A Rateless Coding Transmission Method Applicable to Dying Channels
A rateless coding and transmission method technology, applied in the field of rateless coding and transmission, can solve problems such as damage, channel interruption, and inability to recover
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0079] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the description of the drawings and the specific embodiments.
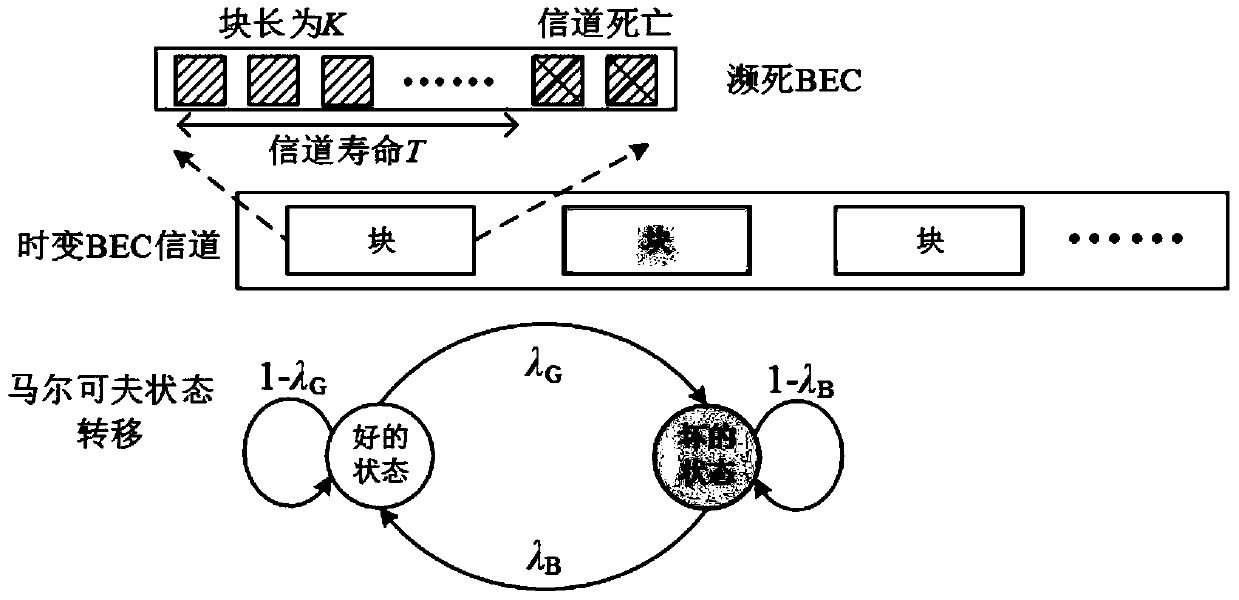
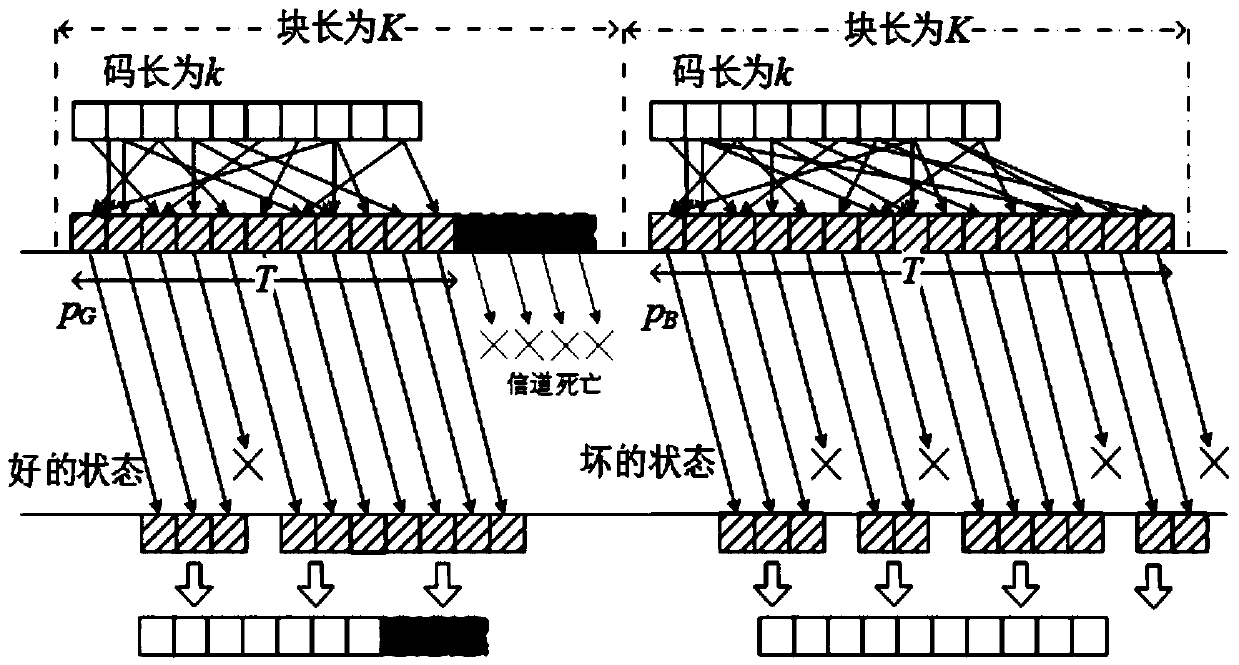
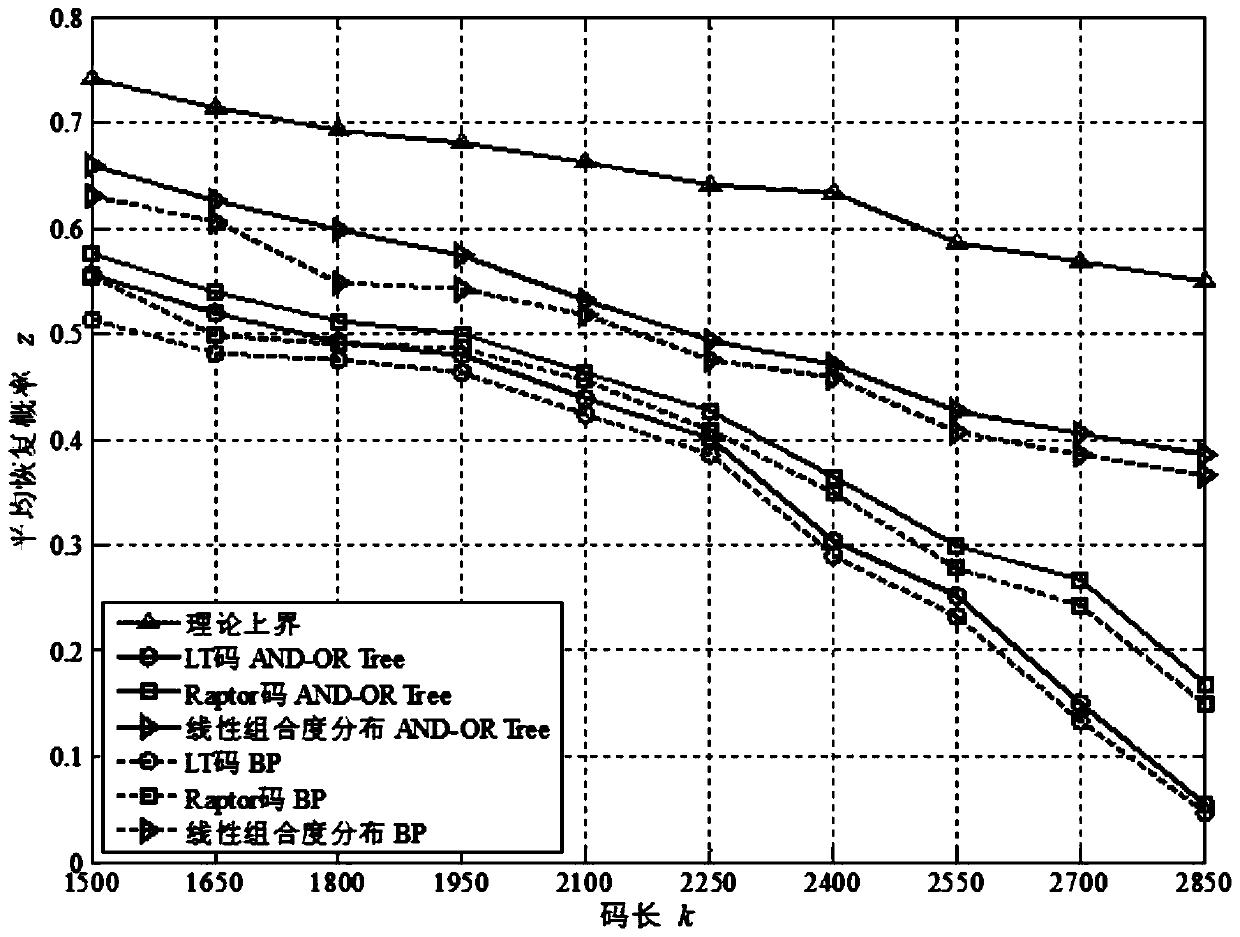
[0080] From the previous technical explanations, it can be known that the present invention first proposes a semi-Markov near-death channel model for the situation that the link in the actual communication system suffers a random attack and is suddenly interrupted. This channel has Markov state transition deletion probability and random channel survival time to simulate the "death" of communication links in cognitive radio networks and wireless sensor networks. Further, in order to ensure the effective transmission of scientific data under the time-varying near-death channel, the present invention patent proposes an optimal transmission strategy based on rateless coding to solve the above problems. First, a heuristic algorithm is used to design the suboptimal distribution of rateless coding based on the AND-OR tree analysis technique. F...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com