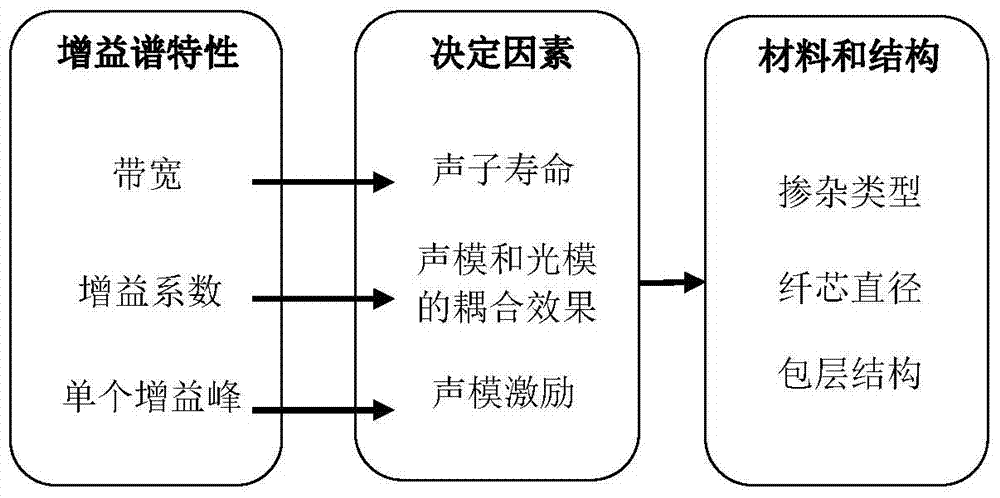
A Stimulated Brillouin Scattering Enhanced Optical Fiber
A technology of stimulated Brillouin and scattering effects, which is applied to clad optical fibers, multi-layer core/clad optical fibers, and optics. It can solve problems such as unsatisfactory performance, suppress four-wave mixing effects, and improve distribution Effect of Liouin gain coefficient and suppression of distortion effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The optical fiber provided by embodiment 1 comprises a core and a cladding surrounding the core;
[0037] Among them, the core radius a is 3 μm, the core doping Ge concentration is 1.646%, and the core refractive index is 1.4616; the cladding doping F concentration is 0.335%, and the cladding refractive index is 1.4551;
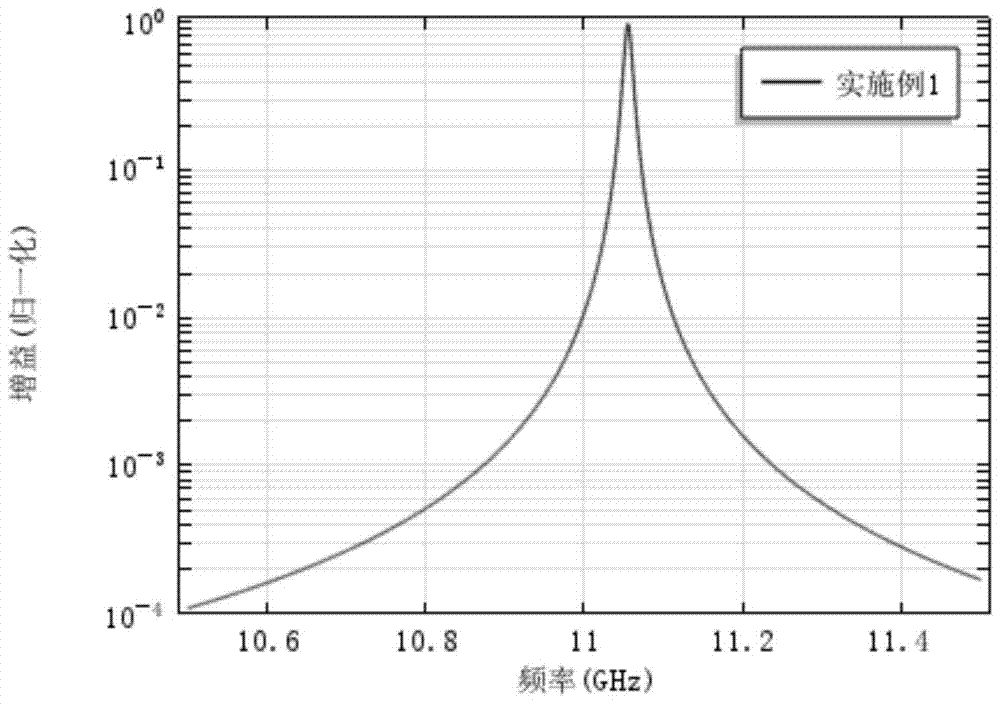
[0038] The doping concentration and core radius of the above-mentioned optical fiber make only one form of optical field exist in the optical fiber, and the optical field parameter a 2 Δn is 0.036μm 2 ; corresponding to a unique β acoust ; among them, β acoust is the component of the acoustic wave vector along the axis of the optical fiber;
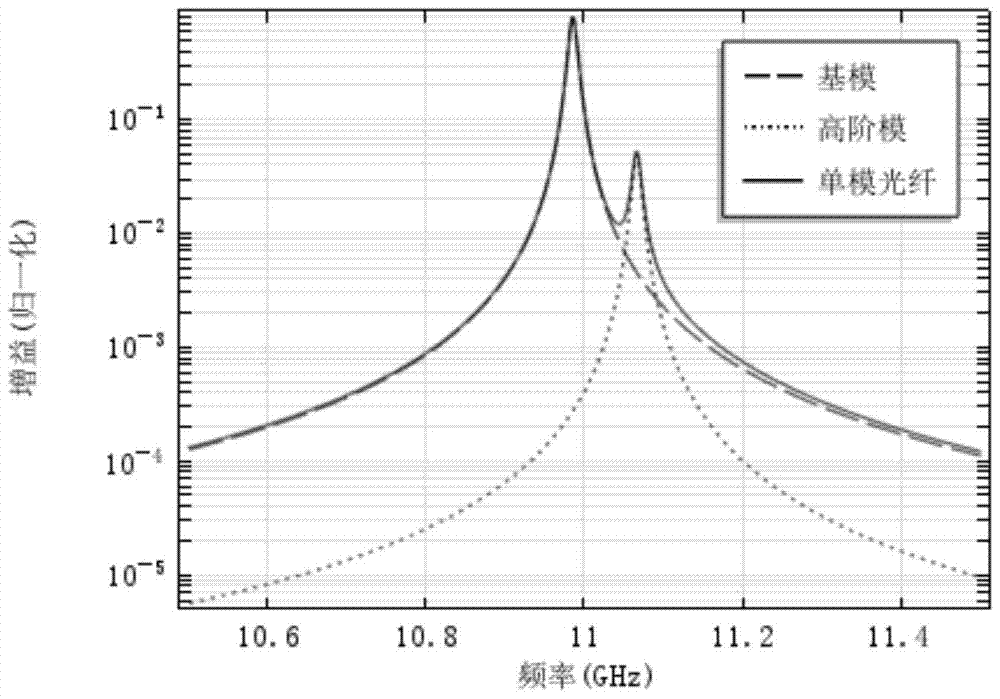
[0039] For the optical fiber provided in Example 1, due to the fiber doping effect, the acoustic velocity difference between the core and the cladding is ΔV l is 16.6m / s; therefore a 2 ΔV l =149.6μm 2 m / s, compared with ordinary single-mode fiber, a 2 ΔV l An order of magnitude smaller, it is a single aco...
Embodiment 14
[0046] The optical fiber provided by Embodiment 14 includes a core and a cladding surrounding the core;
[0047] Among them, the core radius a is 2 μm, the core doping Ge concentration is 3.704%, and the refractive index is 1.4634; the cladding layer doping F concentration is 0.748%, and the refractive index is 1.4544; the optical field is a single-mode characteristic, and the parameter a 2 Δn is 0.0364μm 2 , corresponding to a unique β acoust ; The fiber doping effect makes the acoustic velocity difference between the core and the cladding ΔV l is 38.4m / s, get a 2 ΔV l =153.6μm 2 m / s;
[0048] Compared with the optical fiber provided in Example 1, the acoustic velocity difference ΔV between the core and the cladding of the optical fiber provided in Example 14 l Raise about 3 times than the optical fiber of embodiment 1, but the fiber core radius reduces to 2 / 3 of the fiber core radius in embodiment 1; The acoustic field normalization parameter a of the optical fiber tha...
Embodiment 15
[0051] The optical fiber provided by Embodiment 15 includes a core and a cladding surrounding the core;
[0052] Among them, the core radius a is 1.5 μm, the core doping Ge concentration is 6.584%, and the refractive index is 1.4676; the cladding doping F concentration is 1.330%, and the refractive index is 1.4516; the parameter a 2 Δn is 0.036μm 2 , corresponding to the only fiber doping effect that makes the parameter a between the acoustic velocity difference of the core cladding and the core radius 2 ΔV l =153.7μm 2 m / s;
[0053] Compared with embodiment 1 and embodiment 14, the optical fiber provided by embodiment 15 has a reduced core radius, while the sound velocity difference between the core and the cladding further increases; the acoustic velocity difference of the optical fiber provided by embodiment 15 is about It is 7 times of that in Example 1, and the sound field normalization parameter a 2 ΔV l Basically unchanged, so the sound field is also a single-mode...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com