Cane sugar-free flavor fermented milk for continuously providing energy and preparation method thereof
A sucrose-free, fermented milk technology, applied to bacteria and lactobacilli used in dairy products and food preparation, can solve the problems of non-sustainable energy and unstudied functional synergy of functional sugars, etc., to reduce atherosclerosis The risk of sclerosis, the risk of reducing blood lipids, and the effect of mellow aroma
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1 A sucrose-free flavored fermented milk that continuously provides energy and its preparation method
[0036] This embodiment provides a sucrose-free flavored fermented milk that continuously provides energy. The raw materials for making it are: 810 kg of raw milk (wherein the protein content is 2.90%, the fat content is 3.2%, and the non-fat milk solids are 8.1%), natural sweeteners 0.25kg (0.15kg of Luo Han Guo powder and 0.1kg of steviol glycoside), 30kg of isomaltulose, 80kg of crystalline fructose, 1kg of pectin and gelatin each as a stabilizer, 22kg of soluble dietary fiber polydextrose, emulsifier diacetyl tartaric acid mono-diglycerol Ester 0.5kg, and mixed strain 280DCU (including Lactobacillus acidophilus strain 180DCU, Lactobacillus bulgaricus strain 100DCU).
[0037] The preparation method of the sucrose-free flavored fermented milk comprises the following steps carried out in sequence:
[0038] ① Ingredients
[0039] i. Heat 100kg of raw milk to ...
Embodiment 2-10
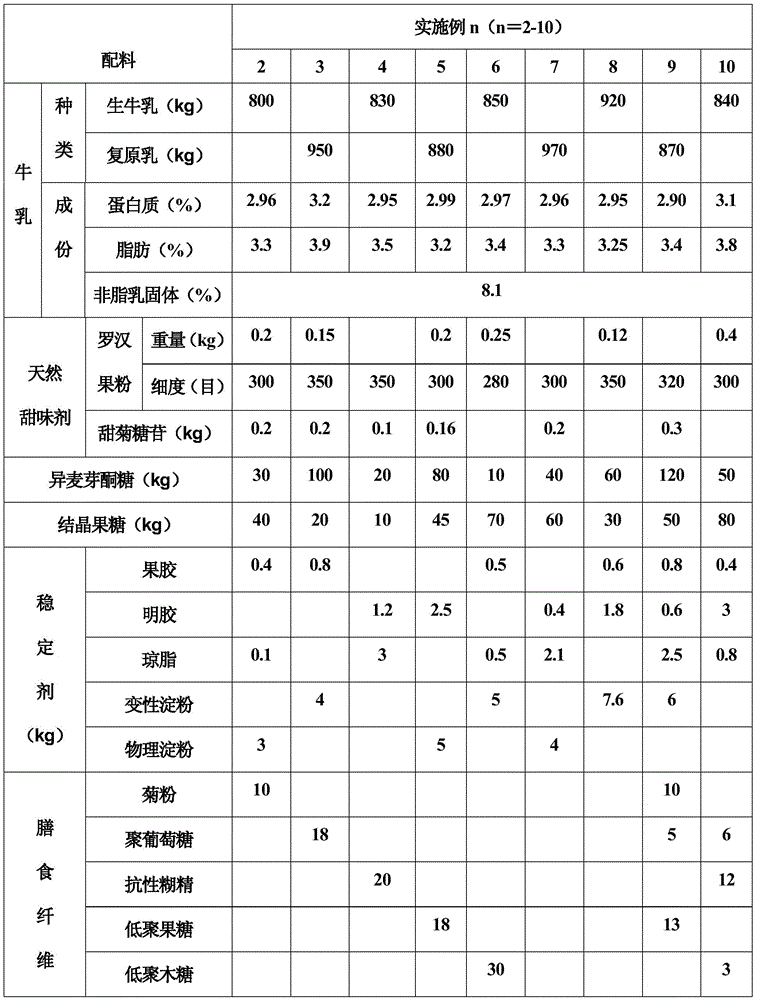
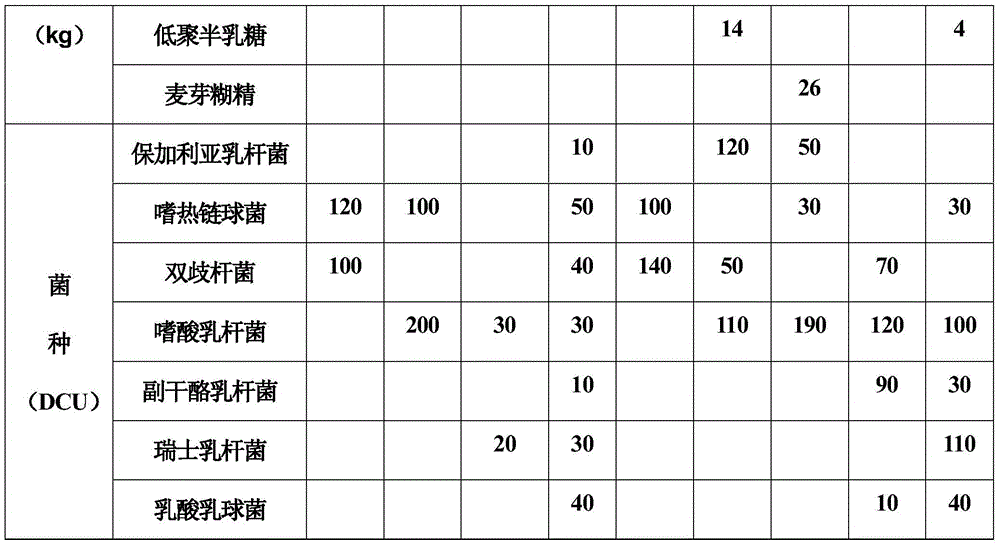
[0053] Examples 2-10 are respectively a sucrose-free flavored fermented milk that continuously provides energy and a preparation method thereof. Their formulas differ from those in Example 1 only in the types and amounts of ingredients. See Table 1 for details. :
[0054] Table 1 Example 2-10 list of ingredients
[0055]
[0056]
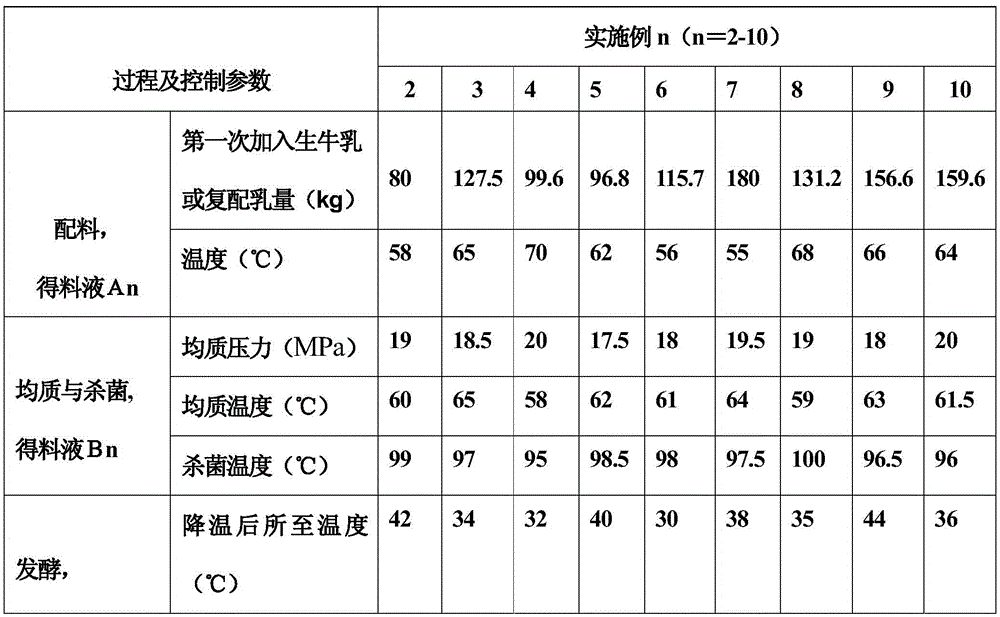
[0057] The method for preparing sucrose-free flavored fermented milk that continuously provides energy in Examples 2-10 differs from the corresponding preparation method in Example 1 only in that the control parameters in the process are different, and the quality of the produced product is also different. Differences, see Table 2 for details:
[0058] Table 2 embodiment 2-10 control parameter statistical table
[0059]
[0060]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com