Preparation method of polymer/keratin composite anticoagulation vascular tissue engineering scaffold
A technology of vascular tissue and keratin, applied in anticoagulant treatment, types of packaging items, special packaging items, etc., can solve problems such as inability to meet the supply demand of small-diameter vascular grafts, low long-term patency rate, and thrombus formation , to achieve the effects of inhibiting the growth of smooth muscle cells, good cell compatibility, and reducing vascular restenosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The preparation method of the polymer / keratin composite anticoagulant blood vessel tissue engineering scaffold comprises the following steps in sequence:
[0028] ① Keratin reduction and stabilization
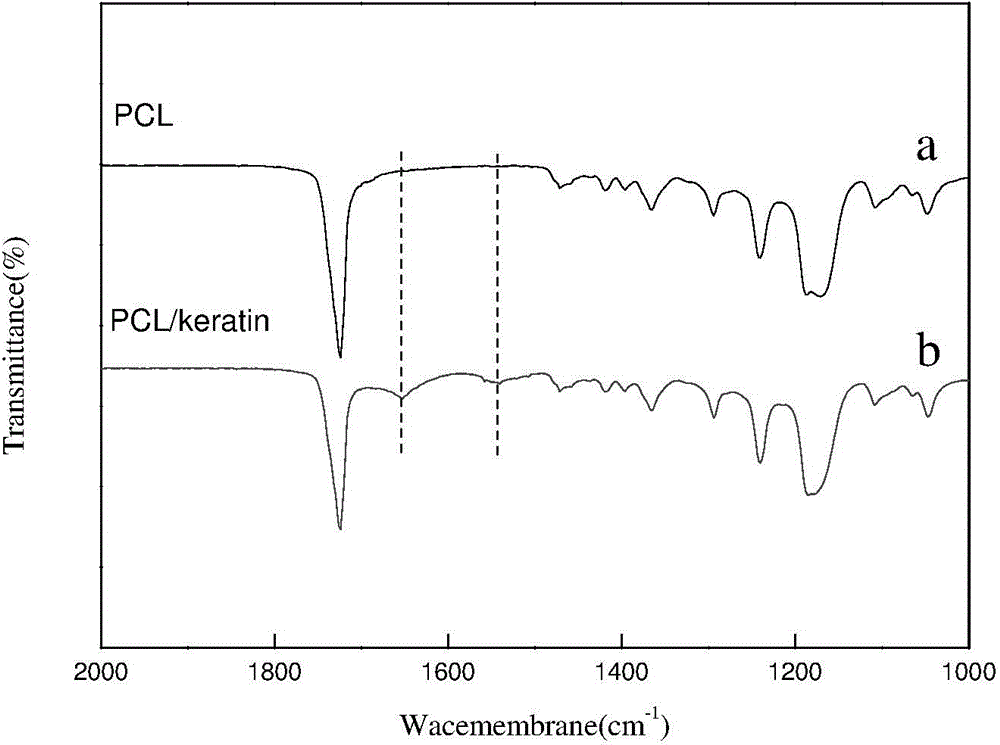
[0029] Human hair is washed sequentially with alkali and methanol to remove oil stains. Cut the crude human hair (1g), put it into a flask, add mercaptoethanol (3g), urea (20g), sodium dodecylsulfonate (1.5g), swell for 1-2 hours, heat to 50°C, and react 12h. After dialysis for 2 days, the keratin solution was obtained by filtration. Measure the sulfhydryl content of keratin after dialysis, calculate the total amount of sulfhydryl according to the volume, and add an excess modifier (iodoacetic acid) to stabilize the sulfhydryl, react in the dark for 12 hours at room temperature, dialyze again for 3 days, and freeze-dry to obtain modified After the keratin.
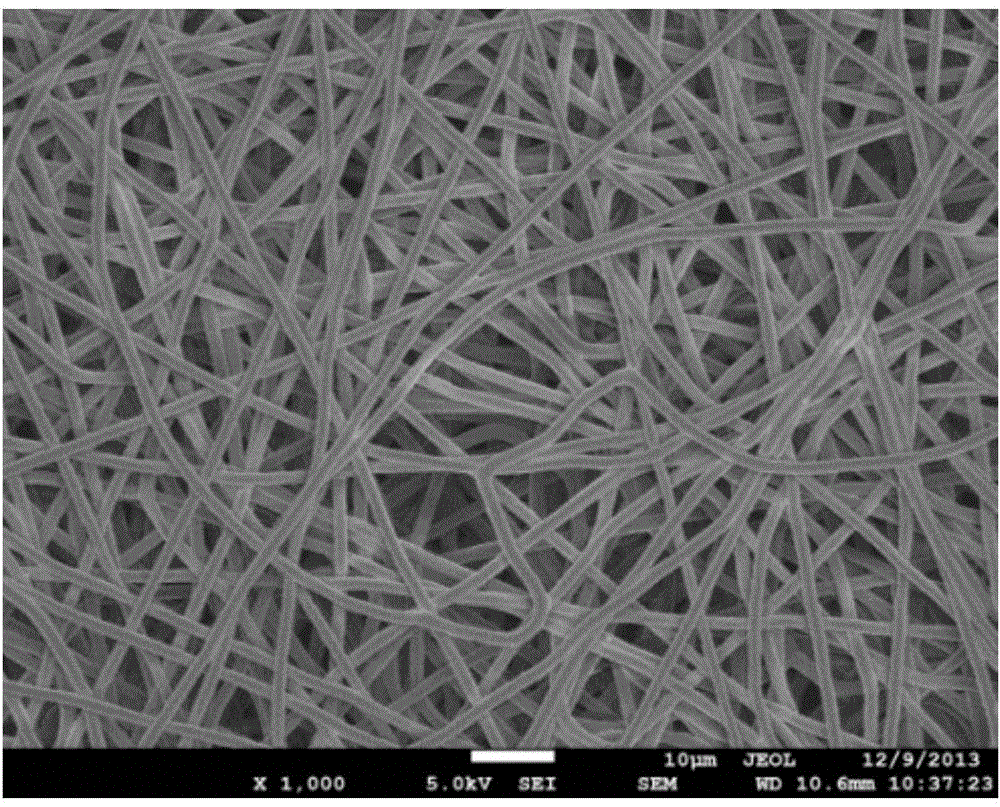
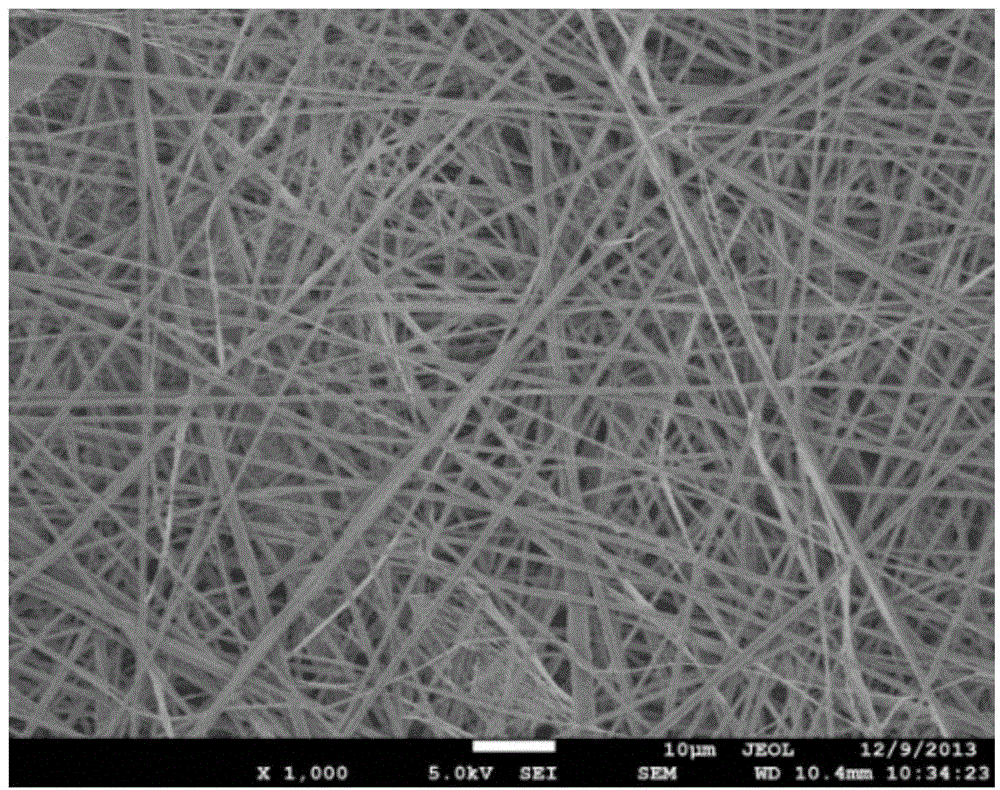
[0030] ②Construction of vascular tissue engineering scaffold by electrospinning
[0031] The polymer PCL is b...
Embodiment 2~3
[0036] The polymer / keratin composite anticoagulant vascular tissue engineering scaffold was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1. In step ② "electrospinning to construct a vascular tissue engineering scaffold", in the blend of polymer PCL and keratin, The mass percentages of keratin are 20% and 30% respectively, and other conditions are the same.
[0037] Fibroblasts and vascular endothelial cells were selected for culture, and cell compatibility was tested by MTT and other methods; the NO release ability was measured by simulating the blood environment, and the results are shown in image 3 and Figure 4 (9 / 1 among the figure represents PCL / keratin mass ratio); Adopt conventional coagulation testing method to measure anticoagulant performance.
[0038] The results showed that the prepared scaffolds had good cytocompatibility and anticoagulant properties, and could catalyze or induce the release of NO from endogenous NO donors in situ.
Embodiment 4
[0040] The preparation method of the polymer / keratin composite anticoagulant blood vessel tissue engineering scaffold comprises the following steps in sequence:
[0041] ① Keratin reduction and stabilization
[0042] Human hair is washed sequentially with alkali and methanol to remove oil stains. Shred the crude product (1g), put it into a flask, add mercaptoethanol (4g), urea (15g), sodium dodecylsulfonate (1.5g), heat to 60°C, and react for 24h. After dialysis for 1 day, the keratin solution was obtained by filtration. Measure the sulfhydryl content of keratin after dialysis, calculate the total amount of sulfhydryl according to the volume, and add excess modifier iodoacetic acid to stabilize the sulfhydryl, react in the dark at room temperature for 12 hours, dialyze again for 2 days, and freeze-dry to obtain the modified of keratin.
[0043] ②Construction of vascular tissue engineering scaffold by electrospinning
[0044] The polymer polyurethane is blended with keratin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com