Molecular markers of rice resistance to brown planthopper qbph3 and qbph4 genes
A technology of molecular markers and brown planthopper resistance, applied in the direction of DNA / RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problem that it is difficult to effectively introduce or aggregate multiple brown planthopper-resistant genes and insect-resistant varieties, so as to improve the efficiency and operability of assisted selection Strong, high primer-specific effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
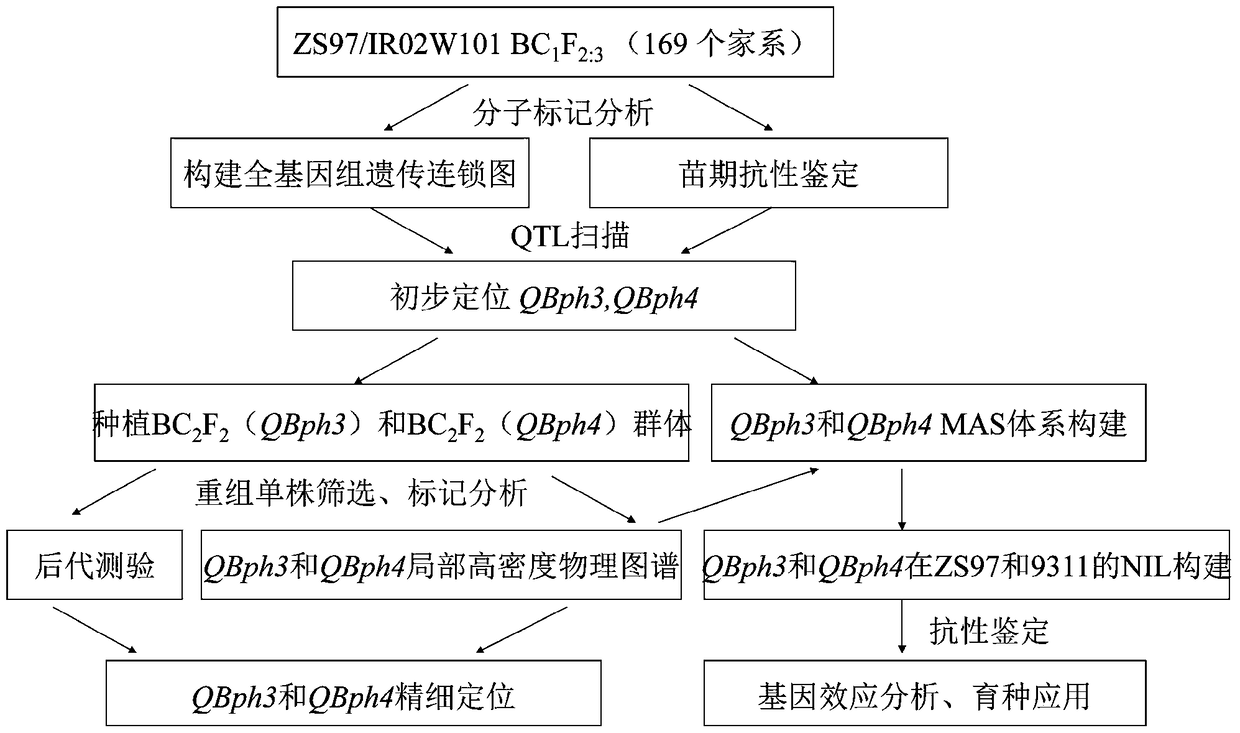
[0076] Example 1: Preliminary localization of QBph3 and QBph4 in the insect-resistant introduction line IR02W101
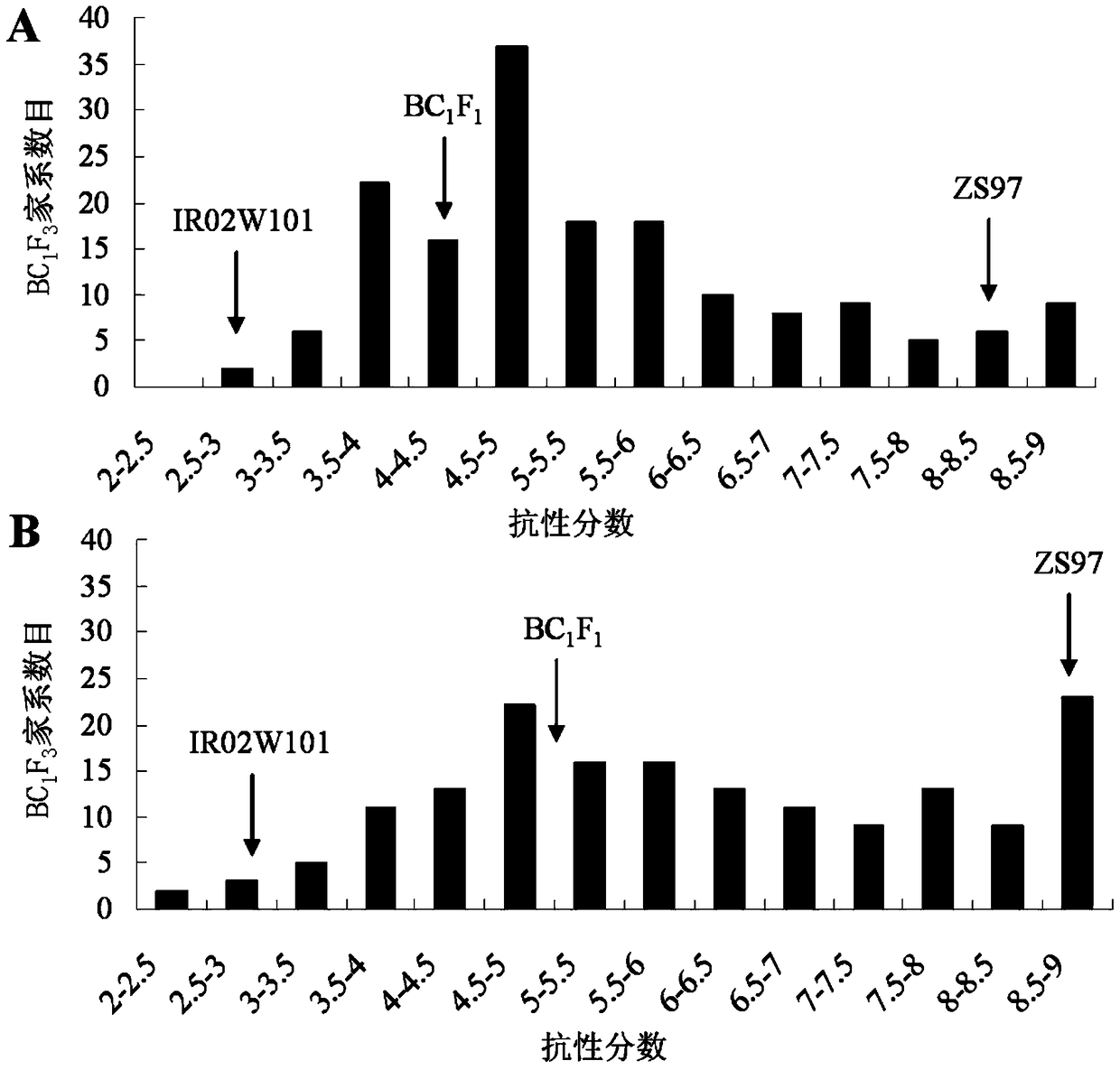
[0077] 1. Build Zhenshan 97 / IR02W101BC 1 f 2 Population and Phenotype Identification
[0078] (1) The insect-resistant parent rice line IR02W101 (formerly known as IR54751-1-2-44-15-2-B) was bred by the Early International Rice Research Institute ("IRRI" in English, Philippines), and was developed by the Kindly provided by Dr. Brar of IRRI. They crossed a conventional indica rice variety IR31917-45-3-2 with a medicinal wild rice variety (Acc number: 100896), and after phenotypic identification and backcross breeding, they finally obtained the introduction of four highly resistant brown planthopper biotypes Line IR02W101 (see literature: Jena and Khush, 1990; Brar and Khush, 1997). The other parent Zhenshan 97 (Zhenshan 97B) used in this example showed high sensitivity to the brown planthopper population in my country. In order to locate the brown planthopper ...
Embodiment 2
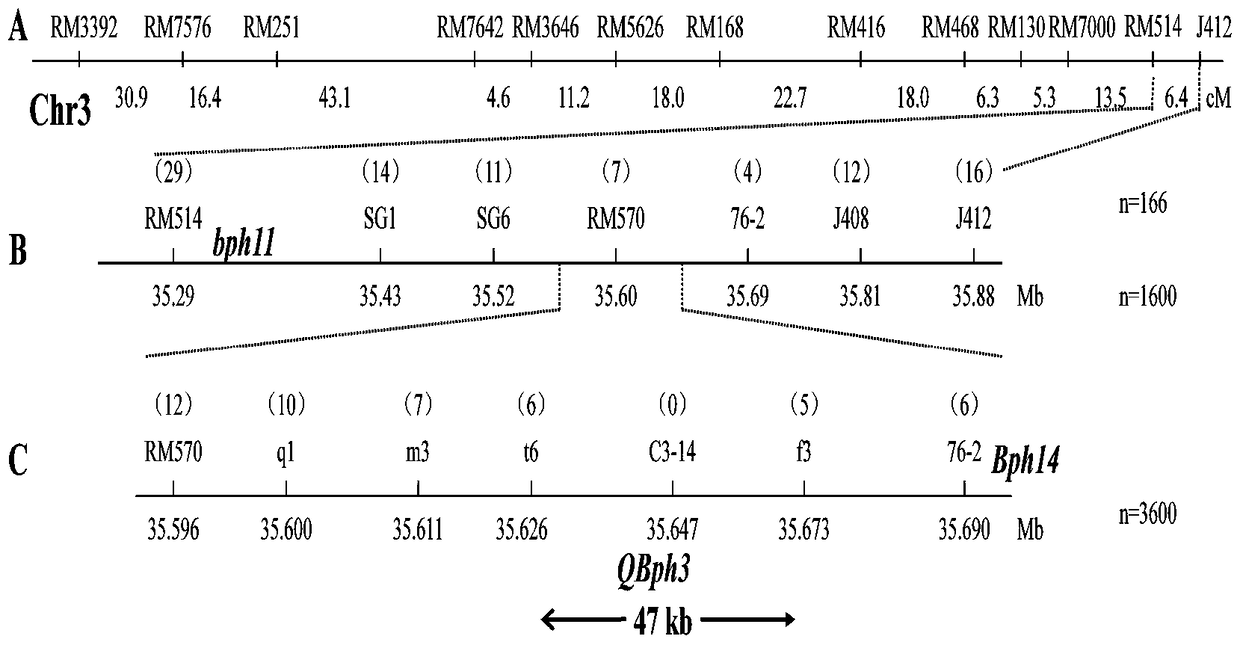
[0091] Example 2: Fine Mapping of QBph3 and QBph4
[0092] 1. Fine positioning of QBph3
[0093] (1) In order to further finely locate QBph3 and improve selection efficiency, select BC 1 f 3 The QBph3 locus in the family is the IR02W101 genotype, and the QBph4 locus is the single plant of the Zhenshan 97 genotype, which was further backcrossed with Zhenshan 97 to obtain BC 2 f 1 , and then use the QBph3 flanking markers RM514 and J412 to identify BC 2 f 1 genotypes, select the individual plants that are heterozygous for the two marker genotypes for further selfing, and obtain BC 2 f 2 group. Then mark RM514 and J412 on both sides of the QBph3 site to detect a total of 6000 BC 2 f 2 In the family, a total of 220 recombined individuals with crossover between markers on both sides were found. And for each recombinant individual plant corresponding F 2:3 The family is identified for insect resistance, and its resistance score is obtained, and then the genotype of the in...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Example 3: Gene effect analysis of QBph3 and QBph4 in Zhenshan 97 background
[0106] 1. Material construction and resistance identification
[0107] According to the method of molecular marker-assisted selection (MAS) combined with conventional backcross breeding, the two main anti-BPH genes QBph3 and QBph4 in IR02W101 were simultaneously introduced into the susceptible parent Zhenshan 97. First select the BC of Zhenshan 97 / IR02W101 2 F 3 A single plant of the IR02W101 genotype at two gene loci in the family was further backcrossed with Zhenshan 97 to obtain BC 3 F 1 , using the markers c3-14 and xc4-27 closely linked to QBph3 and QBph4 to identify the genotype of the individual plants, and screened out the individual plants whose marker genotypes were heterozygous at the QBph3 and QBph4 loci and further selfed to obtain BC 3 F 2 Segregated populations, at this time, the two genes QBph3 and QBph4 should be segregated at the same time, and the genotypes of the offs...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com