Natural pyrite based photocatalysis method for synergic removal of heavy metal-organic pollutants from water
A technology for organic pollutants and natural yellow, which is applied in the field of photocatalysis, and achieves the effects of simple treatment process, low treatment cost and a wide range of applicable targets.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] First crush, grind, and sieve the catalyst pyrite so that the particle radius is within the range of 20-40 μm; adjust the pH value of the water body containing heavy metal Cr(Ⅵ) and organic malachite green to 2-7; under the condition of ultraviolet light , add 1.0g / L of treated catalyst pyrite to the water body containing 10mg / L heavy metal Cr(Ⅵ) and 30mg / L organic matter malachite green, and keep stirring at a constant speed under 10-20W ultraviolet light irradiation , carry out the reaction, react for 100-120min, redox synergistically remove Cr(Ⅵ) and malachite green in the water body. The concentration changes of Cr(Ⅵ) and malachite green in the water before and after the reaction were measured.
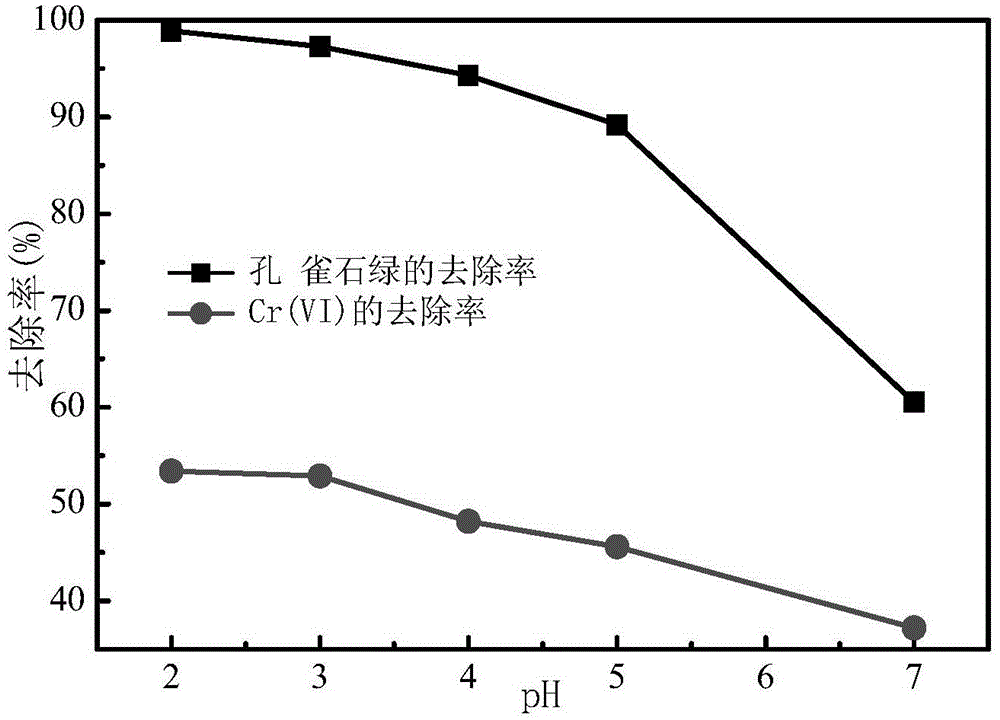
[0033] In Example 1 results such as figure 1 shown by figure 1 It can be seen that after 120 min of reaction, the removal rate of Cr(Ⅵ) and malachite green showed a downward trend with the increase of pH, among which, the removal rate of malachite green and Cr(Ⅵ) was the ...
Embodiment 2
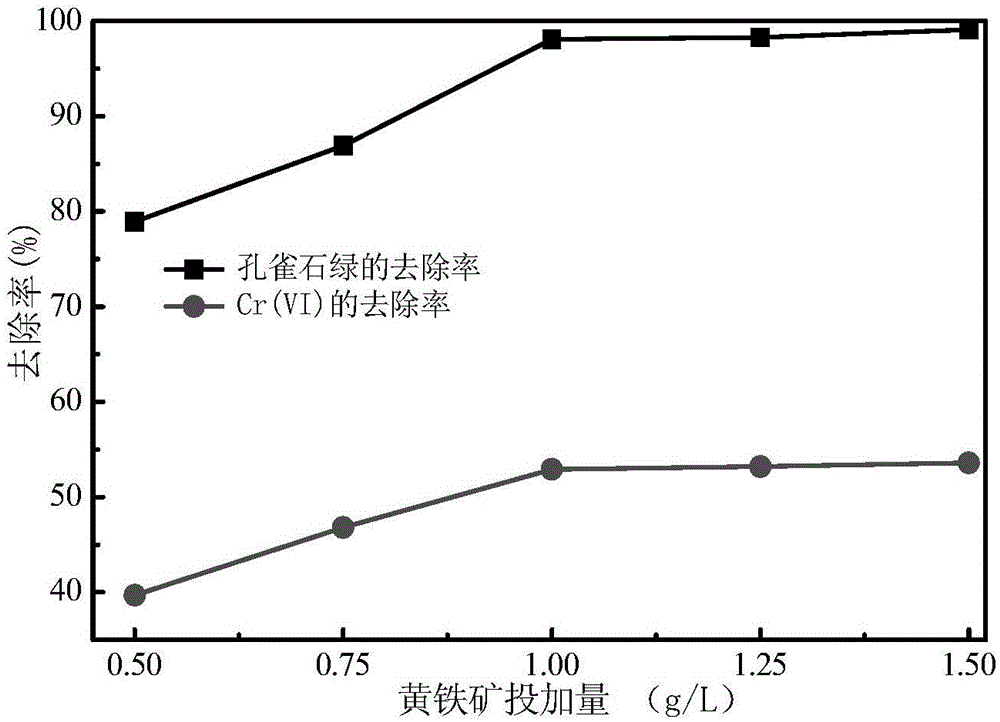
[0041] The difference from Example 1 is that the initial pH value of the polluted water body is adjusted to be 3, the dosage of the catalyst pyrite is 0.5~1.5g / L, and the concentration of Cr(Ⅵ) and malachite green in the water body before and after the reaction is measured. Variety. In Example 2 results such as figure 2 shown by figure 2 It can be seen that after 120 minutes of reaction, the removal rate of malachite green and Cr(Ⅵ) showed an upward trend with the increase of the dosage of pyrite photocatalyst. When the dosage was 1.0g / L, The removal rate of malachite green and Cr(Ⅵ) almost reached the maximum value. When the dosage exceeds 1.0g / L, the removal rate of malachite green and Cr(Ⅵ) has no change.
Embodiment 3
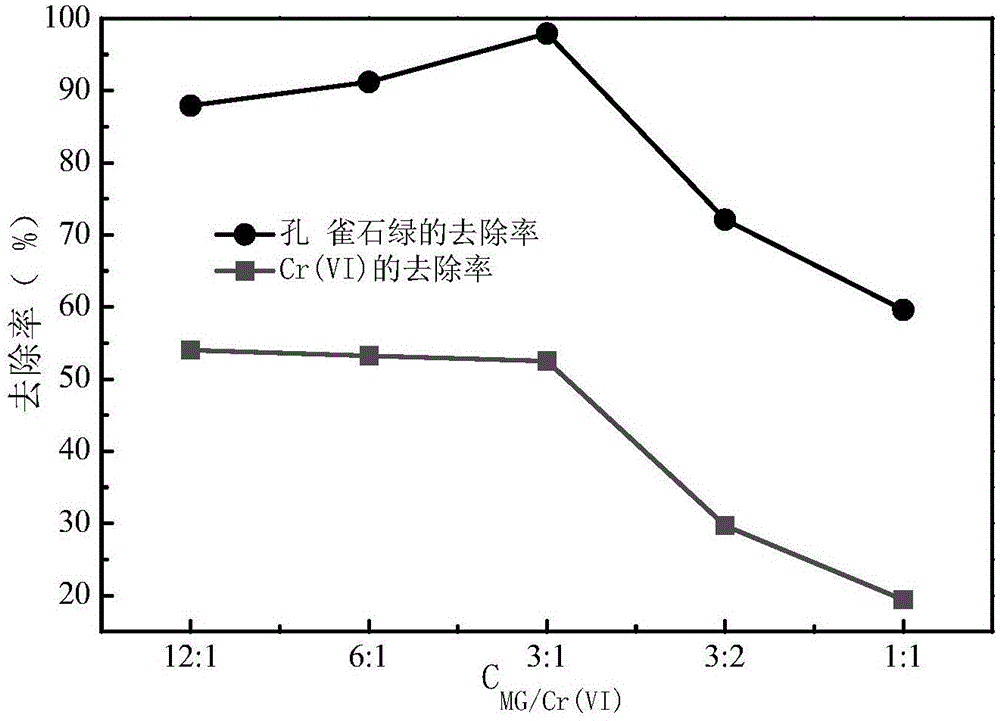
[0043] The difference from Example 1 is that the concentration ratio of malachite green and Cr(VI) should be adjusted to 12:1-1:1, and the concentration changes of Cr(VI) and malachite green in the water before and after the reaction were measured. In embodiment 3 results such as image 3 shown by image 3 It can be seen that after 120 min of reaction, the removal rate of Cr(Ⅵ) decreased with the decrease of the concentration ratio, while the removal of malachite green first increased with the decrease of the concentration ratio. When the concentration ratio exceeded 3:1, the malachite green The removal rate of stone green decreased with the decrease of the concentration ratio. Therefore, when the ratio of malachite green / Cr(Ⅵ) was 3:1, the removal rates of malachite green and Cr(Ⅵ) reached the maximum respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com