Wireless self-networking system and routing method thereof
A wireless ad hoc network and routing technology, applied in wireless communication, network topology, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of small routing overhead, short service establishment delay, and prolongation of service establishment, so as to reduce routing overhead and route establishment The effect of shortening the time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1: Adjacent node information broadcast and local routing table establishment
[0047] It is set that each node in the network broadcasts its neighbor node information to each other, then each node can know its one-hop neighbor and two neighbors by receiving the broadcast message of the neighbor node, so as to establish a local routing table, the routing table contains one-hop node and two-hop node information. In this way, addressing for routes within two hops can be done by looking up the local routing table, without requiring higher layers to initiate routing requests, thereby shortening the time for link establishment within two hops and avoiding routing overhead.
[0048] In order to reduce the signaling overhead caused by routing search, the transit nodes of routing messages are defined in the network. After receiving routing messages, such nodes will forward them if they judge that the number of hops propagated by routing messages does not exceed the ma...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2: Selection of transit nodes
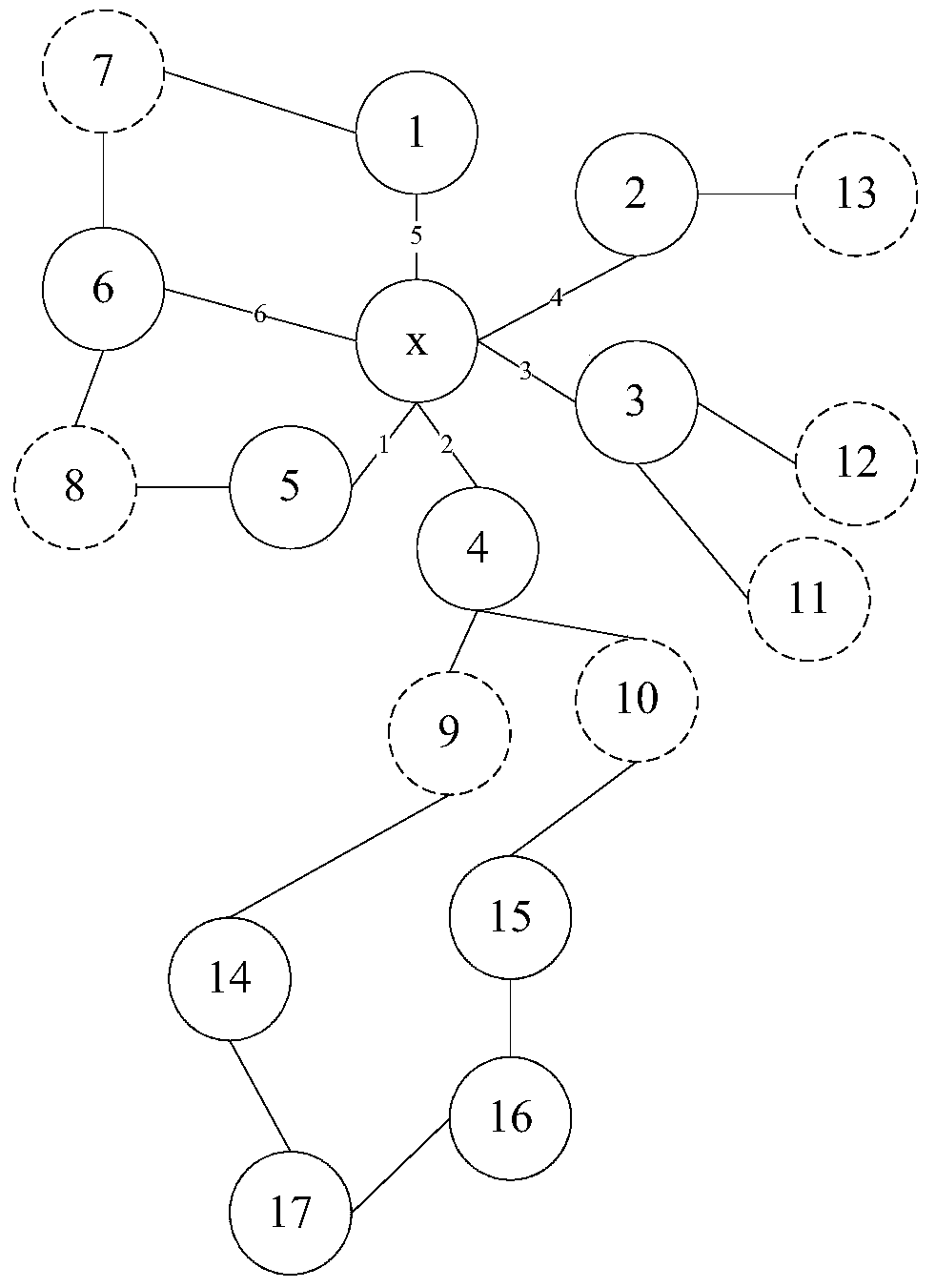
[0051] Assume that the set of one-hop neighbors of node x is S1, the set of two-hop neighbors is S2, where S2 does not contain node x itself, and does not contain all the elements in S1; the set of transit nodes is S3. Define D(s), s∈S1, is the degree of connectivity of node s, which means the number of symmetric nodes other than S1 of node s. Symmetric nodes mean that the link between two nodes is bidirectional. Define C(s), s∈S1, as the link metric value (LinkMetric) of node s, which represents the link metric value of the link between node x and node s, and the link metric value is used as the weight to evaluate each link , which can represent the link attainable rate or link quality, etc.
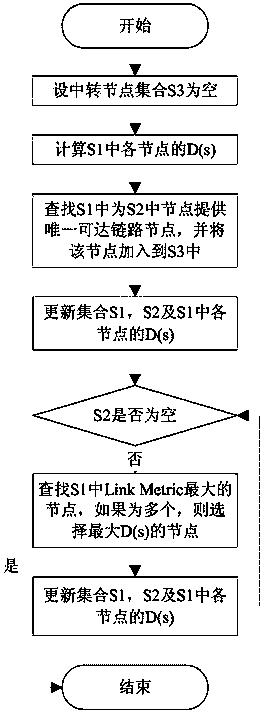
[0052] Please refer to the attached figure 1 , the selection method of the transit node of node x is as follows:
[0053] Step 1: Calculate D(s) of each node in S1;
[0054] Step 2: Find the node in S1 that provides the only reachable l...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Embodiment 3: Route lookup within two hops
[0061] The steps to find a route within two hops are as follows:
[0062] Step 1: Add each symmetric neighbor as a 1-hop neighbor to the routing table by receiving broadcast messages from neighbor nodes;
[0063] Step 2: Add the non-1-hop symmetric node as a 2-hop neighbor to the routing table through the received neighbor list message broadcast by the neighbor node;
[0064] The one-hop and two-hop neighbors of each node can be determined by the above two steps, and the routing table is updated by receiving broadcast messages continuously. When a node needs to communicate with neighbors within two hops, it can directly query the stored routing table and send it.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com