Recombinant escherichia coli with high osmotic pressure resistance and application thereof
A technology for recombining Escherichia coli and Escherichia coli, applied in the field of genetic engineering of Escherichia coli, can solve the problems of cell growth and metabolism inhibition, affecting strain growth and metabolism, high osmotic pressure, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0119] Embodiment 1: Construction of strain Suc-T110 and HX-024
[0120] Using wild-type Escherichia coli ATCC8739 as the starting strain, the lactate dehydrogenase gene ldhA was knocked out, the pyruvate formate lyase encoding gene pflB was knocked out, the phosphoenolpyruvate-sugar phosphotransferase I gene ptsI was knocked out, and half The lactose MFS transporter GalP activates phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase PCK to obtain the strain Suc-T110 (for the specific construction process, please refer to Chinese patent application 201310198953.9, and Tan et al., Appl Environ Microbiol.2013,79:4838- 4844).
[0121] Starting from Suc-T110, continue to knock out the phosphoacetyltransferase gene pta and the acetate kinase gene ackA, activate the malate synthase AceA and isocitrate lyase AceB, and activate the dicarboxylic acid Dcu transporter DcuC to obtain the strain NZ-037.
[0122] Then NZ-037 was evolved for 1080 generations to obtain strain HX021.
[0123] Starting from r...
Embodiment 2
[0129] Embodiment 2: Construction of recombinant Escherichia coli NZ-502
[0130] (1) Construction of plasmid pXZ-CS for gene knockout, regulation of gene expression and integration of exogenous genes.
[0131] There are four steps in the plasmid construction procedure:
[0132] The first step, using the pACYC184 plasmid (Mok et al., 1991, Nucleic Acids Res19:2321-2323) DNA as a template, using primers 184-cat-up / 184-cat-down (SEQ ID No.: 16 / SEQ ID No.: 17), the amplified chloramphenicol resistance gene, the gene fragment size is 994bp, contains the chloramphenicol gene promoter sequence, called fragment I.
[0133] Amplification system: 10 μl of NewEngland Biolabs Phusion5X buffer, 1 μl of dNTP (10 mM for each dNTP), 20 ng of DNA template, 2 μl of each primer (10 μM), 0.5 μl of Phusion High-Fidelity DNA polymerase (2.5 U / μl), distilled water 33.5 μl for a total volume of 50 μl.
[0134] Amplification conditions were pre-denaturation at 98°C for 2 minutes (1 cycle); denat...
Embodiment 3
[0155] Embodiment 3: Construction of recombinant Escherichia coli NZ-504
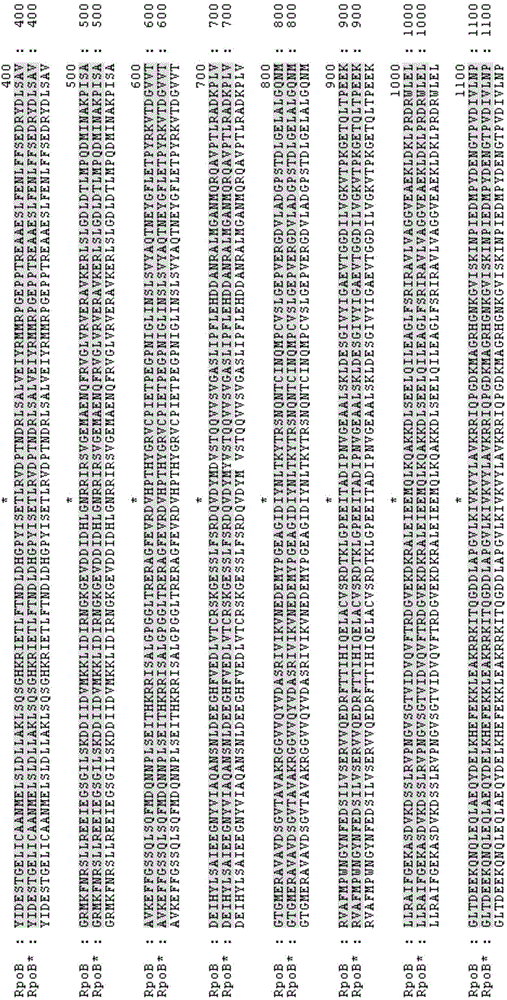
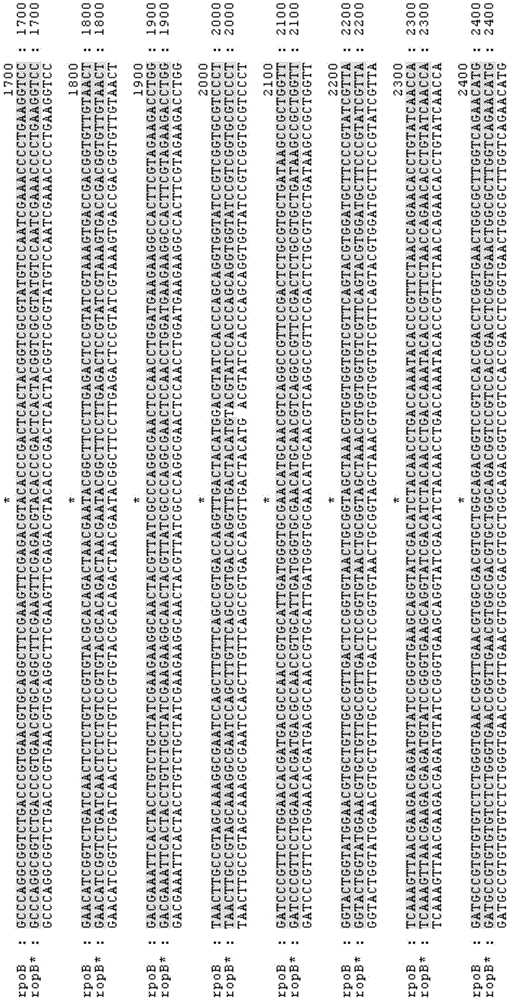
[0156] Starting from the recombinant Escherichia coli Suc-T110, the cusS* mutant gene was integrated to replace the wild-type cusS gene according to the method of two-step homologous recombination in part (2) of Example 2 to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli NZ-504. The primer sequences used are shown in Table 3, where the names of the primers correspond to the names of the primers used in the process of rpoB*mutating the gene, and only rpoB is replaced with cusS.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com