Preparation method of porous adsorption material
A technology of porous adsorption materials and porogens, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, alkali metal oxides/hydroxides, inorganic chemistry, etc., and can solve problems such as the need to improve adsorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
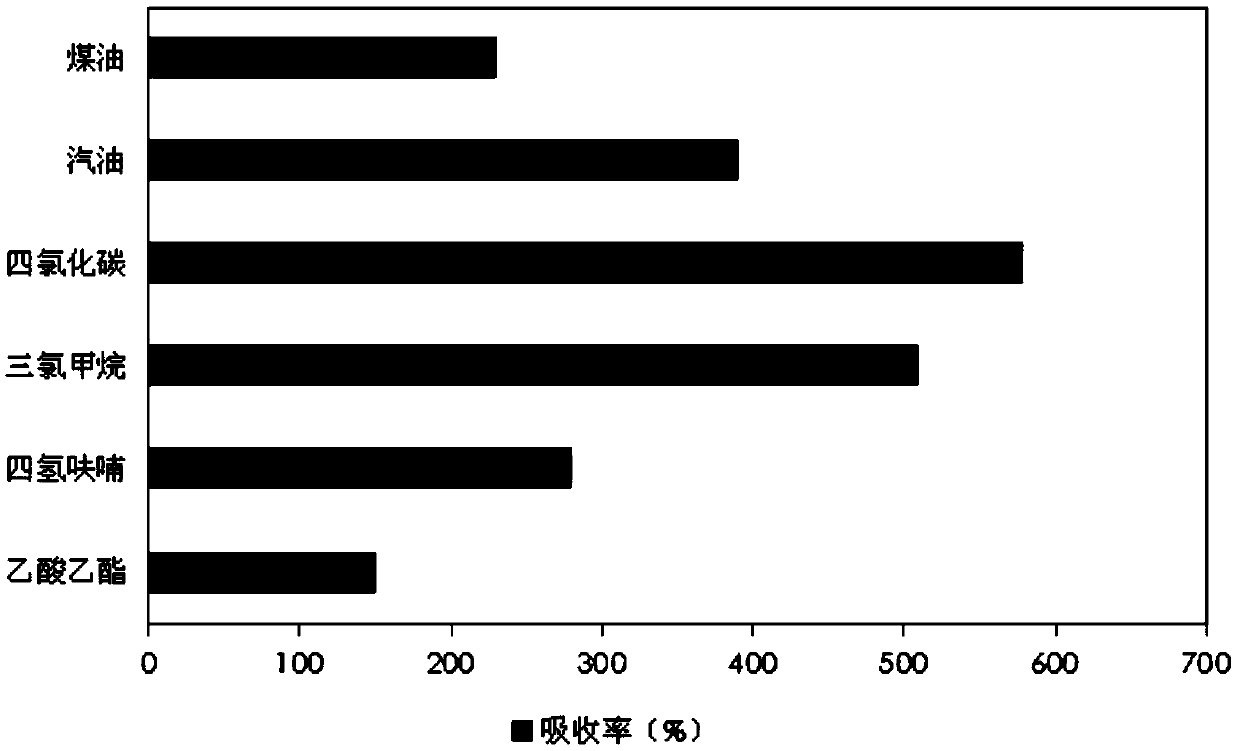
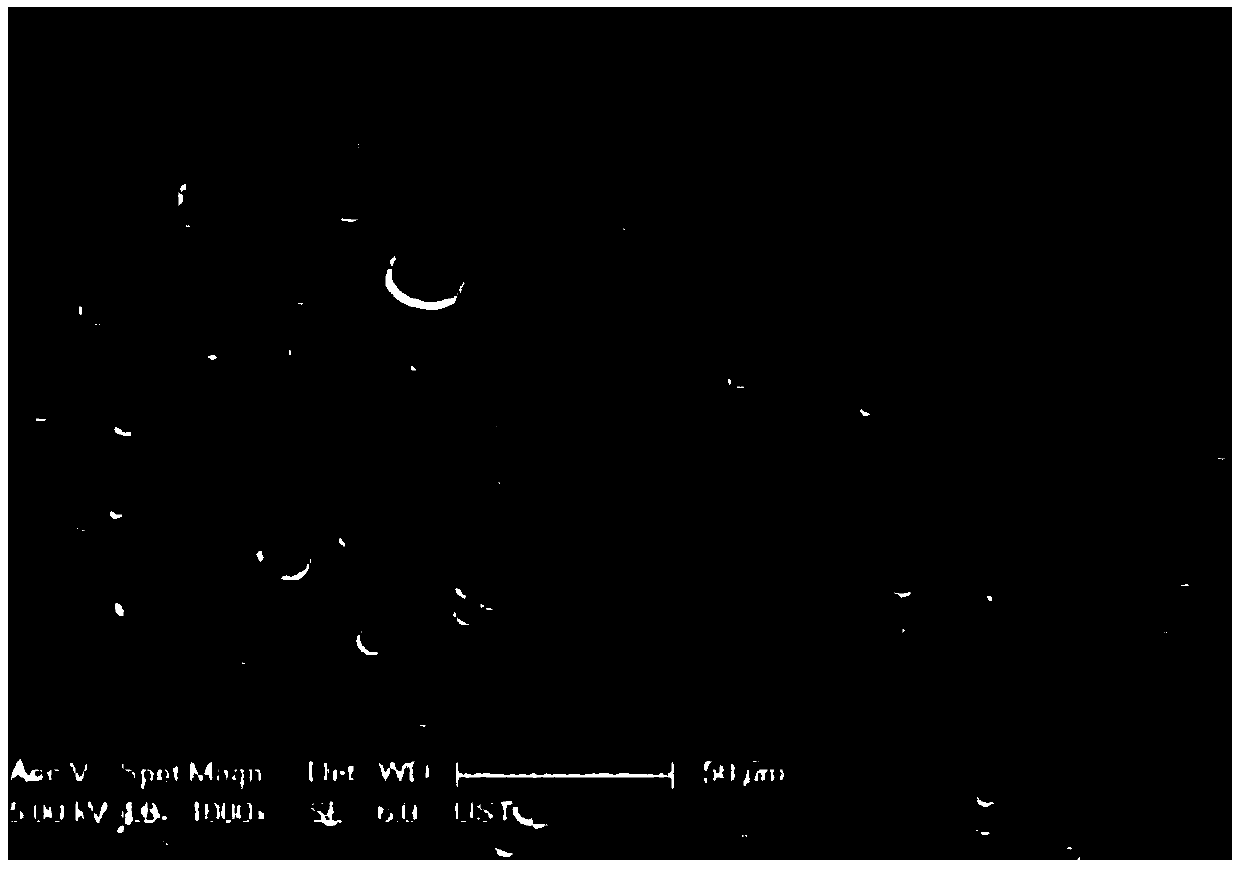
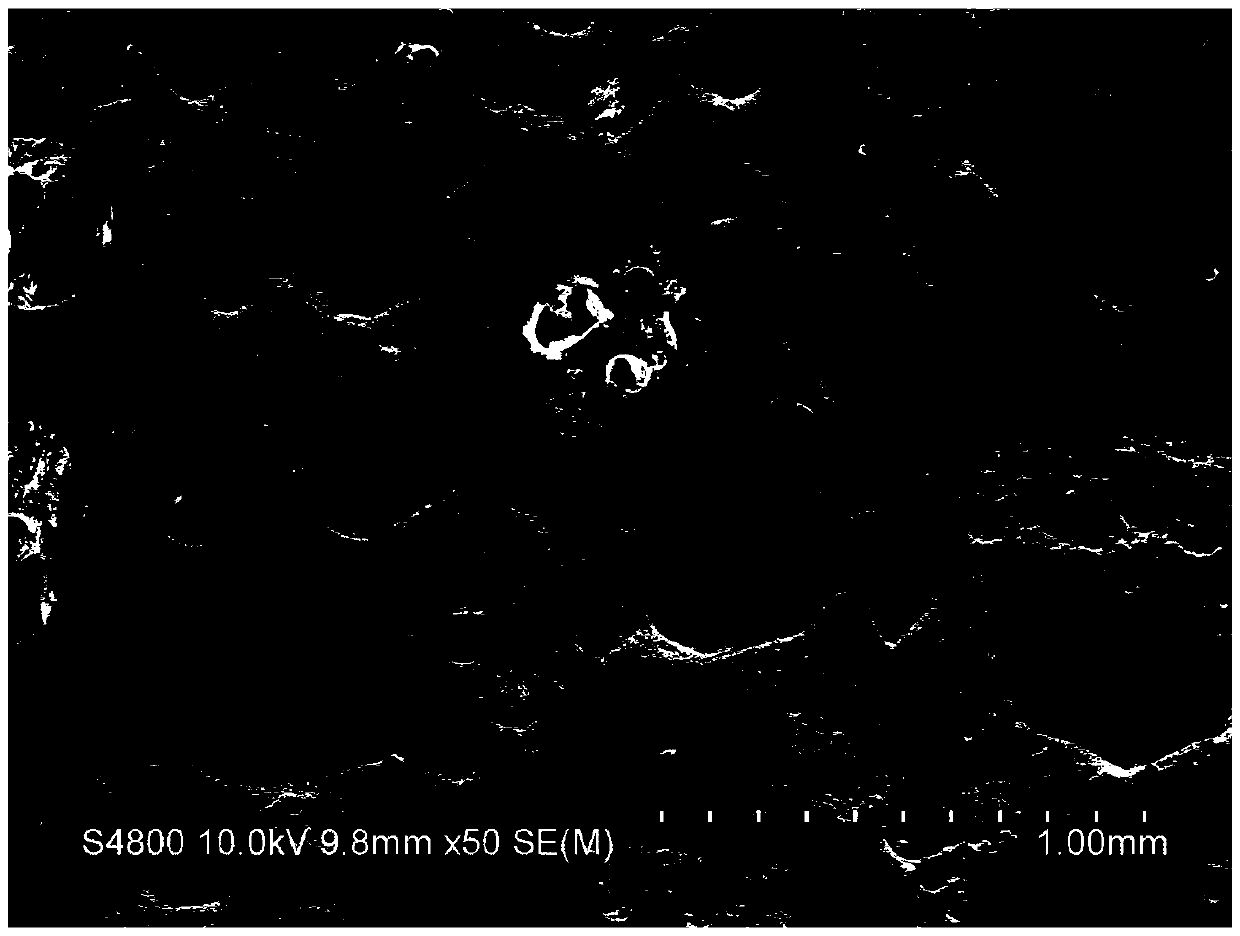
[0036] Example 1: Accurately weigh 5.0g Sylgard-184A, 0.5g Sylgard-184B, 4.125g carbon tetrachloride, 4.125g n-octane and stir well. Drop by drop into 50 mL of saturated sodium bicarbonate solution with a syringe. The stirring speed is 150r / min, and the stirring temperature is 80°C. After stirring for 2 hours, the material was taken out, soaked in concentrated HCl solution for 5 hours to remove sodium bicarbonate solution, and then washed with hot distilled water and ethanol several times to remove concentrated HCl. Put it in an oven at 70°C for 12 hours to remove the moisture. The scanning electron microscope image of the material after drying is shown in image 3 shown. The adsorption capacity of materials to various oils such as Figure 4 shown. The adsorbed material was extruded and placed in absolute ethanol to remove the adsorbed oil. Repeat the test more than 20 times, the adsorption capacity of carbon tetrachloride is as follows: Figure 5 shown.
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: Accurately weigh 5.0 g of hydroxyl-terminated polydimethylsiloxane, 1.0 g of dibutyltin dilaurate, 6.0 g of carbon tetrachloride, and 6.0 g of tetrahydrofuran after stirring evenly. Drop by drop into 60mL of saturated sodium carbonate solution with a syringe. The stirring speed is 200r / min, and the stirring temperature is 70°C. After stirring for 3 hours, the material was taken out, soaked in concentrated HCl solution for 6 hours to remove sodium bicarbonate solution, and then washed with hot distilled water and ethanol several times to remove concentrated HCl. Put it in an oven at 80°C for 12 hours to remove the moisture therein. The adsorption capacity of materials to various oils such as Figure 6 shown. The adsorbed material was extruded and placed in absolute ethanol to remove the adsorbed oil. Repeat the test more than 20 times, the adsorption capacity of carbon tetrachloride is as follows: Figure 7 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3: Accurately weigh 5.0 g of PDMS dimethylsiloxane, 2.0 g of tetraethyl silicate, 10.0 g of carbon trichloride, and 10.0 g of cyclohexane and stir evenly. Drop by drop into 100mL of ammonium bicarbonate with a syringe. The stirring speed is 100r / min, and the stirring temperature is 90°C. After stirring for 3 hours, the material was taken out, soaked in concentrated HCl solution for 8 hours to remove sodium bicarbonate solution, and then washed with hot distilled water and ethanol several times to remove concentrated HCl. Put it in an oven at 80°C for 12 hours to remove the moisture therein. The adsorption capacity of materials to various oils such as Figure 8 shown. The adsorbed material was extruded and placed in absolute ethanol to remove the adsorbed oil. Repeat the test more than 20 times, the adsorption capacity of carbon tetrachloride is as follows: Figure 9 shown.
[0039] It can be seen from the examples and drawings that the porous oil-absorbing...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com