Method for detecting drug-resistant genes of pathogenic microorganisms of human body
A technology of pathogenic microorganisms and detection methods, applied in the field of detection of drug resistance genes of human pathogenic microorganisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
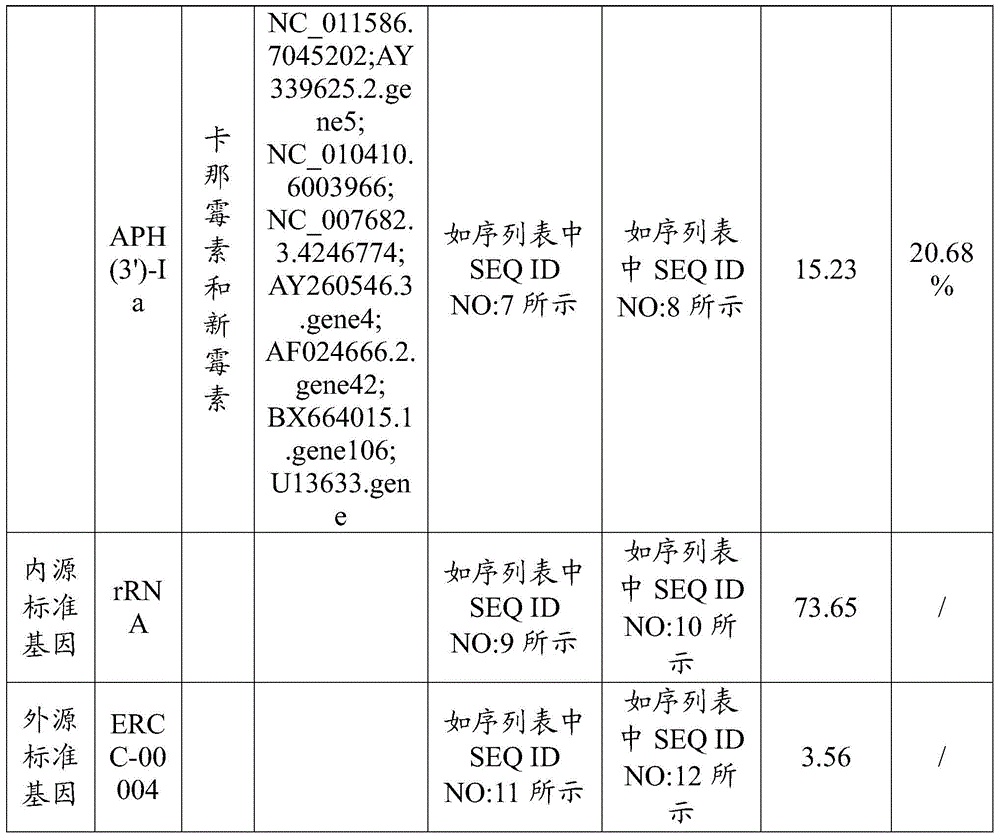
[0029] Example 1. Drug resistance gene detection of human feces microorganisms
[0030] The sample to be tested can be human organs and tissues, a part of human organs and tissues, human body fluid, human secretion or human excrement, and in this embodiment, the sample to be tested is human feces (human excrement), and human feces microbial reaction The types and quantities of pathogenic microorganisms in the human intestinal tract are determined, which is the basis for the diagnosis and treatment of intestinal diseases. The human feces used in this example were taken from a patient with enteritis diagnosed by a doctor, and the detection of the drug resistance gene of microorganisms in the feces was to provide evidence for the doctor to use antibiotics to treat the patient's enteritis. This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0031] Step 1. Determine the drug resistance gene of the microorganism to be detected in the sample to be tested, the endogenous standard gene in...
Embodiment 2
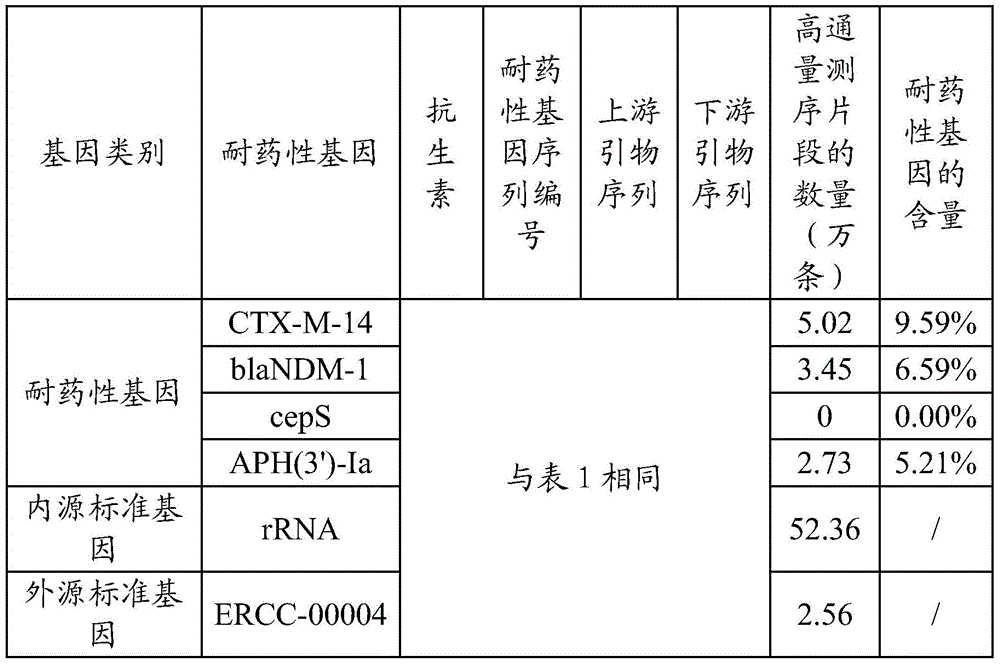
[0063] Embodiment two, the drug resistance gene detection of human blood microorganism
[0064] Human blood microbes reflect the types and quantities of pathogenic microorganisms in various diseases of the human body, and are the basis for disease diagnosis and treatment. The cryopreserved human blood samples used in this example are taken from cold patients, and the detection of the drug resistance genes of microorganisms in the blood is to provide evidence for doctors to use antibiotics for treatment. The steps of this implementation are roughly the same as those in Embodiment 1, and the following focuses on the differences:
[0065] By the same method as in Example 1, determine the drug resistance gene of the microorganisms to be detected in the sample to be tested, the endogenous standard gene in the sample to be tested, and the exogenous standard gene of the sample to be tested; The multiple amplification primers of the test regions of sex genes, endogenous standard gene...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com