A method of irradiation pretreatment and batch feeding to realize enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose with high substrate concentration
A lignocellulose and cellulase technology, applied in the direction of fermentation, can solve the problems of unfavorable system material transfer and heat transfer, increased system viscosity, low enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency, etc., and achieves reduction of ethanol distillation energy consumption and no material loss. , the effect of simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Effects of Radiation Irradiation on Biochemical Components of Lignocellulose and Sugar Production by Enzymatic Hydrolysis
[0025] 1. The effect of radiation irradiation on the biochemical components of lignocellulose
[0026] Irradiation treatment can directly break the molecular chain of lignocellulose, reduce its degree of polymerization, and realize the degradation of lignocellulose. Lignocellulosic materials are sun-dried or oven-dried, with a moisture content of ≤10%, bundled and placed in an irradiation box, and used under experimental conditions. 60 Co-γ rays are irradiated for pretreatment. The irradiation dose rate is 2kGy / h, and the treatment dose is 400-1200kGy. The lignocellulosic material pretreated by ray irradiation is crushed through a 20-mesh sieve to obtain lignocellulose raw material. Such as figure 1 As shown in the results of changes in the content of biochemical components in rice straw and corn stalks, the content of cellulose, hemicellulose an...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Optimization of Initial Conditions for Batch Enzymatic Hydrolysis (i.e. Adding Feedstock and Enzyme at One Time)
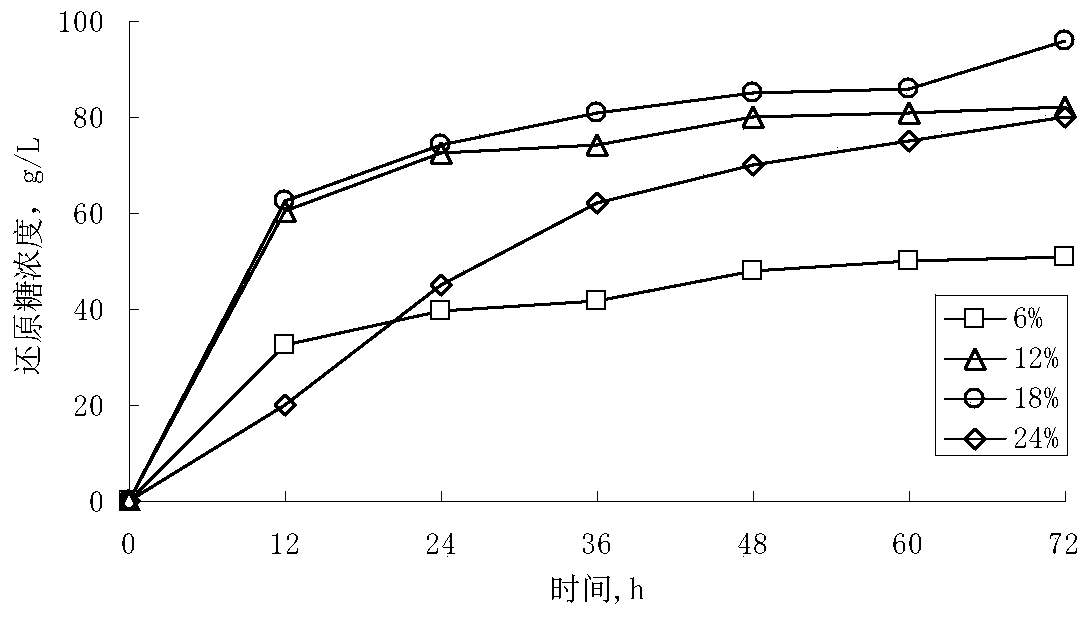
[0031] The key factors affecting the enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency of lignocellulose include initial substrate concentration, enzyme addition amount, hydrolysis time and substrate structural properties. Add the corn stalk raw material treated with a radiation dose of 1200kGy to 0.05M acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer (pH4.8), add 45FPU / g substrate cellulase ( CTec2, Novozymes, Denmark), under the conditions of pH 4.8, temperature 50°C and rotation speed 160rpm, enzymatic hydrolysis for 72 hours, the concentration of reducing sugar in the enzymatic hydrolyzate was determined by DNS method, and the initial conditions of batch enzymatic hydrolysis were optimized. Firstly, the effect of initial substrate concentration on feed saccharification was investigated, starting from image 3 It can be seen that when the initial substrate concentration is 6%, 12%, a...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Fed-batch and batch-add cellulase hydrolysis
[0035] Obtaining high-concentration reducing sugar hydrolyzate of lignocellulosic raw materials is a necessary condition to realize its high-concentration fermentation and reduce the production cost of cellulosic ethanol. In order to obtain high-concentration reducing sugar enzyme hydrolyzate, the fed-batch saccharification strategy of corn stover pretreated by radiation irradiation was studied under the optimized conditions of batch enzyme hydrolysis test. Add corn stalk 6% (wt) at 12h and 36h, add 45FPU per gram of added corn stalk substrate, the substrate concentration of final treatment is 30%, enzymatic hydrolysis reaction 144h, such as Figure 5 As shown, the final reducing sugar concentration obtained is 152.1 g / L, which is 58.4% higher than that in the batch enzyme hydrolyzate with a substrate concentration of 18%.
[0036] In order to further increase the reducing sugar concentration in the enzymatic hydrolyzate, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com