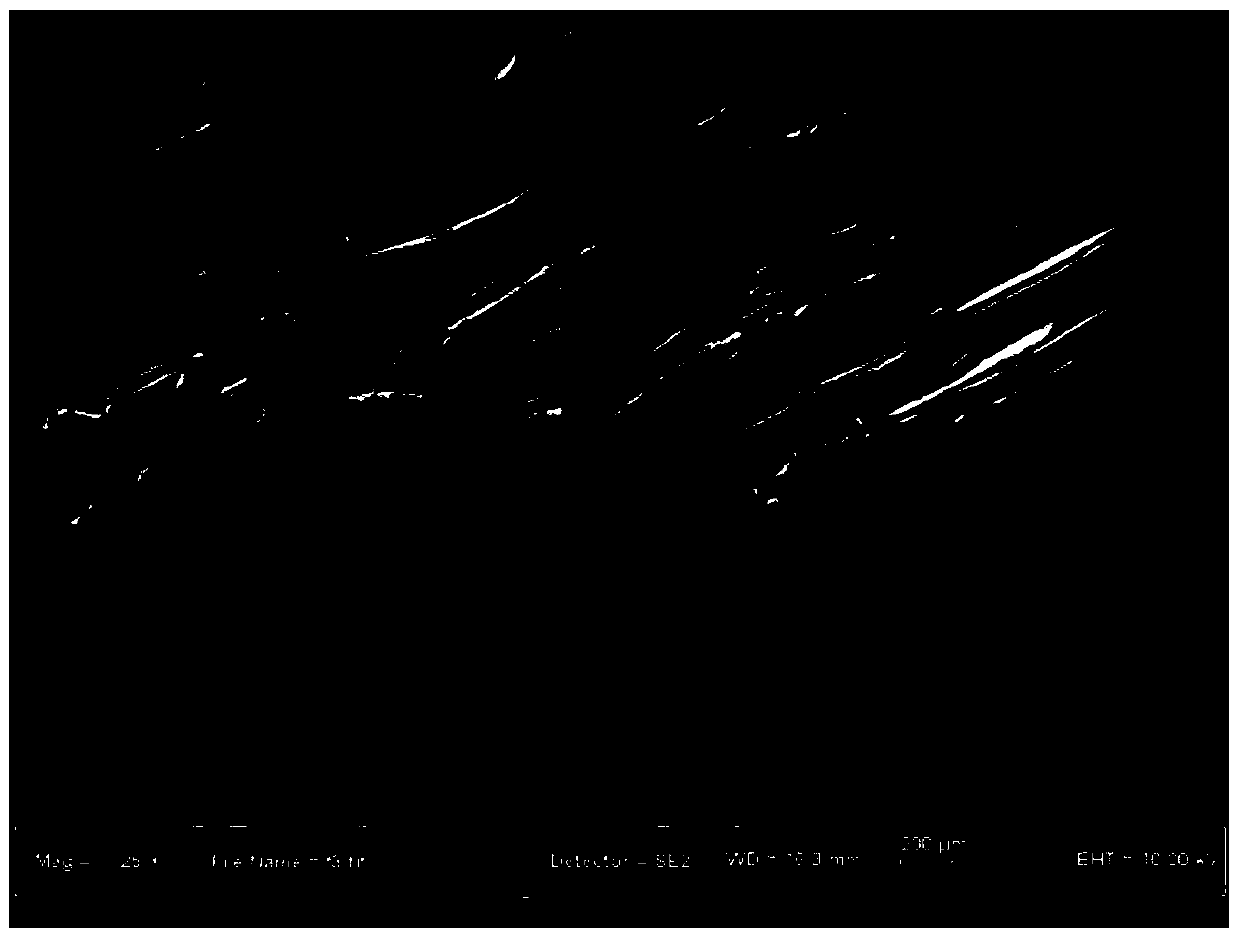
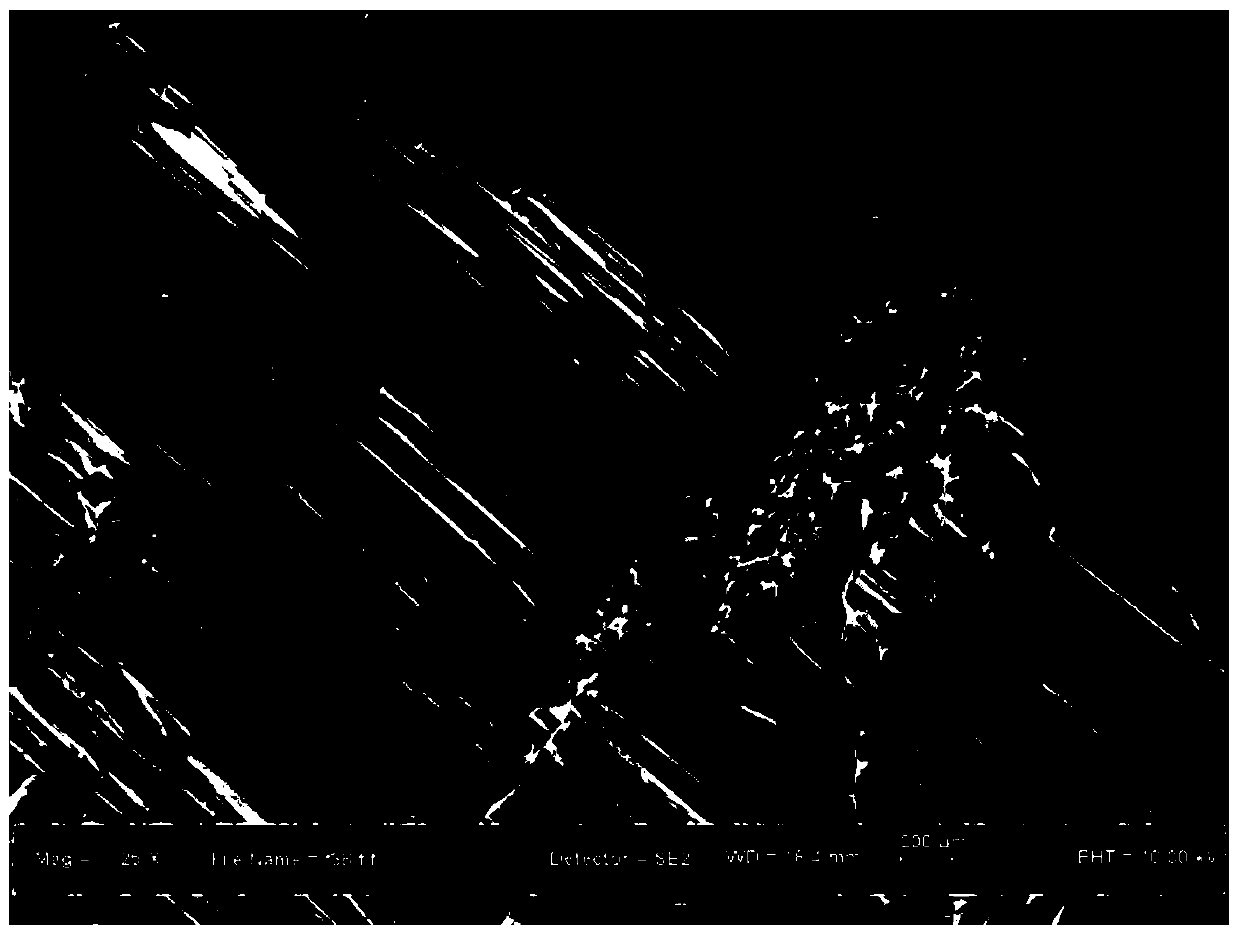
A kind of preparation method and product of polyacrylate macroporous crosslinked polymer
A polyacrylate, cross-linked polymer technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes and other directions, can solve the problems of poor oil absorption, high cost, and poor mechanical strength of macroporous polymers, and achieves simple preparation methods, The effect of low cost, convenient porosity and pore morphology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] (1) Dissolve 0.2mlMMA, 0.02mlEGDMA and 10mgBPO in 1.8mlDMSO at 20°C to form a solution, add 0.01mlDMA, shake to obtain a homogeneous solution, wherein the mass fraction of the monomer in the solution is 10wt%;
[0054] (2) Put the solution obtained in step (1) in a low-temperature box to react at -10°C for 24 hours to obtain an intermediate product;
[0055] (3) Place the intermediate product in step (2) at room temperature, and after the crystallized solution melts, compress the intermediate product to squeeze out the solvent in the pores; then soak it in deionized water for 72 hours, and change it every 4 hours Deionized water to ensure that the deionized water completely replaces the solvent in the sample, and finally dried under reduced pressure to obtain a macroporous cross-linked polymer.
Embodiment 2
[0057] (1) Dissolve 0.2mlMMA, 0.02mlEGDMA and 10mgBPO in 1.8mlDMSO at 20°C to form a solution, add 0.01mlDMA, shake to obtain a homogeneous solution, wherein the mass fraction of the monomer in the solution is 10wt%;
[0058] (2) Place the solution obtained in step (1) in a low-temperature box to react at -20°C for 24 hours to obtain an intermediate product;
[0059] (3) Place the intermediate product in step (2) at room temperature, and after the crystallized solution melts, compress the intermediate product to squeeze out the solvent in the pores; then soak it in deionized water for 72 hours, and change it every 4 hours Deionized water to ensure that the deionized water completely replaces the solvent in the sample, and finally dried under reduced pressure to obtain a macroporous cross-linked polymer.
Embodiment 3
[0061] (1) Dissolve 0.2mlMMA, 0.02mlEGDMA and 10mgBPO in 1.8mlDMSO at 20°C to form a solution, add 0.01mlDMA, shake to obtain a homogeneous solution, wherein the mass fraction of the monomer in the solution is 10wt%;
[0062] (2) Put the solution obtained in step (1) in a low-temperature box to react at -30°C for 24 hours to obtain an intermediate product;
[0063] (3) Place the intermediate product in step (2) at room temperature, and after the crystallized solution melts, compress the intermediate product to squeeze out the solvent in the pores; then soak it in deionized water for 72 hours, and change it every 4 hours Deionized water to ensure that the deionized water completely replaces the solvent in the sample, and finally dried under reduced pressure to obtain a macroporous cross-linked polymer.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com