The method of water depth adjustment to control the growth of submerged plants to control the eutrophication of lakes
A submerged plant, eutrophication technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biological water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. Slow recovery and other problems, to save manpower and material resources, increase species diversity, and improve water quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
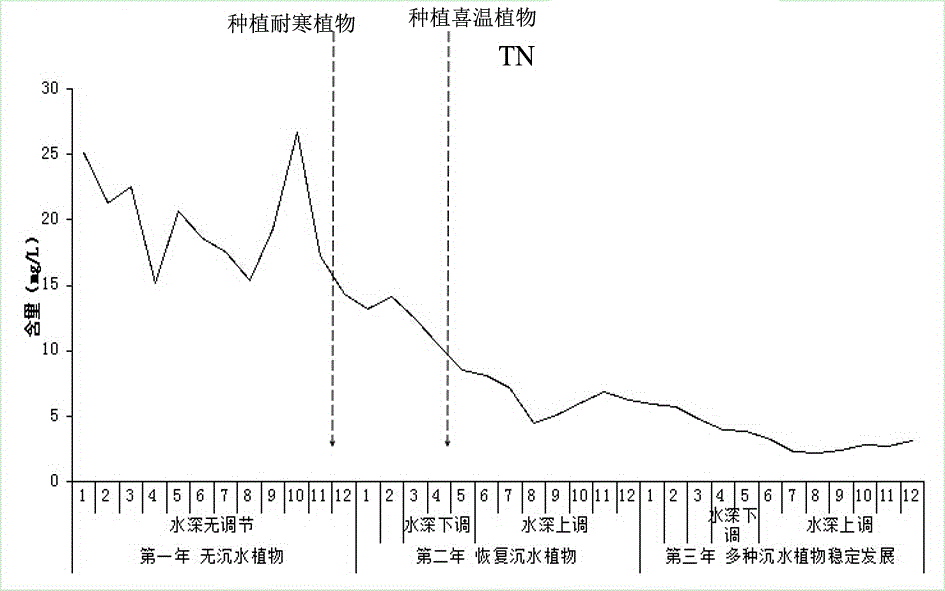
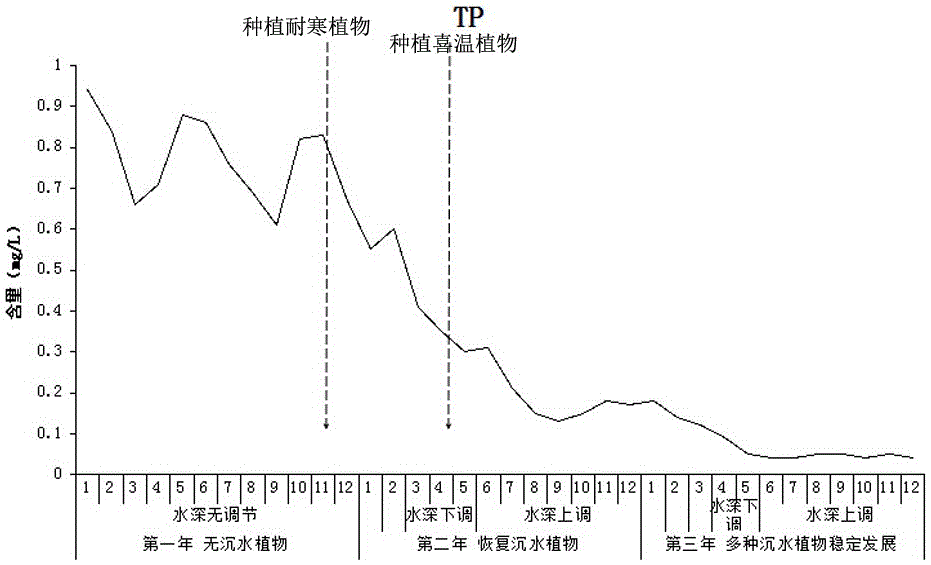
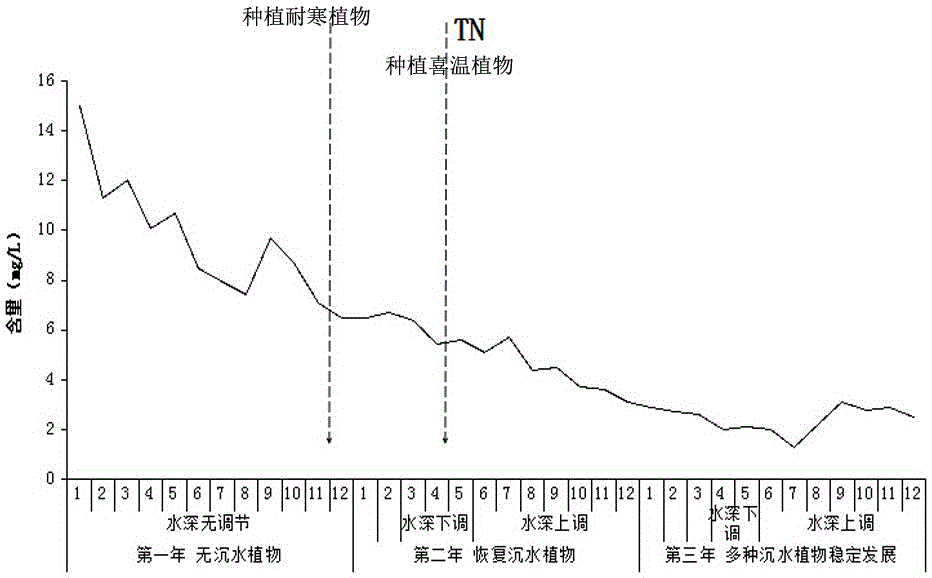
[0030] A small lake is selected as the experimental area. The maximum water depth of the experimental area is 2.4m. The water depth of the experimental area is 0-0.5m for 15%, 0.5-1.0m for 32%, 1.0-1.5m for 33%, and 1.5-2.0m. The area accounts for 15%, the 2.0-2.4m area accounts for 5%, and the experimental area is a water body with severe eutrophication. Plant the hardy plant Potamogeton crispus in November of the first year at a planting density of 100 plants / m 2 In the following seasons, as the temperature decreases, the algae in the eutrophic water body will gradually decay and settle, and the transparency of the water body will gradually increase, which will provide a better living environment for the survival and growth of plants. Therefore, Potamogeton crispus will continue from November to December. Sprouting and growing, the survival rate of plants is higher. Generally, the water body freezes from the end of December to the beginning of March in northern my country. At...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A small artificial pond reservoir is selected as the experimental area. The experimental area is a rectangular pond with a length of 120m and a width of 80m. The bottom of the experimental area is relatively flat, and the surrounding area is built with vertical stones. Therefore, the water depth of the experimental area is 0%, 0.5 -1.0m area accounts for 0%, 1.0-1.5m area accounts for 0%, 1.5-2.0m area accounts for 95%, and 2.0-2.5m area accounts for 5%. The experimental area is a breeding pond for many years, which was later abandoned, and the water body has been eutrophication. Plant the hardy plant Potamogeton crispus in November of the first year at a planting density of 100 plants / m 2 ; Potamogeton crispus will sprout and grow from November to December.
[0037] The water depth was adjusted when the ice on the water surface began to melt in early March of the second year, and the water depth was adjusted by extraction. At this time, the water depth was lowered by 0.5m...
Embodiment 3
[0043] A small lake is selected as the experimental area. The experimental area is rectangular, 250m long and 115m wide. The bottom of the experimental area is relatively flat. The water depth of the experimental area is 0-0.5m for 20%, 0.5-1.0m for 31%, and 1.0-1.5m. The area accounts for 14%, the area 1.5-2.0m accounts for 11%, the area 2.0-2.5m accounts for 4%, the area greater than 2.5m water depth accounts for 20%, and the area greater than 2.5m water depth is relatively concentrated. Eutrophication already exists in the water bodies in the experimental area.
[0044] Plant the hardy plant Potamogeton crispus in November of the first year at a planting density of 100 plants / m 2 ; Potamogeton crispus will sprout and grow from November to December.
[0045] At the beginning of March of the second year, the water depth was adjusted when the ice on the water surface began to melt, and the water depth was adjusted by means of draining the gate. At this time, the water depth was low...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com