Vanadium battery capacity attenuation reducing method
A capacity decay, vanadium battery technology, applied in the field of vanadium batteries, can solve the problems of the repeatability and stability of diaphragm production, reduce the voltage efficiency and energy efficiency of vanadium batteries, etc., to reduce vanadium ion penetration, reduce water The effect of migration and improving coulomb efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
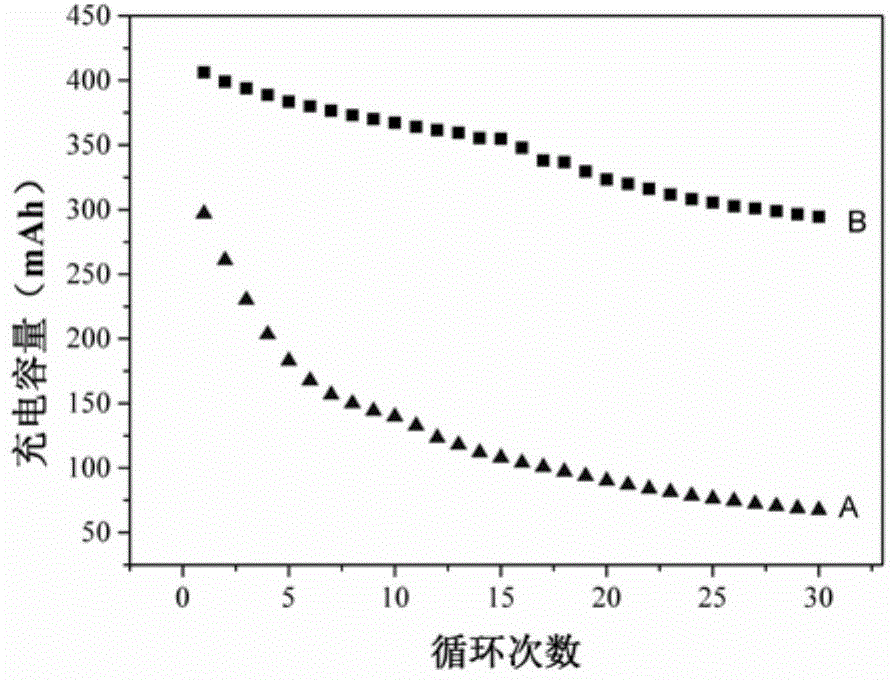
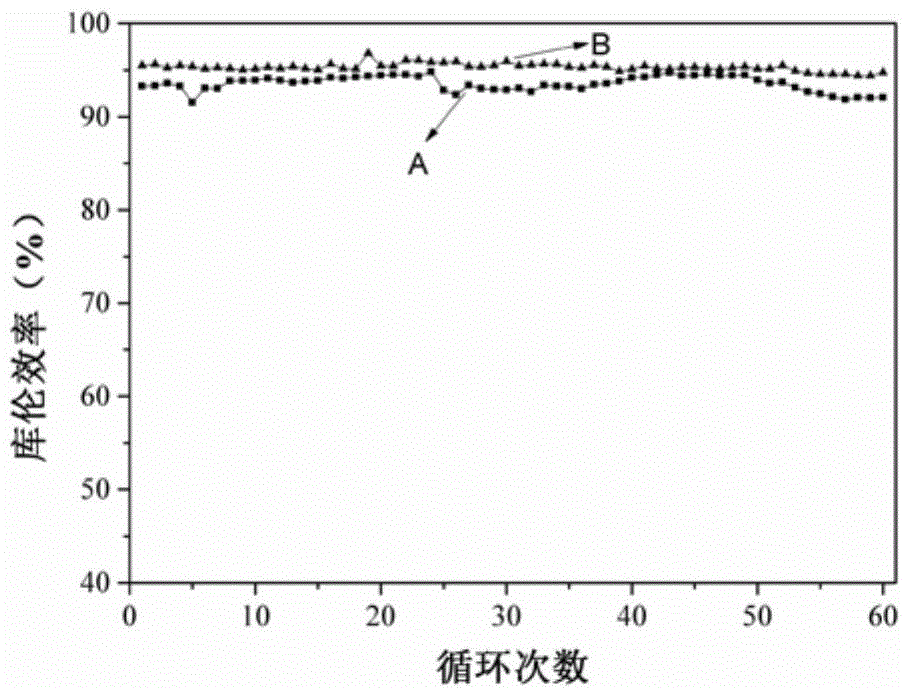
[0019] use as figure 1 The schematic diagram of the device is shown to assemble a vanadium battery, in which the battery separator A is a cation exchange membrane. The vanadium battery without additives has a current density of 30mAcm -2 After 30 cycles, the charging capacity is reduced by 74.4%, and the osmotic pressure of the negative electrode electrolyte of the vanadium battery is reduced. Reassemble the vanadium battery, add 2-methylimidazole with a mass fraction of 1.0% in the negative electrode electrolyte, and keep other operating conditions unchanged. After 30 charge-discharge cycles at the same current density, the charge capacity of the vanadium battery only decays by 19.8%. , see the relationship diagram of capacity decay before and after the addition of additives figure 2 . image 3 It is a comparison chart of vanadium battery coulombic efficiency after 60 charge-discharge cycles before and after adding additives. It can be seen that the performance of vanadiu...
Embodiment 2
[0021] use as figure 1 The schematic diagram of the device is shown to assemble a vanadium battery, in which the battery diaphragm A is an anion exchange membrane, and the vanadium battery without additives has a current density of 30mAcm -2 After 30 cycles, the charging capacity is reduced by 58.6%, and the osmotic pressure of the positive electrode electrolyte of the vanadium battery is reduced. The vanadium battery was reassembled, and 5.0% EDTA disodium salt was added to the positive electrolyte. Other operating conditions remained unchanged. After 30 charge-discharge cycles at the same current density, the charge capacity of the vanadium battery only decayed by 22.4%. The coulombic efficiency of the vanadium battery after 60 charge-discharge cycles before and after adding the additives was compared. The coulombic efficiency was 93% before the additives were added, and 94% after the additives were added. The addition of additives effectively reduces the capacity fading of...
Embodiment 3
[0023] use as figure 1 The schematic diagram of the device is shown to assemble a vanadium battery, in which the battery diaphragm A is an anion exchange membrane, and the vanadium battery without additives has a current density of 30mAcm -2 After 30 cycles, the charging capacity is reduced by 58.6%, and the osmotic pressure of the positive electrode electrolyte of the vanadium battery is reduced. Reassemble the vanadium battery, add magnesium chloride with a mass fraction of 2.5% in the positive electrolyte, and keep other operating conditions unchanged. After 30 charge-discharge cycles at the same current density, the charge capacity of the vanadium battery only decays by 23.6%. The coulombic efficiency of the vanadium battery after 60 charge-discharge cycles before and after adding the additives was compared. The coulombic efficiency was 93% before the additives were added, and 94% after the additives were added. The addition of additives effectively reduces the capacity f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com