Light heating compensating lens and application method thereof
A technology of compensating mirrors and light heating, which is applied in the direction of lasers, laser parts, electrical components, etc., to achieve the effects of convenient operation, simple structure, and good thermal compensation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
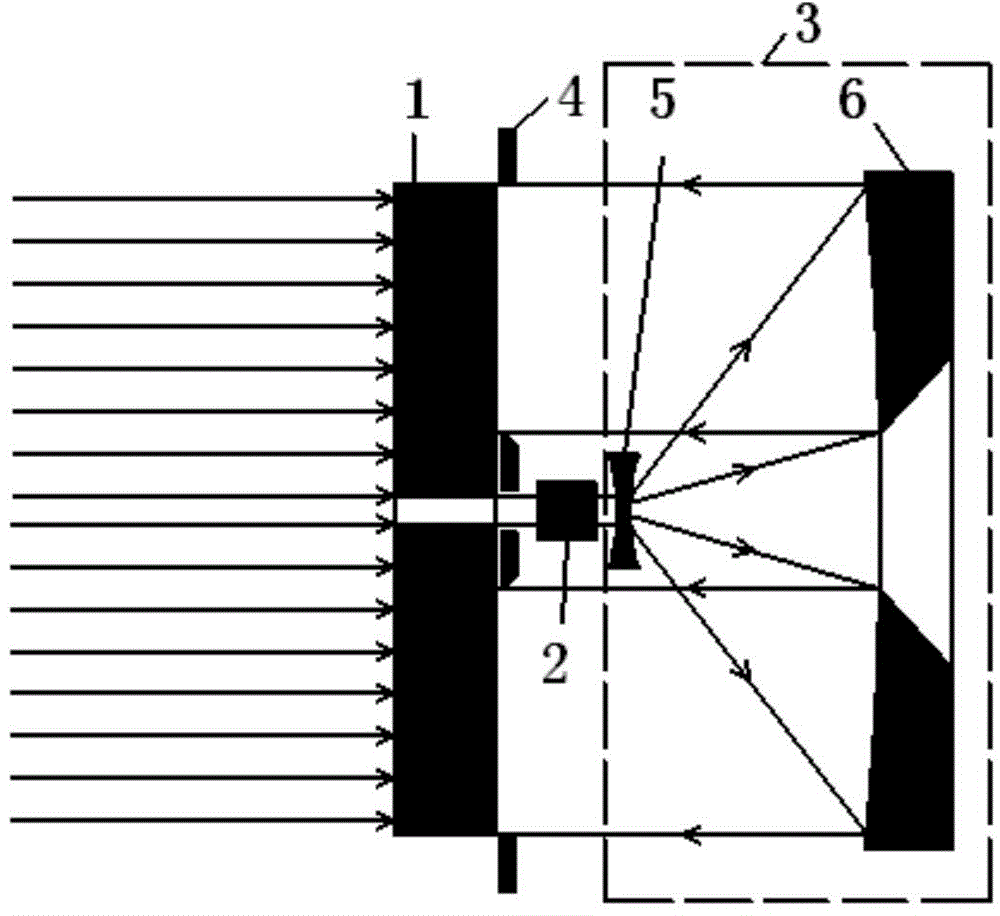
[0035] see figure 1 and figure 2 shown. An optical heating compensation mirror provided by the present invention comprises a mirror body 1, a laser attenuator 2, a laser beam expander system 3 and an aperture 4;
[0036] The center of the mirror body 1 has a through hole for allowing part of the laser light to transmit from the front surface to the rear surface for thermal compensation of the laser cavity mirror;
[0037] Both sides of the mirror body 1 are optically polished, its front surface is coated with a high reflection film, and its rear surface is coated with a high absorption film. The high-reflection film is used to minimize the absorption of laser energy by the mirror body, while the high-absorption film is used to absorb as much laser energy as possible, so as to achieve the best thermal compensation effect with the least energy;
[0038] The laser attenuator 2 is used to attenuate the laser energy transmitted from the front surface to the back surface to an a...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The following uses a specific calculation example to illustrate the ability of the present invention to efficiently reduce the thermal deformation of the spot part of the laser cavity mirror.
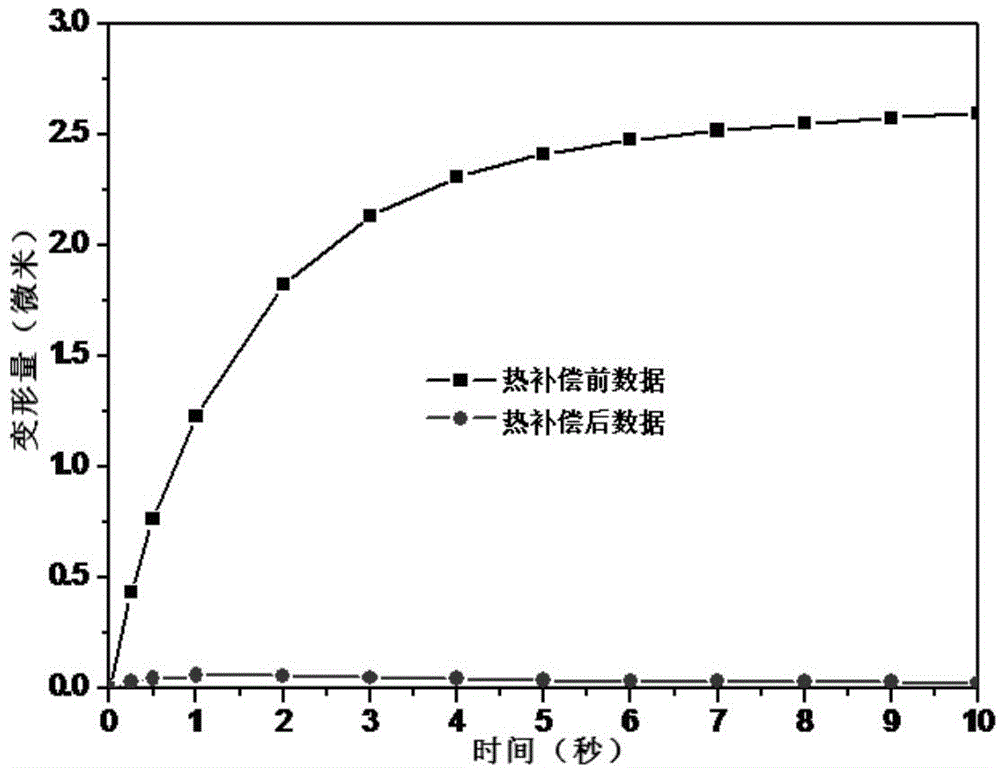
[0047] Using ANSYS software, the thermal compensation effect of single crystal silicon optical heating compensation mirror was simulated and calculated. image 3 The result of the simulation calculation. Among them, the black line is the thermal deformation of the spot part of the laser cavity mirror before thermal compensation, and the red line is the thermal deformation of the spot part of the laser cavity mirror after thermal compensation. It can be seen that during the whole working time, the maximum thermal deformation of the spot part of the laser cavity mirror before thermal compensation is 2.6 microns, while the maximum thermal deformation of the spot part of the laser cavity mirror after thermal compensation is 0.06 microns, which is higher than that before thermal stres...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com