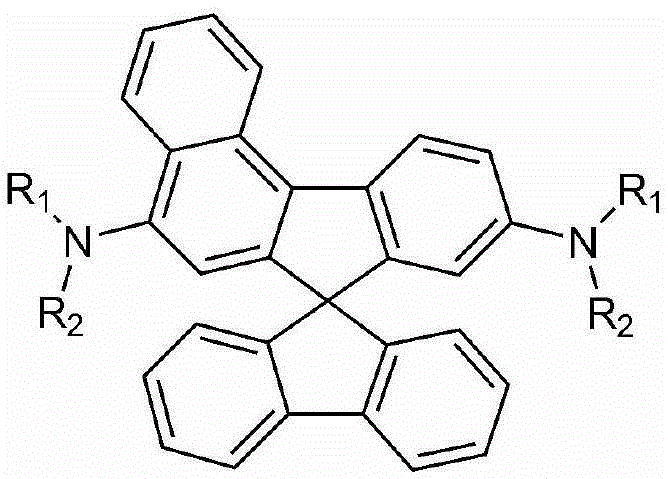
Spiro-type organic material, and organic electroluminescent device using same
A technology for organic light-emitting elements and compounds, which is applied in the field of organic electroluminescent elements and can solve the problems of obtaining a blue light-emitting layer in a short wavelength region, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0101] Intermediate 2-1 (8.2 g) was added to a 1 L three-neck round bottom flask, and stirred for 30 minutes under an argon atmosphere. After stirring for 30 minutes, Intermediate 1 (10 g) was added and melted through toluene (250 mL), followed by the addition of palladium(II) acetate (0.21 g), tri-tert-butylphosphine (0.9 g), sodium tert-butoxide (7.3 g ) was refluxed and stirred for 18 hours. After the reaction, the above solution was filtered in a hot state, and then the filtered solid was washed with hot toluene and dichloromethane, and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The substance produced by concentration was purified using silica gel column chromatography (eluent: N-hexane:dichloromethane=1:1), and then recrystallized using tetrahydrofuran, whereby a yellow-green solid having the following structure was obtained.
[0102]
[0103] 1 HNMR (500MHz, CDCl 3 ,TMS)δ(PPM)8.20(d,2H),8.05(m,4H),7.69(d,2H),7.51(d,2H),7.32(m,4H),7.21(m,6H),7.13 (m,6H),...
Embodiment 2 to Embodiment 76
[0105] The compound of Example 2-76 was prepared by the same method as in Example 1, using Intermediates 2-2 to 2-76 instead of Intermediate 2-1. The structures and NMR data of Examples 2-76 prepared respectively are shown in Tables 6-70 below.
[0106] Table 6
[0107]
[0108] Table 7
[0109]
[0110] Table 8
[0111]
[0112] Table 9
[0113]
[0114] Table 10
[0115]
[0116] Table 11
[0117]
[0118] Table 12
[0119]
[0120] Table 13
[0121]
[0122] Table 14
[0123]
[0124] Table 15
[0125]
[0126] Table 16
[0127]
[0128] Table 17
[0129]
[0130] Table 18
[0131]
[0132] Table 19
[0133]
[0134] Table 20
[0135]
experiment example 1
[0137] Experimental example 1: Fabrication of the organic electroluminescent element using Example 1
[0138] Put an indium tin oxide (ITO) transparent electrode substrate with a film thickness of 100nm into distilled water dissolved in a cleaning agent in a size of 40mm×40mm×0.7m, clean it with ultrasonic waves for 10 minutes, and wash it twice in distilled water for 10 minutes.
[0139] After cleaning with distilled water, ultrasonic cleaning and drying are performed on solvents such as isopropanol, acetone, and methanol in sequence. After wet purification, oxygen plasma and argon plasma are used for dry cleaning, and then the glass substrate with transparent electrode lines is installed on the substrate holder of the vacuum evaporation device, and the indium tin oxide with transparent electrode lines formed A compound represented by the following chemical formula A was thermally vacuum-evaporated to a thickness of 3 nm on the (ITO) side surface to form a hole injection laye...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com