Spirobifluorene trifluoromethylpyridine iridium complex and its preparation method and application
A technology of spirobifluorene trifluoromethylpyridine iridium and trifluoromethylpyridine iridium, which is applied to the spirobifluorene trifluoromethylpyridine iridium complex and the fields of preparation and application thereof, and can solve the problem that the color purity needs to be improved, the electroporation The problem of high wavelength dependence of luminescence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
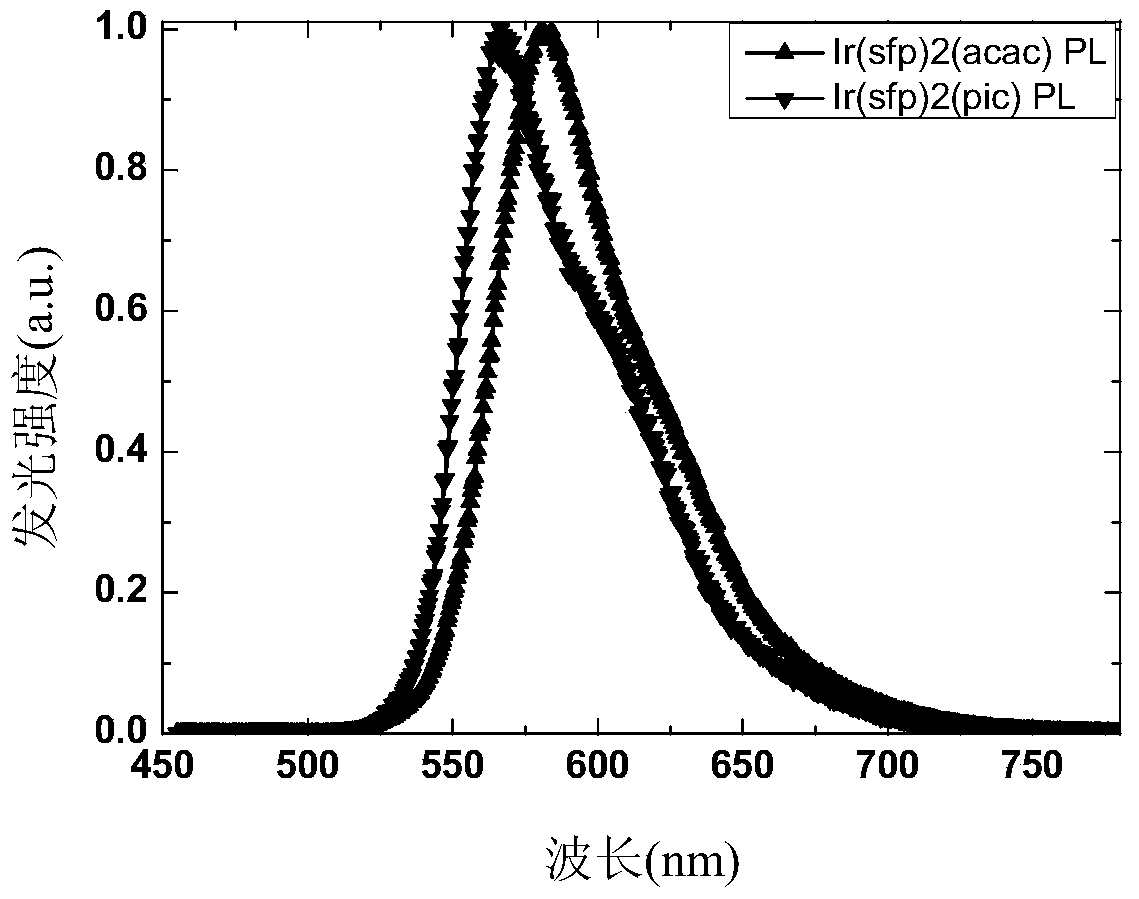
[0044] Example 1: Preparation of two orange-emitting iridium complexes 5 and 6
[0045] Bis[2-(9,9'-spirobifluoren-2-yl)-5-trifluoromethylpyridine-C 3 , N]iridium (pentanedione) (complex 5) and bis[2-(9,9'-spirobifluoren-2-yl)-5-trifluoromethylpyridine-C 3 , N] the synthesis of iridium (2-pyridine acid) (complex 6):
[0046] (1) Under the protection of argon, 2-bromo-9,9'-spirobifluorene (compound 1) (11.85 g, 30 mmol) was dissolved in 230 ml tetrahydrofuran in a 100 mL round bottom flask successively, and cooled to -78 °C. After n-butyllithium (1.6M, 28.1ml, 45mmol) was added dropwise, the reaction was carried out for 1 hour, and trimethyl borate (8.83g, 45mmol) was added in one portion. After reacting for 30 minutes, the temperature was raised to room temperature, and the reaction was continued for 30 minutes. The mixture was treated with dilute acid, extracted with ether, dried, concentrated, and the solid was separated by silica gel column chromatography to obtain 9,9-s...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2: Application of two orange light-emitting iridium complexes 5 and 6 in orange organic electroluminescent devices
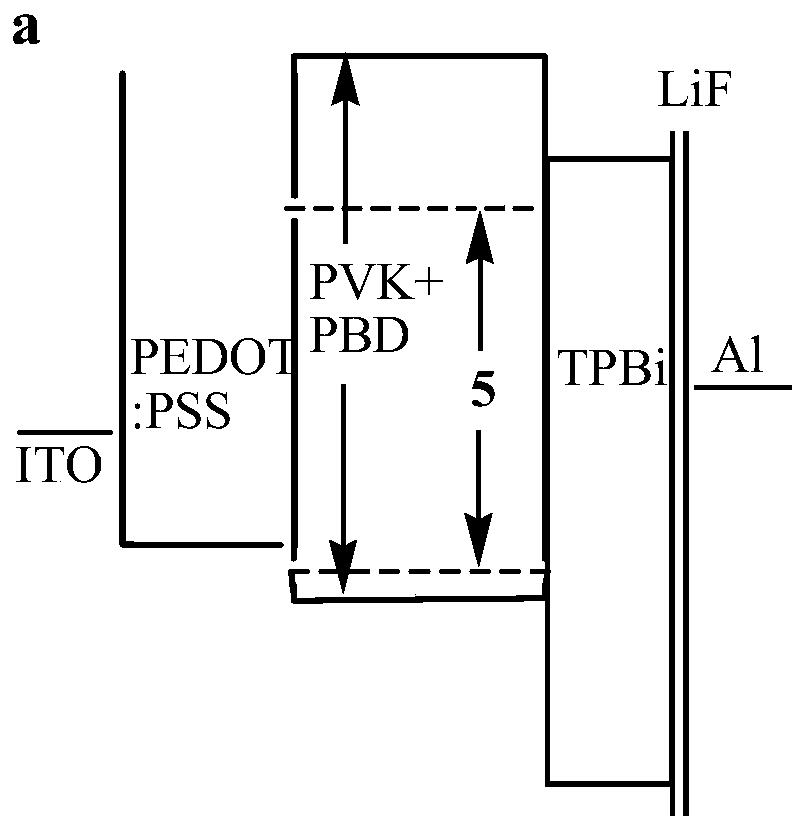
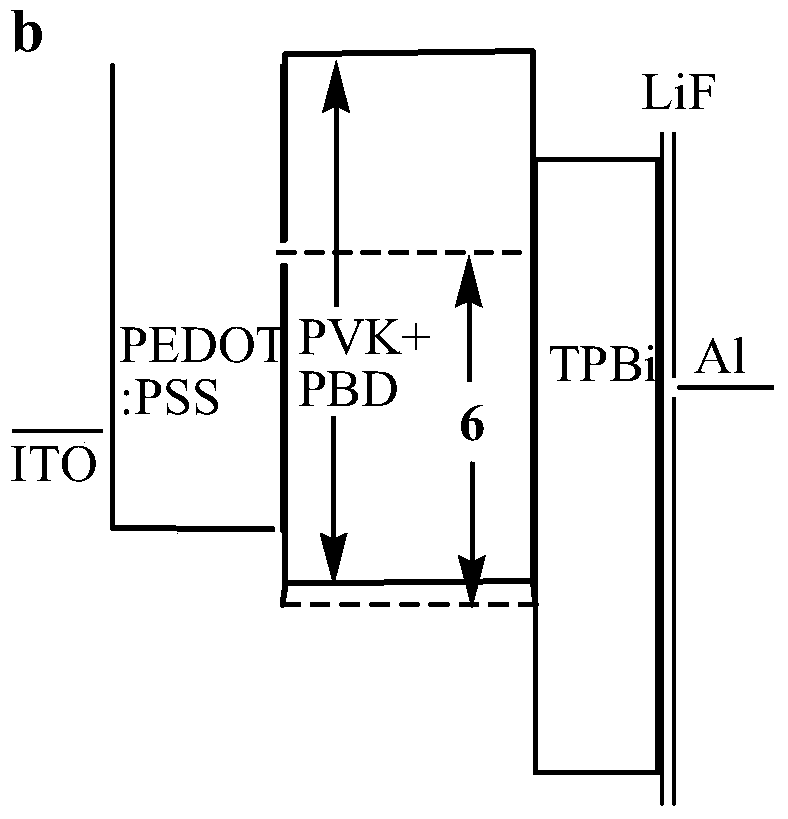
[0055] Orange device structures and designs based on two novel iridium complexes 5 and 6, such as Figure 2-a and Figure 2-b shown, respectively, device A1 (sfp-5CF 3 -py) 2 Ir(acac) and device B1(sfp-5CF 3 -py) 2 Ir (pic).
[0056] Among them, PEDOT:PSS refers to poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonic acid), which is used as a hole injection layer and spin-coated on ITO glass; PVK refers to polyvinylcarbazole, which has a void The host material for hole transport; PBD is 2-tert-butylbenzene-5-biphenyl-1,3,4-dioxazole as the electron transport material. The light-emitting layer is composed of PVK:PBD:complex 5 (or complex 6), the weight ratio of PVK / PBD is 3 / 2, iridium complex 5 or 6 is doped in the mixture of PVK and PBD with 2w%, and then spin Apply over PEDOT:PSS layer. 1,3,5-Tris(1-phenyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)benzene (TPB...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Example 3: Application of two orange light-emitting iridium complexes 5 and 6 in white organic electroluminescent devices
[0059] The structure and design of white light-emitting devices based on two new iridium complexes 5 and 6, such as Figure 4-a and Figure 4-b As shown, respectively, the device WOLED (white organic electroluminescence) 1 (sfp-5CF 3 -py) 2 Ir(acac) and device WOLED 2(sfp-5CF 3 -py) 2 Ir (pic).
[0060] Among them, PEDOT:PSS is poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonic acid), which is used as a hole injection layer and spin-coated on ITO glass; PVK is polyvinylcarbazole, which has a hole Transferred body material. The orange light-emitting layer is composed of PVK:complex 5 or 6 (8% by mass), which is spin-coated on the PEDOT:PSS layer. The blue light-emitting layer is composed of CBP:FIrPic (mass ratio 8%), CBP is 4,4'-N,N'-dicarbazole biphenyl, and FIrPic is difluorophenylpyridine iridium pyridine acid, which is vacuum-copolyme...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com