Method for Determining Sequencing Digestion Combination in Sequencing Genotyping Technology
A genotyping and genome technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the efficiency of enzyme digestion, reducing the density of SNP mining, increasing the cost of experiments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0099] Example 1 uses the bovine genome to illustrate the analysis method provided by the present invention.
[0100] 1. Prediction of the number of digested fragments
[0101]Write the perl script Site_predict.pl as follows, and the input files are the chromosome name and sequence of the bovine genome and the cleavage site sequence of the predicted enzyme. The running command is: perl Site_predict.pl. The genome sequence of cattle is downloaded from Ensembl, the version number is:
[0102]
[0103]
[0104] After obtaining the result of single restriction enzyme digestion, it is necessary to process the simulation results of restriction enzymes combined in pairs to obtain the simulation results of the simultaneous action of two enzymes. Taking EcoR I and Msp I as examples, the commands are as follows:
[0105] less-S ecor1.pos|awk'OFS="\t"{print$1,$2,"1"}' less-S>ecor
[0106] less-S msp1.pos|awk'OFS="\t"{print$1,$2,"2"}'|less-S>msp
[0107] cat ecor msp|sort -k1,1...
Embodiment 2
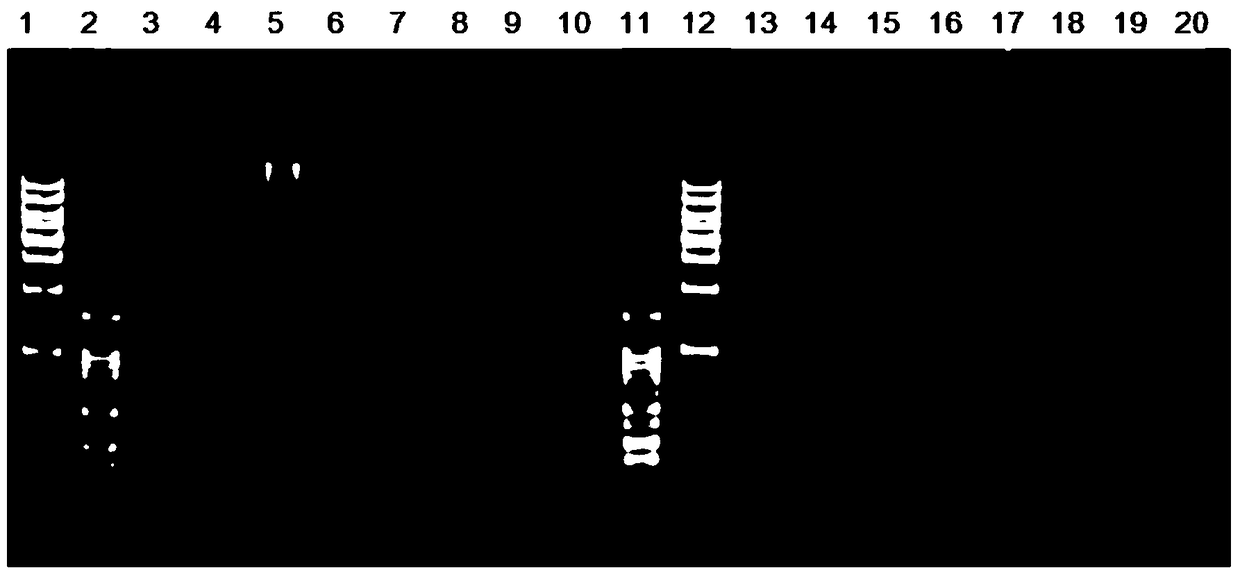
[0186] The inventor has carried out experiments on sheep, an important agricultural economic animal. The blood samples of three Dorper sheep were collected, and the experimental procedure was the same as in Example 1, and the enzyme digestion and SNP of the sheep genome were analyzed. The actual digestion results of each enzyme digestion combination are shown in Table 6.
[0187] Table 6
[0188] Sheep Digestion Combination
[0189] From the analysis in the above table, it can be seen that the number of SNPs obtained by the enzyme digestion combination of EcoR I-Msp I is relatively moderate (this experiment is 3 individuals, and the number of SNPs for large-scale group experiments will increase), and the enzyme digestion will not be affected by formazan. Due to the influence of modification such as kylation, the restriction fragments were evenly distributed, so the combination of EcoR I-Msp I was selected as the restriction combination used in the analysis of sheep ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com