Self-adaptive weight three-dimensional matching method based on SIFT descriptor
An adaptive weight, stereo matching technology, applied in image data processing, instruments, calculations, etc., can solve the problems of low matching accuracy and cannot meet the needs, and achieve the effect of overcoming the low matching accuracy and wide application prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
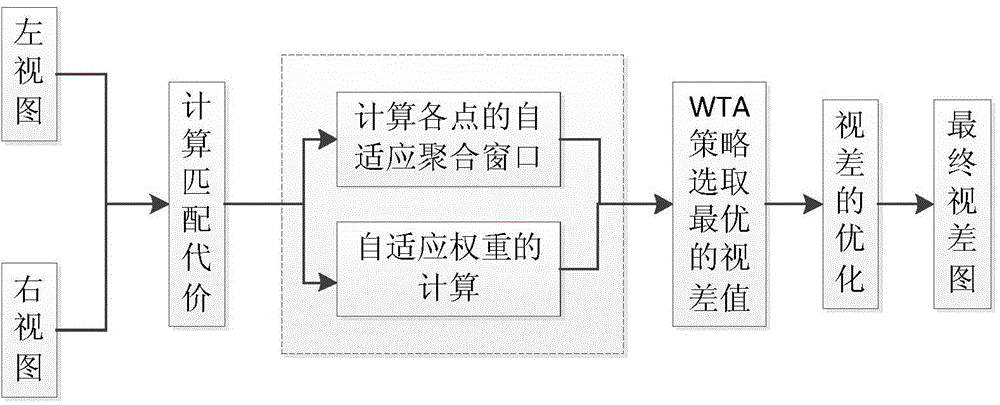
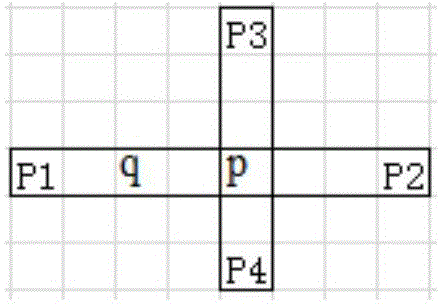
[0027] 101: Obtain the adaptive aggregation window of each center point through the similarity area judgment criterion;
[0028] 102: Perform adaptive weight calculation through the L1 norm of the SIFT descriptor at each point, and complete the optimization of the matching cost according to the initial joint matching cost and the adaptive aggregation window;
[0029] 103: For the optimized matching cost, use the WTA strategy to select the optimal disparity value for each point, then use the left-right consistency detection method to detect the optimal disparity value, and use the background filling method to perform Padding to get the final disparity map.
[0030] Among them, the initial joint matching cost is specifically:
[0031] Using the magnitude and phase of the gradient field of the left and right views, the matching cost is calculated for the left and right views, and the initial joint matching cost is obtained.
[0032] Among them, the judgment criterion of the sim...
Embodiment 2
[0041] 201: Using the magnitude and phase of the gradient field of the left and right views, calculate the matching cost for the left and right views, and obtain the initial joint matching cost;
[0042] Among them, the traditional stereo matching algorithm uses the color difference of pixels, or the method based on census transformation and rank transformation to calculate the matching cost, which is easily affected by noise and local illumination changes. In view of the strong robustness of the gradient domain to noise and local illumination changes, the embodiment of the present invention uses the magnitude and phase of the gradient domain to calculate the matching cost, so as to improve the robustness of the algorithm.
[0043] For any pixel (x, y) in the view to be matched , When the disparity value is d, its gradient domain-based joint matching cost function is defined as:
[0044] C(x,y,d)=α·min(C c (x,y,d), T c )+β·min((C g (x,y,d),T g )+μ·min(C p (x,y,d),T p ))...
Embodiment 3
[0087] The technical solutions in Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with specific examples.
[0088] The present invention selects the stereoscopic image database provided by the Computer Vision Research Center of Middlebury University in the United States: http: / / vision.middlebury.edu / stereo as the test picture. The image database covers various situations that are likely to cause false matching, including low-textured areas. , depth discontinuity area, occlusion area, etc., to verify the effectiveness of the method of the present invention.
[0089] image 3 They are the experimental results of VariableCross algorithm, SNCC algorithm, HistoAggr algorithm and the present invention respectively. Among them: picture (a) is 4 standard test images, picture (b) is the real disparity map of 4 standard test pictures, picture (c) is the disparity map obtained by using SNCC algorithm, picture (d) is using V...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com