Quantum dot light-emitting diode sub-pixel array, its manufacturing method and display device
A quantum dot light-emitting and sub-pixel technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as high technical difficulty, high commodity prices, and low product yield, and improve process yield and cost. Reduced, easy-to-prepare effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
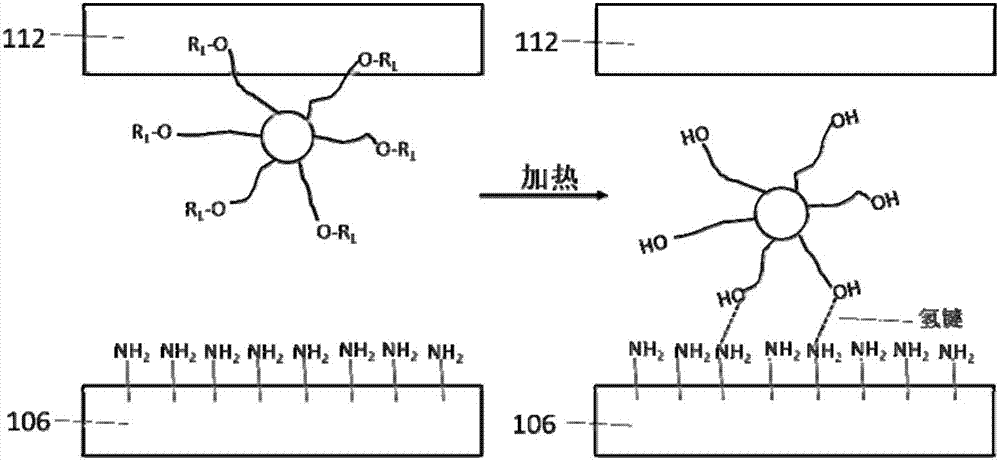
[0061] Figures 2A-2K It is a schematic diagram illustrating each stage of the method for preparing a quantum dot light-emitting diode sub-pixel array according to the first embodiment of the present invention through cross-sectional views. In a specific example, for example, green, blue, and red three-color quantum dot light-emitting diode sub-pixel arrays can be respectively prepared on the substrate by a laser heating method.
[0062] first, Figure 2A The initial structure of this embodiment is shown. The initial structure is a base substrate 202, the material of which is well known in the art, such as glass or quartz. The base substrate 202 may be transparent or opaque. The base substrate 202 is cleaned using standard methods.
[0063] Next, if Figure 2B An optional thin film transistor (TFT) array 204 is fabricated on a base substrate 202 as shown. There is no limitation on the specific preparation method and structure of the TFT array, which may be methods and st...
no. 2 example
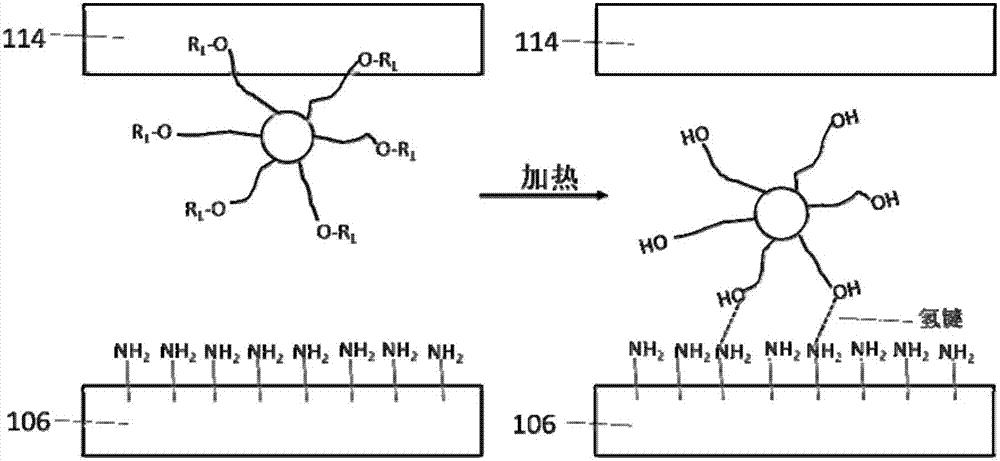
[0086] In the second embodiment, using a method similar to that of the first embodiment, the transfer of each thermally sensitive quantum dot material layer to the corresponding sub-pixel area is realized independently. The difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment is that the heat-sensitive quantum dot material layer is not used on the carrying substrate, but directly uses a thermal conductivity mask to carry the heat-sensitive quantum dot material. In the following description, the parts in the second embodiment that are similar to those in the first embodiment will not be described in detail.
[0087] Figures 3A-3H It is a schematic diagram illustrating various stages of the method for preparing a quantum dot light-emitting diode sub-pixel array according to the second embodiment of the present invention through cross-sectional views.
[0088] Such as Figure 3A and 3B As shown, an optional TFT array 304 is prepared on the cleaned base substrate ...
no. 3 example
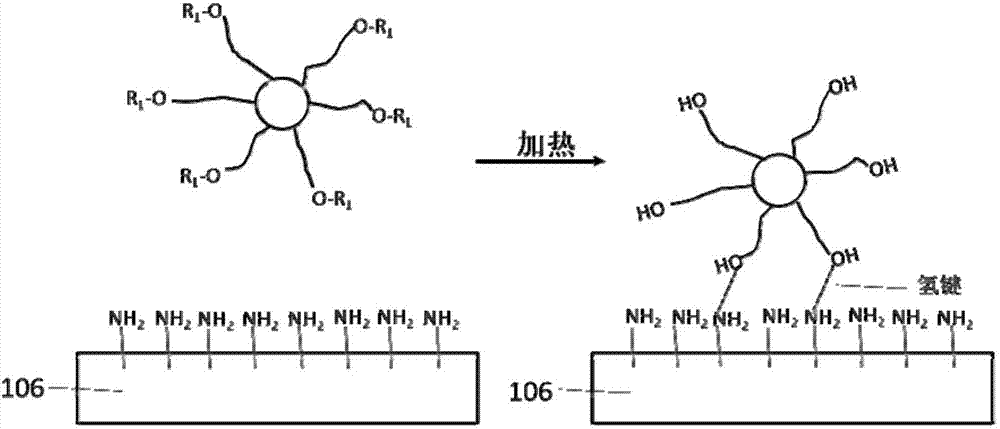
[0104] In the third embodiment, the transfer of each heat-sensitive quantum dot material layer to the corresponding sub-pixel area is realized independently by using a heating method similar to that of the first embodiment. The main difference between the third embodiment and the first embodiment is that instead of using a carrier substrate for the thermally sensitive quantum dot material layer, the thermally sensitive quantum dot material layer is directly coated on the quantum dot receiving layer. In the following description, the parts of the third embodiment that are similar to those of the first embodiment will not be described in detail.
[0105] Figures 4A-4H It is a schematic diagram illustrating various stages of a method for preparing a quantum dot light-emitting diode sub-pixel array according to a third embodiment of the present invention through cross-sectional views.
[0106] Such as Figure 4A and 4B As shown, an optional TFT array 404 is prepared on the cle...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com