Method for recovering iron in steel slag and using tailing thereof
A technology for steel slag and tailings, which is applied in the field of comprehensive utilization and treatment of steel slag, can solve the problems of insufficient utilization of tailings and low iron recovery rate, and achieve the effect of reducing sintering cost and realizing comprehensive recycling and utilization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
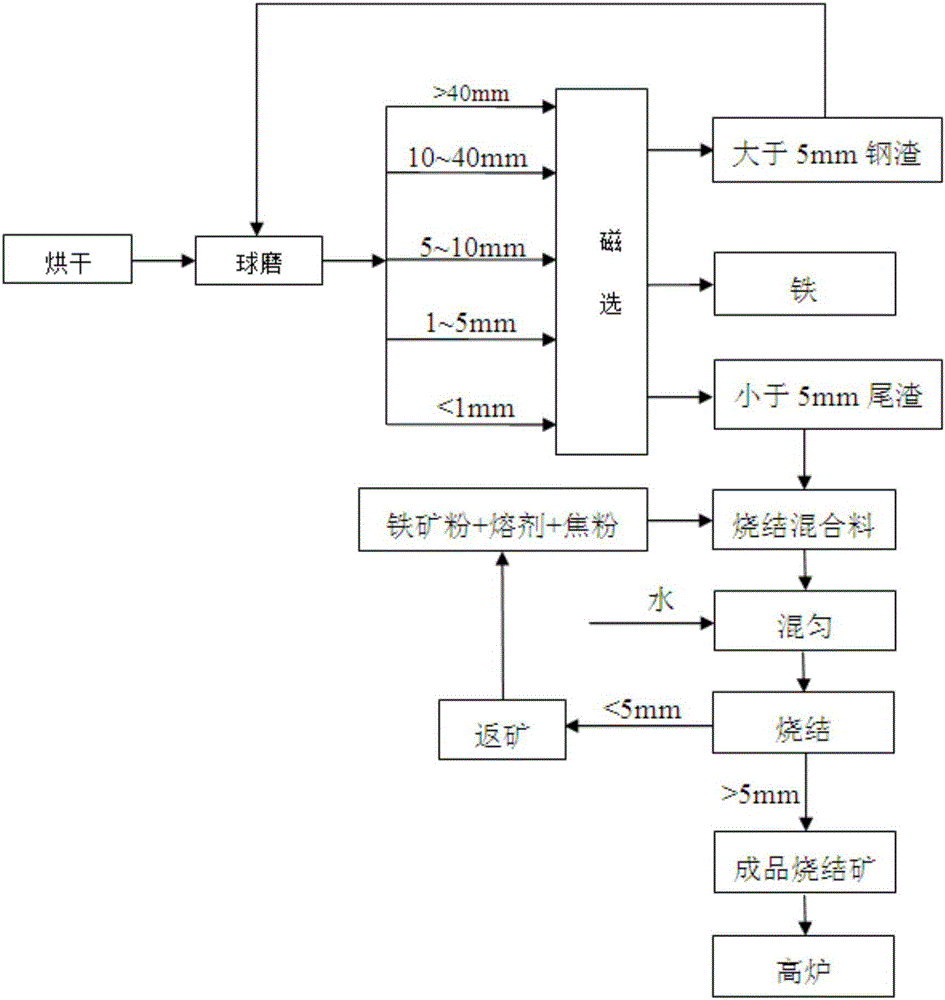
[0032] The present embodiment selects the steel slag that certain enterprise steelmaking produces, a kind of method for reclaiming the iron in steel slag, it is characterized in that, comprises the following steps:
[0033] 1) Ball milling
[0034] The dried steel slag is placed in a ball mill, the rotating speed of the ball mill is 240r / min, and the ball milling time is 25min; in the ball mill process, steel balls with the same weight as the steel slag are added in the ball mill, and the diameter of the steel ball is 25mm.
[0035] 2) Screening
[0036] Sieve the steel slag after ball milling obtained in step 1), and divide it into steel slags of five particle sizes: >40mm, 10-40mm, 5-10mm, 1-5mm, and <1mm; conduct.
[0037] 3) Magnetic separation
[0038] The steel slag of five particle sizes is subjected to magnetic separation, and the iron-containing steel slag of each particle size and the tailing slag of each particle size are recovered respectively; the magnetic sep...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The non-magnetic tailings obtained in Example 1 are used for secondary utilization of resources. The steps described are as follows:
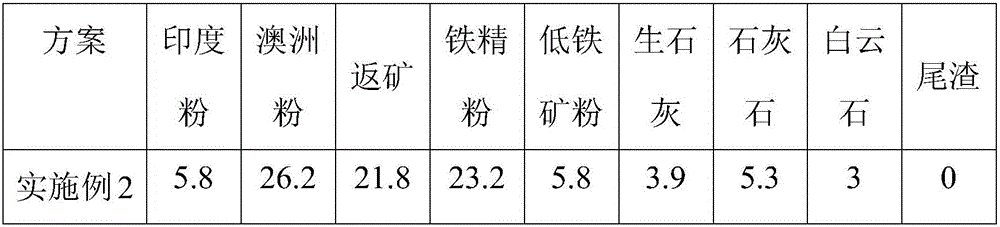
[0043] 5.1) Mix the tailings obtained in step 4) with iron ore powder, sintering flux, and coke powder to obtain a sintering mixture; keep the sintering basicity (R=CaO / SiO 2 ) is 2.0.
[0044] The iron ore powder includes five types of Indian powder, Australian powder, return ore, iron concentrate powder and low iron ore powder, and the sintering flux includes limestone, quicklime and dolomite.
[0045] The ingredients (percentage / %) of the tailings, iron ore powder, sintering flux and coke powder are shown in Table 1.
[0046] Table 1
[0047]
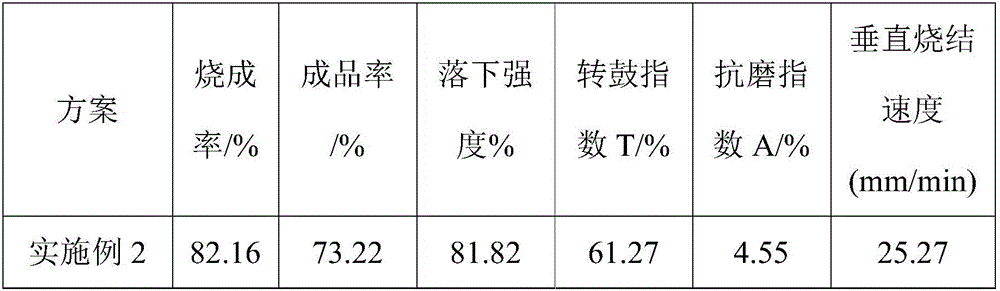
[0048] After testing, the chemical composition of the sintered raw materials is shown in Table 2.
[0049] Table 2
[0050] product name
TF
SiO 2
CaO
MgO
al 2 o 3
h 2 o
Indian powder
56.35
7.08
0.64
0.22
6....
Embodiment 3
[0063] The non-magnetic tailings obtained in Example 1 are used for secondary utilization of resources. The steps described are as follows:
[0064]5.1) Mix the tailings obtained in step 4) with iron ore powder, sintering flux, and coke powder to obtain a sintering mixture; keep the sintering basicity (R=CaO / SiO 2 ) is 2.0.
[0065] The iron ore powder includes five types of Indian powder, Australian powder, return ore, iron concentrate powder and low iron ore powder, and the sintering flux includes limestone, quicklime and dolomite.
[0066] The ingredients (percentage / %) of the tailings, iron ore powder, sintering flux and coke powder are shown in Table 5.
[0067] table 5
[0068]
[0069] After testing, the chemical composition of the sintered raw materials is shown in Table 2.
[0070] 5.2) Put the sintered mixture obtained in step 5.1) into a mixer for granulation. During the mixing process, 7.5±0.5% of water by weight of the sintered mixture is added; the granula...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com