Method for degrading antibiotic pharmaceutical wastewater
A technology for pharmaceutical wastewater and antibiotics, applied in natural water treatment, water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of complex preparation process of boron-doped diamond electrodes, high price of platinum electrodes, low current efficiency, etc. Effects of high oxygen evolution potential and electrochemical stability, reduced crystal size, and improved catalytic activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
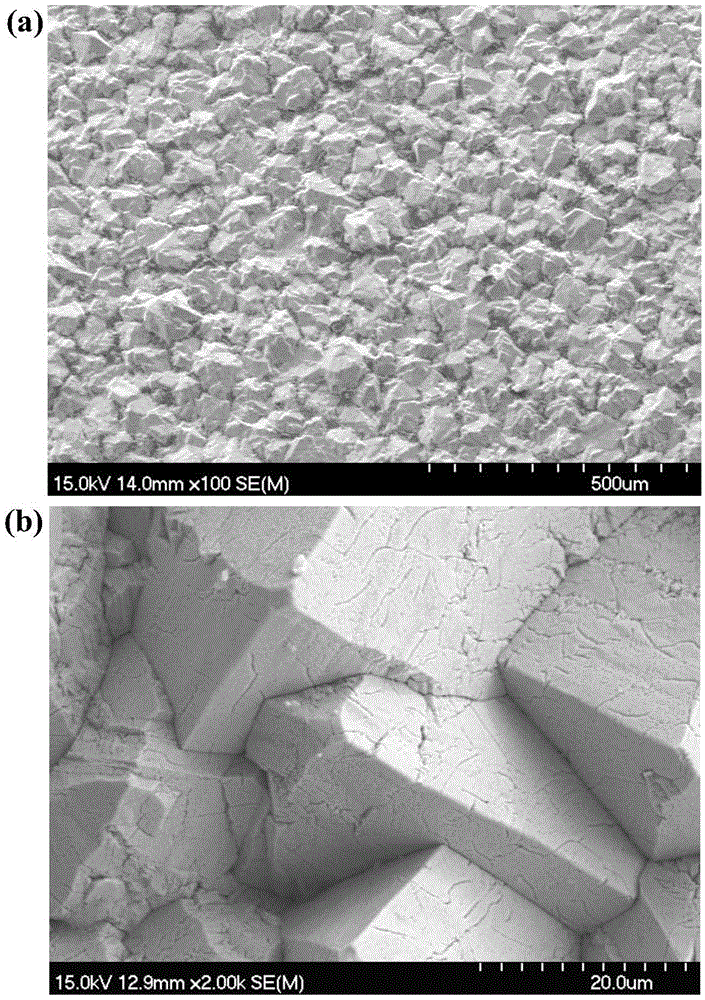
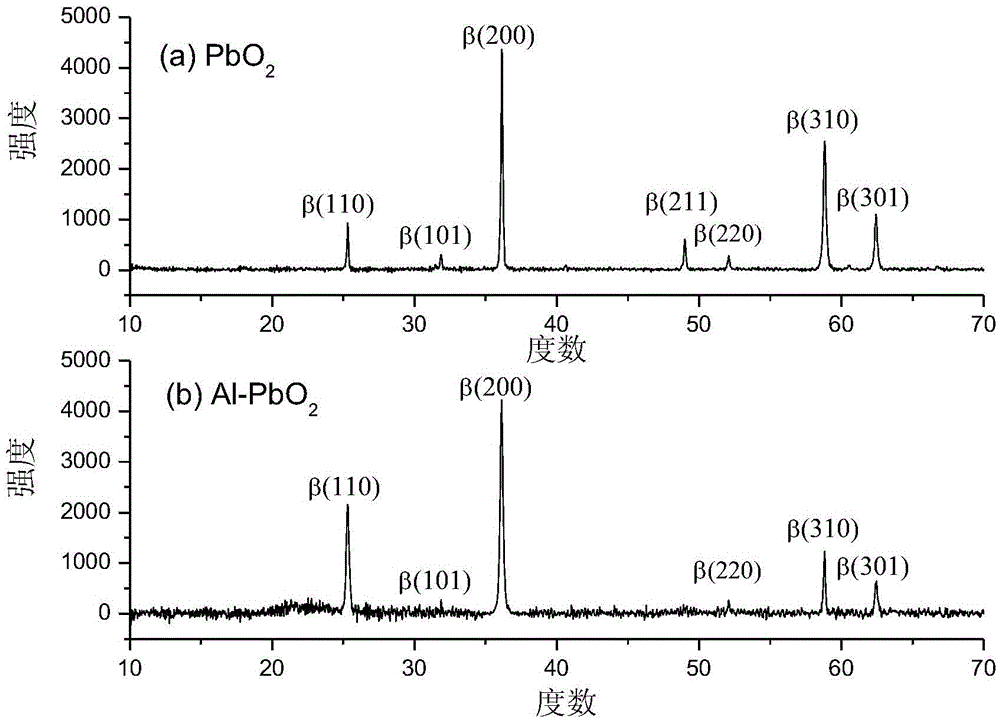
[0041] A method for preparing an aluminum-doped lead dioxide electrode. The aluminum-doped lead dioxide electrode uses titanium as a matrix, and the titanium matrix is a titanium sheet. The titanium sheet is pretreated by grinding, alkali cleaning, degreasing, pickling and etching. The pretreated titanium substrate is prepared by brushing and pyrolysis to prepare the bottom layer of tin antimony oxide, and then the electrodeposition method is used in the prepared electroplating solution. α-PbO 2 Intermediate layer and fluorine-containing β-PbO doped with a certain amount of Al 2 active layer.
[0042] The concrete steps of described method are as follows:
[0043] (1) Titanium substrate pretreatment: the thickness is 0.1mm, the size is 14cm 2 (7cm×2cm) pure titanium sheet was polished with 120-mesh, 600-mesh and 1200-mesh sandpaper in turn until the titanium substrate showed a silvery-white metallic luster, and was rinsed with deionized water; the polished and cleaned tit...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The prepared Al-doped lead dioxide electrode was used to electrocatalyze the oxidation degradation of chloramphenicol.
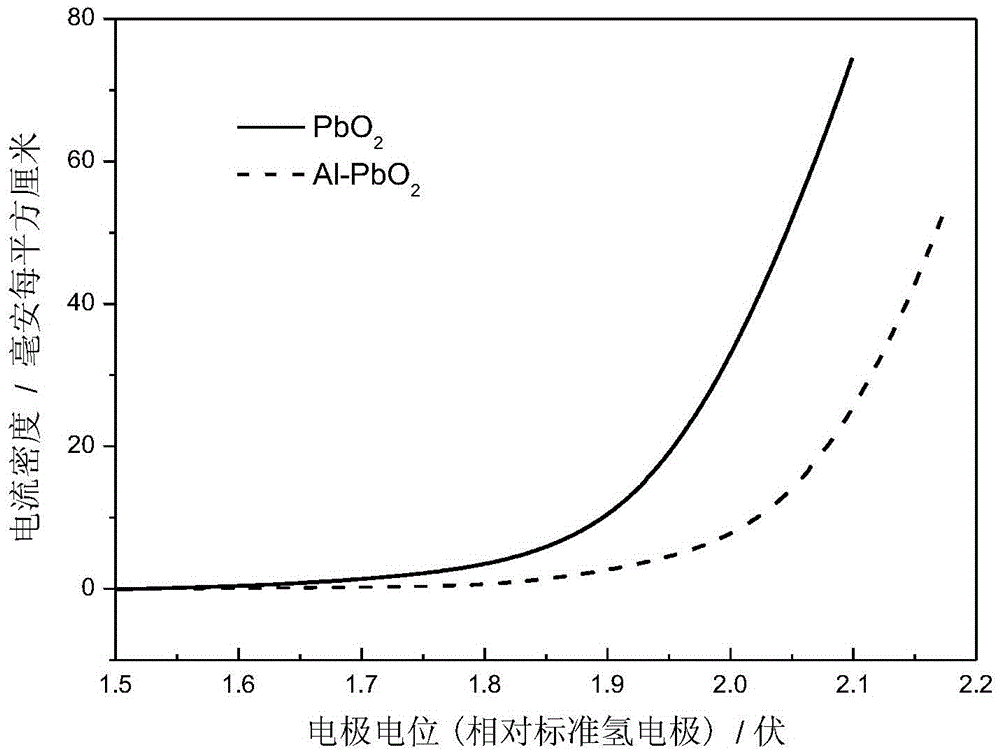
[0054] The prepared Al-doped lead dioxide electrode or undoped lead dioxide electrode is used as the anode, and the titanium sheet is used as the cathode, and the electrode area is 14cm 2 , electrochemical degradation using constant current electrolysis. The constant current density is 50mAcm -2 , The electrode spacing is 4cm. to contain 0.1molL -1 Electrolyte Na 2 SO 4 500mgL -1 Chloramphenicol is a simulated wastewater with a reaction volume of 250mL. Under the action of magnetic stirring, the wastewater is treated, and samples are taken for analysis at different times during the degradation reaction. The changing situation of the concentration of chloramphenicol at different times is measured by HPLC, and the changing situation of total organic carbon content (TOC) is measured by a TOC measuring instrument. The experimental results are shown ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] The prepared Al-doped lead dioxide electrode was used to electrocatalyze the oxidation degradation of levofloxacin.
[0058] The prepared Al-doped lead dioxide electrode or undoped lead dioxide electrode is used as the anode, and the titanium sheet is used as the cathode, and the electrode area is 14cm 2 , electrochemical degradation using constant current electrolysis. The constant current density is 50mAcm -2 , The electrode spacing is 4cm. to contain 0.1molL -1 Electrolyte Na 2 SO 4 500mgL -1 The levofloxacin is a simulated wastewater with a reaction volume of 250mL. Under the action of magnetic stirring, the wastewater is treated, and samples are taken for analysis at different times during the degradation reaction. The change of the concentration of levofloxacin at different times is measured by HPLC, and the change of total organic carbon content (TOC) is measured by a TOC analyzer. The experimental results are shown in Figure 6 . Figure 6 Al doped PbO ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Oxygen evolution potential | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com