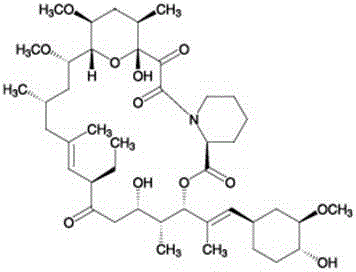
Method of preparing ascomycin through fermentation
A technology of ascomycin and fermentation broth, applied in the field of microbial fermentation, can solve the problems of high cost, less ascomycin, restricted use, etc., and achieve the effects of low production cost, low equipment requirements, and mild conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1 fermentation bottle produces ascomycin
[0034] 5 ml of mature shake flask seeds were inoculated into the prepared fermentation flask, and the shake flask was cultured at a temperature of 28° C. and a rotation speed of 250 rpm for 7 days. From the second day, samples were taken every day to measure the fermentation broth unit and pH of the fermentation bottle.
[0035] The experimental results are shown in Table 1 below:
[0036]
[0037] It can be seen from the results in Table 1 that the unit of fermentation bottle can reach 1300 mg / L in 7 days, the unit growth is stable in the middle and late stages of fermentation, and the pH of the feed liquid has been maintained at about 5.5.
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2 fermentor produces ascomycin, does not control pH
[0039] Inoculate 1.8L mature shake flask seeds into the prepared fermenter, control the temperature of the fermenter to 28°C, the pressure to 0.05Mpa, the ventilation to 1.0-1.5VVM, and the speed to 100-600rpm, set the initial dissolved oxygen in the fermenter 100%, keep dissolved oxygen above 30% during the cultivation process, and ferment and cultivate for 7 days. From the second day, samples were taken every day to measure the fermentation broth unit and pH.
[0040] The experimental results are shown in Table 2 below:
[0041]
[0042]From the results in Table 2, it can be seen that the 7-day unit of the fermenter is only 1020 mg / L, and the growth rate of the unit in the middle and late stages of fermentation is significantly lower than that of the fermentation bottle.
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3 fermentor produces ascomycin, controls pH with sulfuric acid simultaneously
[0044] Inoculate 1.8L mature shake flask seeds into the prepared fermenter, control the temperature of the fermenter to 28°C, the pressure to 0.05Mpa, the ventilation to 1.0-1.5VVM, and the speed to 100-600rpm, set the initial dissolved oxygen in the fermenter 100%, keep dissolved oxygen above 30% during the cultivation process, and ferment and cultivate for 7 days. After cultivating for about 60 hours, the pH of the fermentation broth stops falling, and the prepared sulfuric acid solution is slowly added to control the pH of the feed solution to 5.5, which is maintained until the end of fermentation. From the second day, samples were taken every day to measure the fermentation broth unit and pH.
[0045] The experimental results are shown in Table 3 below:
[0046]
[0047] It can be seen from the results in Table 3 that the 7-day unit of the fermenter reached 1325mg / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com