Non-enveloped virus quantum dot marking method and application
A labeling method and non-encapsulated technology, which is applied in the fields of virology and aquatic animal medicine, can solve the problems of loss, weak light resistance, and reduced virus activity, and achieve high efficiency, improved quality and quantity, and excellent performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Labeling method and labeling efficiency of non-enveloped virus quantum dots
[0034] 1) SMReV amplification culture:
[0035] According to conventional methods, the grass carp fin ray cell line (GCF) [Keetal.BMCGenomics2011,12:323] was subcultured, and the cells grew into a monolayer after 16h, and each 25cm 2 Cells in the culture flask were inoculated with 100 μl of turbot reovirus (SMReV) stock solution, and cultured at 20°C. After 7 days, the diseased cells were collected and frozen and thawed three times. The supernatant was collected by centrifuging at 4° C. with differential (4,000 g and 12,000 g) for 20 min to obtain a suspension of turbot reovirus SMReV.
[0036] 2) in incl. 10 7Add 300 μL of sulfo-NHS-LC-biotin (Thermo) solution at a concentration of 0.01 mg / μl to 300 mL of SMReV suspension containing 1 RNA copy, place on a shaker at 25° C., and react for 2 h. Centrifuge at 110,000g (BeckmanSW41 rotor) at 4°C for 1.5h, collect the precipitate, add PBS (137mM...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Application of a non-enveloped virus quantum dot labeling method in the invasion trace of non-enveloped virus
[0041] 1) The monolayer cells inoculated with the quantum dot-labeled non-enveloped virus in Step 3) of Example 1 were stained with a cytoplasmic membrane dye (CellMask TM , Invitrogen) for staining;
[0042] 2) Then place the small dish in the culture system attached to the high-speed laser confocal microscope for online culture and fluorescence observation;
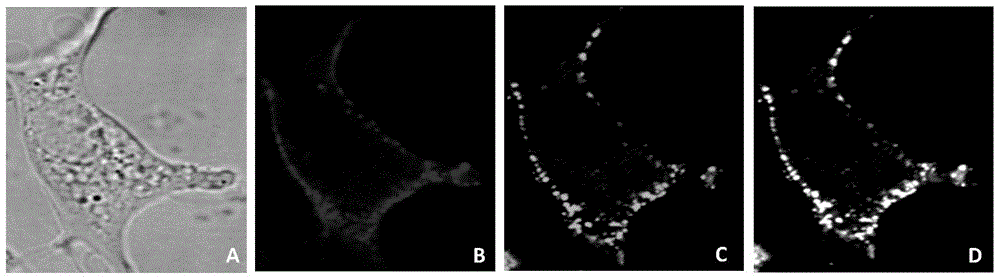
[0043] 3) Choose 561nm laser beam to excite DQs605, use 617 / 73 filter to observe quantum dot-labeled non-enveloped virus (red); choose 640nm laser beam to excite CellMask TM , use a 685 / 40nm filter to observe the cell membrane (green);
[0044] 4) Take pictures continuously or at regular intervals, and use image software to obtain a series of images of the trajectory of a single non-enveloped virus particle and its colocalization (yellow) or relative position with the cell membrane at the correspondin...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Spatiotemporal Tracing of Non-enveloped Viruses in the Endosome-Lysosome System
[0048] 1) Subculture GCF cells in multiple glass-bottomed dishes until they grow into a monolayer;
[0049] 2) Transfect the pRFP-Rab5 plasmid to mark the early endosome, transfect the pRFP-Rab7 plasmid to mark the late endosome, and use the green fluorescent probe dye (LysoTrackerGreen, Invitrogen) to mark the lysosome;
[0050] 3) re-inoculate the biotinylated non-enveloped virus SMReV obtained in step 2) of Example 1, and use quantum dot DQs705 (Wuhan Jiayuan) to label the non-enveloped virus SMReV;
[0051] 4) After incubating each small dish for different time (30min, 60min and 90min), fix the cells with 4% paraformaldehyde respectively;
[0052] 5) Choose 488nm laser beam to excite DQs705, use 685 / 40nm filter to observe and observe quantum dot-labeled non-enveloped virus (red false color); choose 561nm laser beam to excite pRFP-Rab5 and pRFP-Rab7 fluorescence, use 617 / 73 filter Lig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com