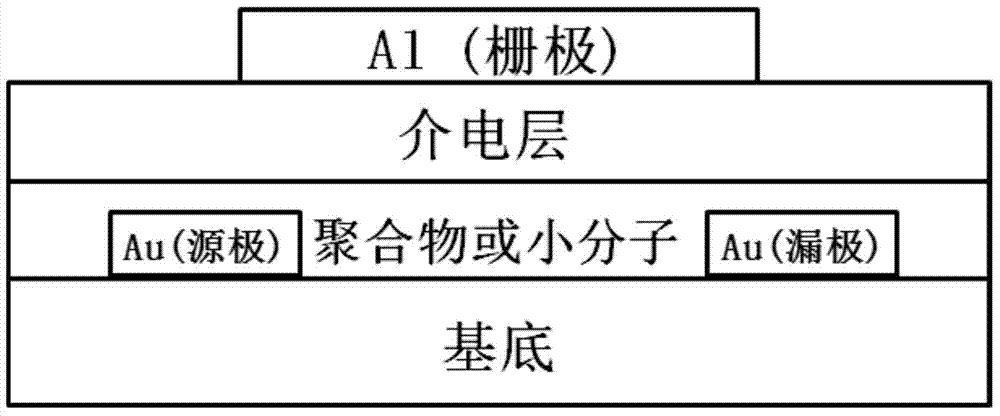
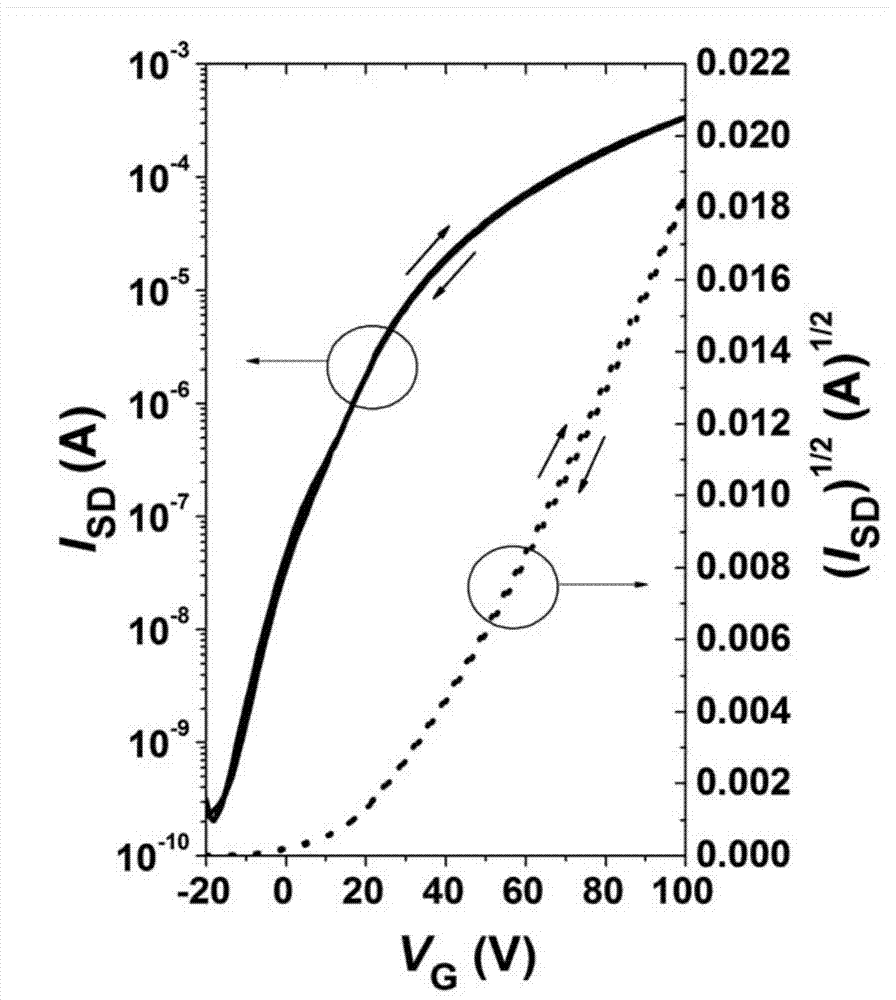
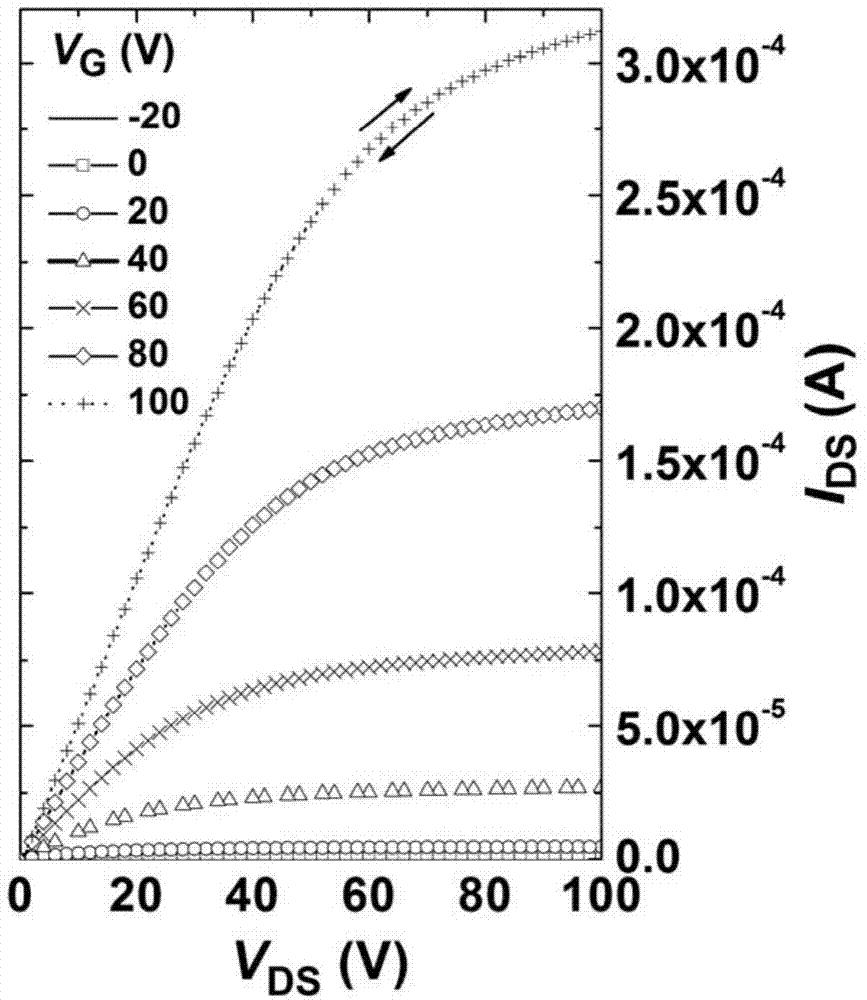
Electron withdrawing group-containing phenylene vinylene compound, and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of p-phenylene vinylene and electron-withdrawing substituents, which is applied in the field of new p-phenylene vinylene compounds containing electron-withdrawing groups, and can solve the problems of low electron mobility and poor stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095]
[0096] The synthesis process of compound 1: Chloral hydrate (9.55g, 57.89mmol) and hydroxylamine hydrochloride (10.97g, 157.89mmol) were added in deionized water (150mL). Na2 SO 4 (100g, 684.19mmol) and H 2 SO 4 (40 mL, 1 M) was added as catalyst. After uniform stirring, 3-bromo-2-fluoroaniline (10 g, 52.63 mmol) was added. After mixing, it was heated to 130°C and refluxed for 30 minutes, then the system was lowered to 80°C and filtered to obtain the product, which was washed with water to obtain light yellow solid compound 1.
Embodiment 2
[0098]
[0099] Synthesis process of compound 2: Add concentrated sulfuric acid (100mL) into a 250ml round bottom flask, heat to 50°C, compound 1 is added in batches under stirring, then warm up to 70°C for 1 hour, and then pour the system into water to quench The reaction was quenched, and after filtration, the ethyl acetate liquid separation was carried out, and the compound 2 (7.80 g, yield 61%) was obtained after separation on a silica gel column. 1 H NMR (DMSO, 400MHz, ppm): δ11.74 (s, 1H), 7.40–7.37 (dd, J H-H =8.0,J H-F =5.6Hz,1H),7.32–7.30(d,J H-H =8.0Hz,1H). 13 CNMR(DMSO,100MHz,ppm):δ182.29–182.25(d,J F-C 4 =3.9Hz), 159.17, 145.23–142.78 (d,J F-C 1 =246Hz), 138.19–138.05(d, J F-C 2 =14.0Hz), 126.47–126.45(d, J F-C 4 =1.7Hz), 121.38–121.34(d, J F-C 3 =3.8Hz), 119.89–119.85(d, J F-C 3 =3.7Hz), 118.42–118.25(d, J F-C 2 =17.3Hz).EI-MS calcd.for[M+H] + :243;found:243.Elemental Anal.calcd.for C 8 h 3 BrFNO 2 :C,39.38;H,1.24;N,5.74;found:C,39.39;H,1.40...
Embodiment 3
[0101]
[0102] The synthesis process of compound 4: Dissolve compound 3 (2.2g, 3.22mmol) in a mixture of tetrahydrofuran (30mL) and N,N'-dimethylformamide (DMF) (30mL), and add compound 6- Bromo-5-fluoroisatin (2,750mg, 3.07mmol) and K 2 CO 3 (635 mg, 4.61 mmol). After reacting at 50°C for 8 hours, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. After dissolving the residue with chloroform, wash with water, and use anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 dry. After the solvent was removed under reduced pressure, it was separated with a silica gel column (eluent: petroleum ether: dichloromethane = 1:1) to obtain an orange-yellow solid 4 (1.8 g, yield: 75%). 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ,400MHz,ppm):δ7.34–7.29(m,2H),3.86–3.82(t,J=7.4Hz,2H),1.69–1.62(m,2H),1.30–1.22(m,71H),0.90 –0.86(t,J=6.8Hz,6H). 13 C NMR (CDCl 3 ,100MHz,ppm):δ181.7(s),157.6(s),146.09–143.62(d,J F–C 1 =248.5Hz), 137.88–137.78(d, J F–C 2 =9.7Hz), 128.19(s), 122.02–121.83(d, J F–C 2 =19.6Hz), 121.60–121.56(d, J F–C 3 =3.9Hz)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com