Formulations of water-soluble derivatives of vitamin E and compositions containing same
A composition and derivative technology, applied in the field of vitamin E water-soluble derivative preparations and compositions containing the same, can solve the problems of non-polar compound amount or concentration limitation, undesired sensory properties and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
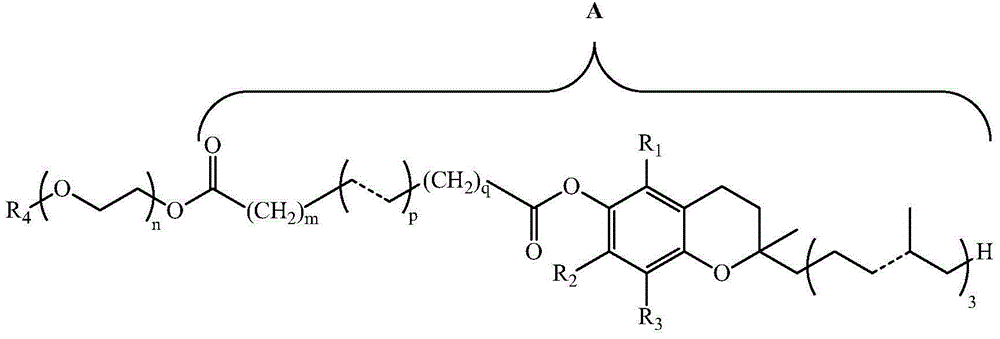
[0338] Described herein are methods of preparing water-soluble vitamin E derivative mixtures (compositions) such as TPGS compositions described herein, e.g., preparing water-soluble vitamin E derivative compositions such as comprising less than 70% by weight of TPGS monomer and more than TPGS composition of 12 wt% TPGS dimer. Existing methods for the preparation of vitamin E derivatives can be used, but modified to produce higher concentrations of the dimeric form by adjusting the reaction conditions. Such adjustments can be determined empirically as necessary, for example, by varying reaction parameters (eg, time, temperature, and reactant concentrations) to determine conditions that favor higher levels of dimer formation.
[0339] A water-soluble vitamin E derivative mixture (e.g., a TPGS monomer-dimer mixture) prepared according to the method may comprise: 25% to 69% by weight or about 25% to 69% by weight monomer, for example at or about 25% by weight, 26% by weight, 27% ...
Embodiment 1
[0774] Method for preparing TPGS compositions
[0775]d-alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS1000) was synthesized from vitamin E succinate according to the following general procedure.
[0776] Polyethylene glycol (PEG) 1000 (168.7 kg) was added to a reaction flask containing 1430 L of toluene, followed by 71.5 kg vitamin E (alpha-tocopheryl acid) succinate and 2.86 kg p-toluenesulfonic acid. The reaction mixture was heated to 110°C to 112°C and refluxed for up to 6.5 hours, water formed during the esterification reaction was removed by azeotropic distillation. The reaction was terminated when the desired amounts of TPGS monomer and TPGS dimer were formed (indicated by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and thin layer chromatography (TLC)), resulting in the TPGS compositions shown in Table 1 below. Each of the TPGS compositions in Table 1 was formed by terminating the reaction at different time points and contained various amounts of TPGS monom...
Embodiment 2
[0794] Evaluation of Clarity of TPGS-Containing Compositions by Turbidity Analysis
[0795] The clarity of the TPGS compositions prepared above was evaluated by turbidity analysis. TPGS Compositions 1-11 were formulated as 1 g concentrate, each dissolved in 8 oz of water. Then, the clarity of the resulting aqueous liquid dilution composition was evaluated by measuring turbidity using a nephelometer. The evaluation results are shown in Table 2 below.
[0796] Each of the eleven TPGS compositions listed in Table 1 above was diluted in water (purified according to the provided method) using the following procedure.
[0797] by putting The beaker was placed on a Thermolyne heating plate (Model #846925) and 8 ounces of water was heated in the beaker until the water reached 49.8°C. Then, add the TPGS composition concentrate to the hot water and stir with a stir bar until dispersed. The resulting aqueous TPGS composition was cooled to room temperature (about 25°C). For evaluat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com