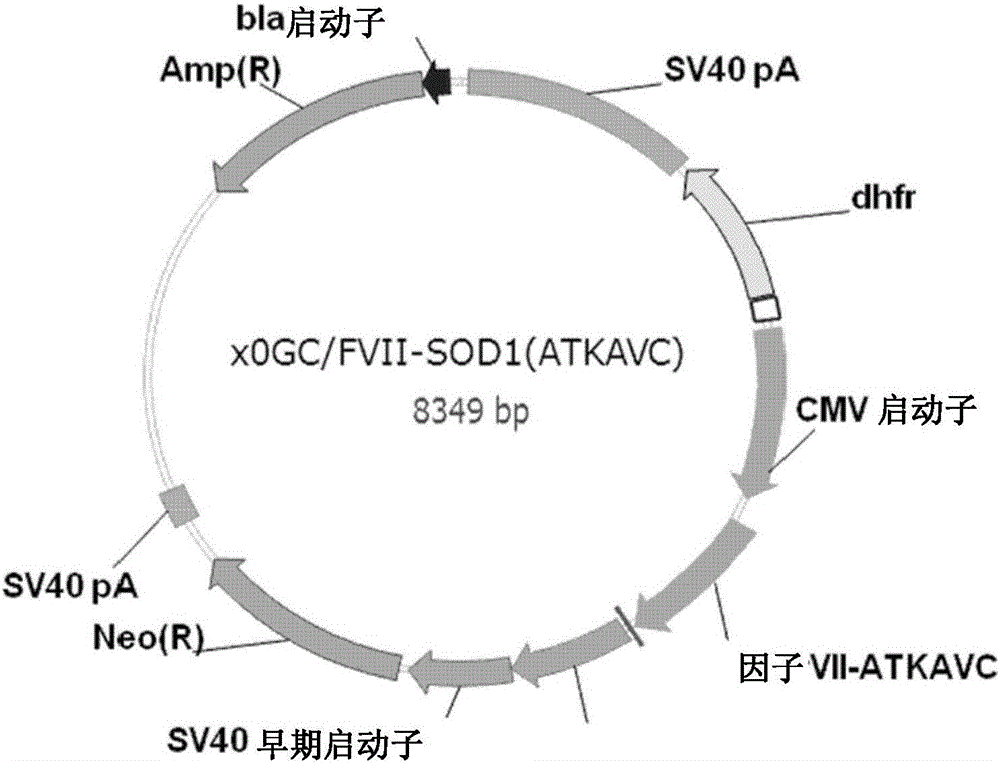
[0075] Embodiment 1: construct the expression vector (pX0GC-hFVII) that is used for recombinant FVII expression
[0076] 1-1. Obtaining human FVII gene
[0077] First, the human FVII gene including the signal sequence was obtained by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). For amplification of the FVII gene, PCR was performed using a human fetal liver cDNA library (TAKARABIO Inc., USA) as a template and forward and reverse primers of SEQ ID NO: 1 and 2 shown below.
[0078] After denaturing the reaction mixture containing the polymerase, primers, cDNA library and dNTPs at 95°C for 1 min, 30 cycles of reactions (30 s at 95°C, 30 s at 60°C, and 30 s at 68°C 90 seconds), and then reacted at 68° C. for 5 minutes.
[0079] Specifically, for the convenience of cloning, a BamHI recognition site was inserted into the primer shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and an XhoI recognition site was inserted into the primer shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. Primers are shown in Table 1.
[0080] 【Table 1】Primers us...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Embodiment 2: construct the expression vector of recombinant FVII derivative
[0087] A polynucleotide encoding a FVII derivative was obtained using an expression vector (pX0GC-FVII) containing a FVII gene, in which part of SOD1 was conjugated to the C-terminus of FVII, and an expression vector capable of expressing the derivative was constructed.
[0088] 2-1. Obtaining Human FVII Derivative Genes
[0089] Construction of an expression vector (pX0GC-FVII-ATKAVC) for expressing a recombinant FVII derivative comprising a polynucleotide encoding SOD1 SEQ ID NO: 1 to 6 (ATKAVC, SEQ ID NO: 5) - the expression vector pX0GC prepared in Example 1 - the 3' end of the FVII gene added in FVII. Specifically, using the expression vector pX0GC-FVII as a template and the forward and reverse primers shown in SEQ ID NO: 6 and 7 shown below, a PCR reaction (denaturation at 95° C. for 1 minute; 30 cycles of reaction (at 95 60 seconds at 60°C, 60 seconds at 60°C, and 90 seconds at 6...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Example 3: Construction of a cell line expressing a human FVII derivative (hFVII-SOD1(ATKAVC))
[0096] The hFVII derivative was expressed using the expression vector constructed in Example 2.
[0097] 3-1. Transformation of FVII derivative (pX0GC-FVII-ATKAVC) using CHO cell line
[0098] The recombinant expression vector pX0GC-FVII-ATKAVC prepared in Example 2-2 was introduced into a DG44 / CHO cell line (CHO / dhfr-) (Urlaub et al., Somat. Cell. Mol. Genet., 12, 555-566, 1986) to obtain transformants, and express FVII-ATKAVC derivatives in the transfectants.
[0099] Specifically, the DG44 / CHO cell line was cultured enough to cover 80% to 90% of the bottom of the culture vessel, and then, the cells were washed three times with Opti-MEM (Gibco, catalog number 51985034).
[0100] Meanwhile, a mixture of 3 mL of Opti-MEM and 5 μg of the expression vector (pX0GC-FVII-ATKAVC) and a mixture of 3 mL of Opti-MEM and 20 μL of lipofectamin (Gibco, catalog number 18324-012) we...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com