Protein amino acid sequence de novo sequencing method based on unequal stable isotope labeling at two ends of polypeptide
A protease lysine and protein technology, applied in the field of de novo sequencing of protein amino acid sequences to identify fragment ions, can solve the problems of reduced probability and intensity, low specificity, complex peptide fragmentation mechanism, etc. Efficient and selective effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] 1. Two-terminal labeling of protein enzymatically digested polypeptides based on dimethylation markers
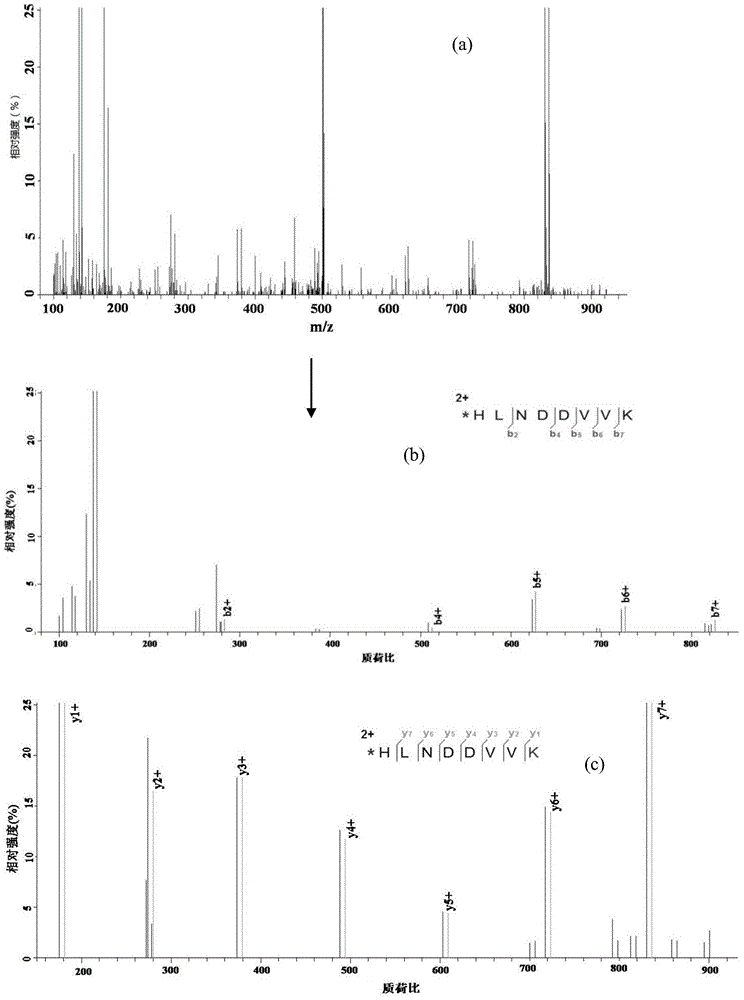
[0023] Such as figure 1 As shown, mark according to the following process:
[0024] 1) Denaturation, reduction, alkylation and enzymatic hydrolysis of protein samples: Dissolve 100 micrograms of protein in 1 milliliter of 8M urea, add 100 microliters of 10mM dithiothreitol, place in a water bath at 56°C for 2 hours, then add 100 μl of 20 mM iodoacetamide was left for 1 hour in the dark. Finally, the solution was diluted with 50mM sodium phosphate (pH7.5) to urea concentration to 0.8M, then the intracellular protease lysine-C was added according to the substrate / enzyme ratio 25 / 1 (w:w), and incubated at 37°C overnight.
[0025] 2) Dimethylation labeling at both ends of the polypeptide: Divide the polypeptide sample obtained in 1) into two equal parts,
[0026] After desalting the first column (C18 pre-column), use formaldehyde solution (5 μL 0.6M sodium cyanoboroh...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Labeling of both ends of protein enzymatic peptides based on metabolic labeling and chemical labeling
[0033] In this example, different methods for labeling both ends of the polypeptide are adopted, and the separation and identification methods for the polypeptide are the same as those in the previous example.
[0034] 1. Cell culture and metabolic labeling: For Hela cells, use DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum for culture. For labeling of lysine, L-lysine-free DMEM and dialyzed fetal bovine serum were used. L-lysine (146 μg / ml) was added to the "light" culture solution, and the same concentration of [ 13 C] L-Lysine.
[0035] 2. Protein extraction and pretreatment: After the cells are collected, they are dissolved in a buffer solution containing 8M urea and protease inhibitors. After the lysate was sonicated three times, the supernatant was collected by centrifugation. Lightly and heavily labeled proteins were reduced using 10 mM dithiothreitol in 50 mM sodi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com