Application of melatonin in delaying paddy leaf senescence and tolerating salt
A technology of melatonin and leaves, which is applied in the application field of melatonin in delaying rice leaf senescence and salt tolerance, and can solve the problems that genes cannot be applied, complex genetic characteristics of transgenic plants, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1. Melatonin plays a key role in delaying rice leaf senescence and cell death
[0036] 1. Melatonin Treatment Concentration Screening
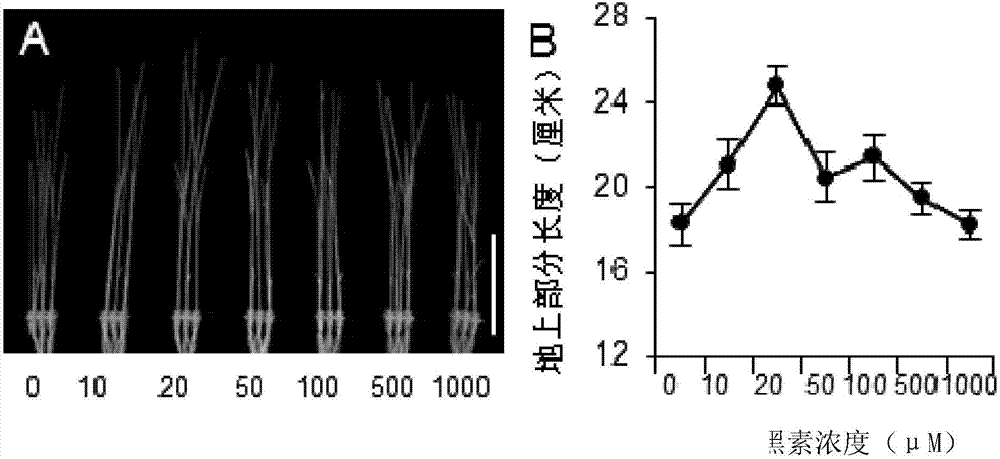
[0037] Take Nipponbare seedlings that have germinated for 2 weeks, and culture them with nutrient solutions containing different concentrations of melatonin for 10 days (16 hours of light / 8 hours of darkness per day), then take pictures, observe the growth of the plants, and measure the length of the aboveground parts of the plants. The concentrations of melatonin were 10 μM, 20 μM, 50 μM, 100 μM, 500 μM, and 1000 μM, and a control treatment without adding melatonin (ie, the concentration of melatonin was 0 μM) was set. Three replicates were performed, with 10 plants treated for each melatonin concentration in each replicate.
[0038] see photos figure 1 A, the length of the above-ground part of the plant see figure 1 b. Low concentration of melatonin (10μM and 20μM) can obviously promote the growth of seedlings. When it wa...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2, Melatonin Improves Salt Resistance of Rice and Delays Salt-Induced Leaf Senescence and Cell Death
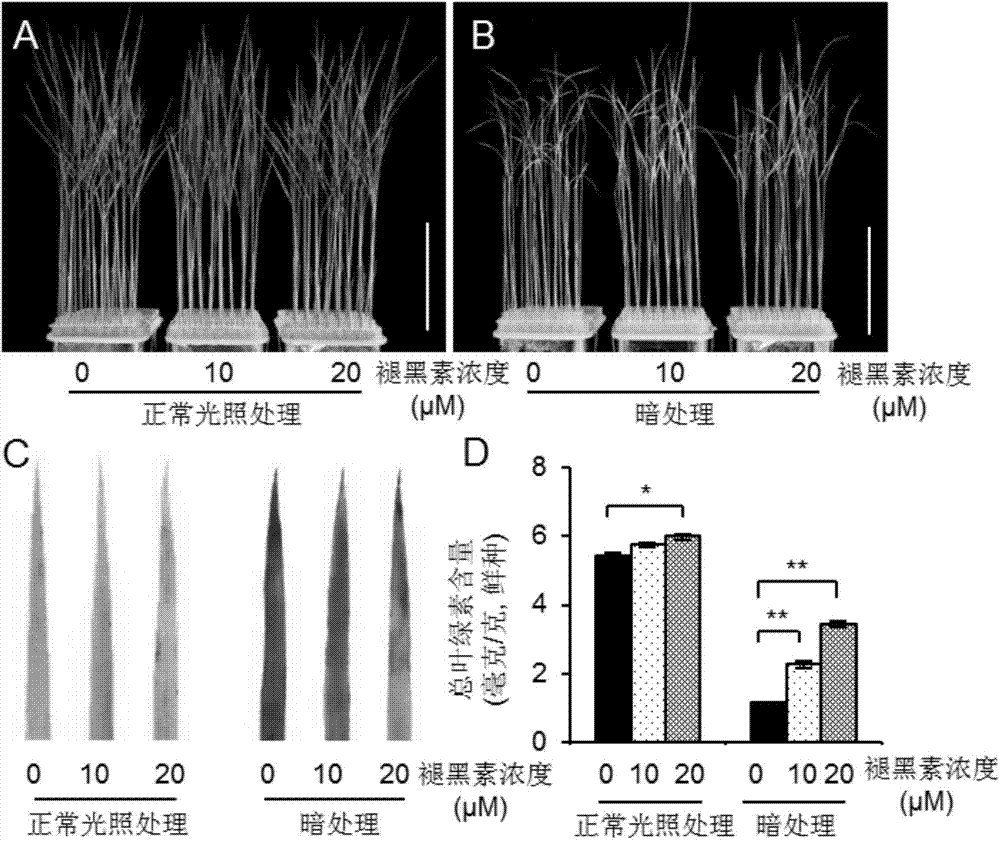
[0049] Salt treatment: Nipponbare seedlings germinated for 2 weeks were taken and cultured in a nutrient solution containing melatonin (10 μM or 20 μM) and 0.5 g / 100 ml sodium chloride for 14 days (16 hours of light / 8 hours of darkness per day) (set without adding melatonin control treatment of melanin), and then the plants were photographed, the leaves were taken for trypan blue staining, and then the leaves were taken to detect the chlorophyll content in the leaves.
[0050] Normal treatment: Nipponbare seedlings germinated for 2 weeks were taken and cultured for 14 days in a nutrient solution containing 10 μM or 20 μM melatonin (16 hours of light / 8 hours of darkness per day) (a control treatment without adding melatonin was set), and then the plants were Take pictures, take the leaves for trypan blue staining, take pictures, take the leaves and detect the ch...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Embodiment 3, melatonin reduces intracellular H 2 o 2 Horizontal delay of leaf senescence and cell death
[0054] 1. Analysis of RNA-seq sequencing results
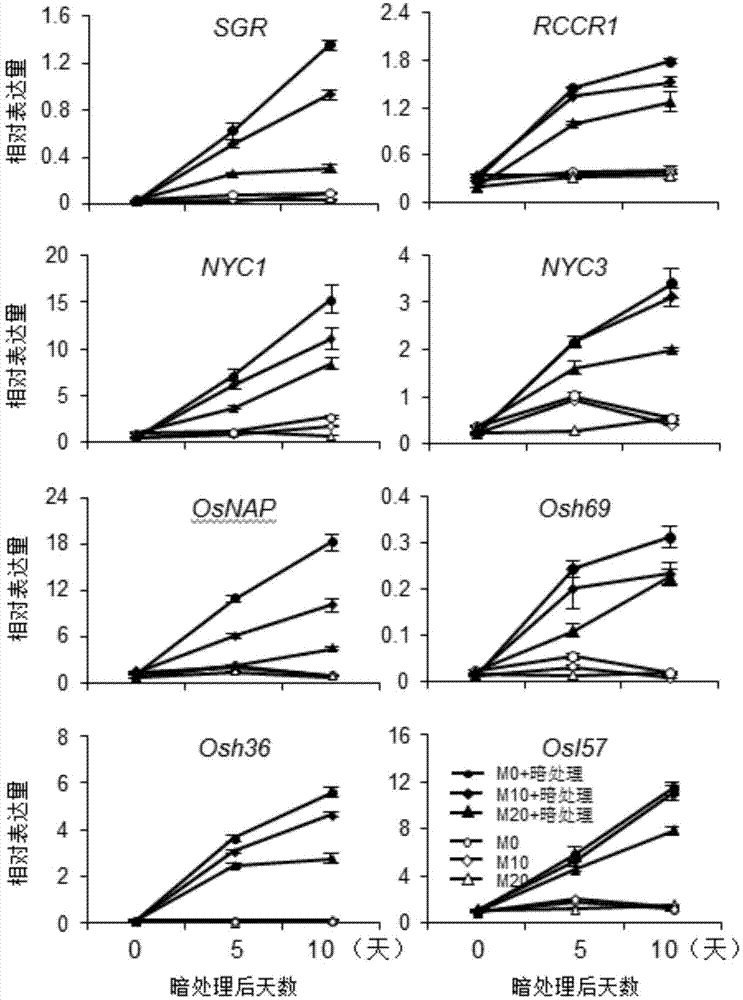
[0055] RNA-seq transcriptome analysis showed that compared with Nipponbare treated with 20 μM melatonin and Nipponbare without melatonin, a total of 457 differentially expressed genes were obtained, including 191 up-regulated genes and 266 down-regulated genes . Cluster analysis of these genes revealed that the most significantly enriched gene category among differentially expressed genes was redox-related genes, including 28 up-regulated and 21 down-regulated antioxidant genes. This result suggests that melatonin may have an important biological function in the process of hydrogen peroxide scavenging.
[0056] 2. Exogenous application of melatonin effectively reduces the content of hydrogen peroxide under dark and salt treatment
[0057] Dark treatment: Nipponbare seedlings germinated for 2 weeks were taken and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com