Sodium alginate oligosaccharide coated slow-release fertilizer and preparation and application thereof
A sodium alginate oligosaccharide and slow-release fertilizer technology, applied in the direction of layered/coated fertilizer, application, fertilizer mixture, etc., to achieve the effect of being suitable for large-scale promotion, low price, and solving food safety problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
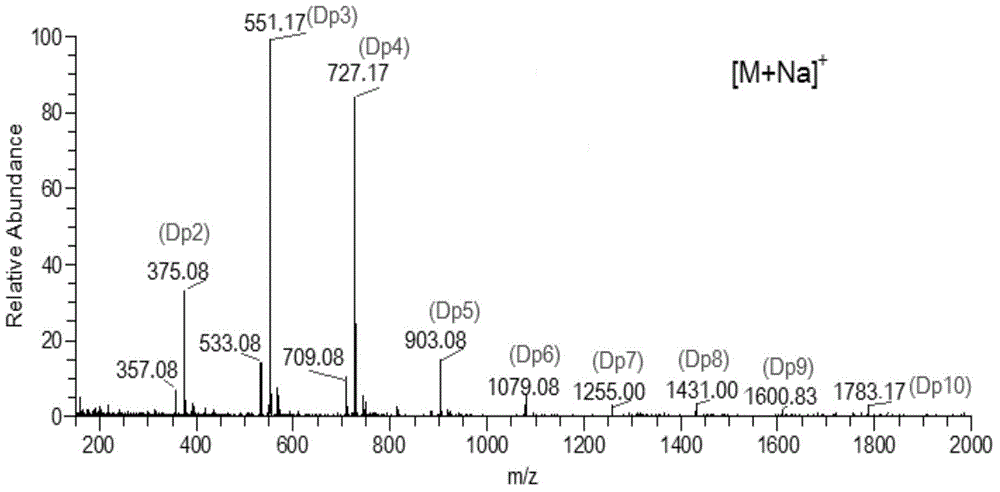
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] The preparation of the coating type slow-release nitrogen fertilizer of embodiment 1 commonly used
[0022] Coating material preparation: Weigh 1.0g starch and 2.5g sodium alginate oligosaccharide, add 100ml water, stir in 75°C water bath until completely gelatinized, this is A liquid; Add 10% potassium hydroxide dropwise to the acrylic acid to adjust the pH to 5.7, and add 0.5g of humic acid to make liquid B, then mix it with the above gelatinization solution (liquid A), add 50ml of water, stir well, add 1g The initiator potassium persulfate and the cross-linking agent polyvinylamide accounted for 1.2% of the total mass fraction, and the temperature was raised to 75°C while stirring according to the program of 5°C / min, and the constant temperature polymerization was carried out for 1h. The mass ratio of humic acid, starch, acrylic acid and sodium alginate oligosaccharide is 5:10:60:25.
[0023] Preparation of slow-release nitrogen fertilizer: Take 500g of dry urea and...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment 2 The nutrient release law of this slow-release nitrogen fertilizer
[0026] Weigh 3 parts of 10.0g (accurate to 0.01g) of the slow-release nitrogen fertilizer of Example 1, put it into a 100-mesh mesh bag, put it in a 250ml plastic bottle, add 200ml of distilled water, seal it with a cover, and let it stand in a thermostat at 25°C soak. The sampling time is 24h, 3 days, 5 days, 7 days, 9 days, 11 days, 14 days, 21 days, 28 days, 35 days. When sampling, shake the solution in the bottle evenly, transfer it to a 250ml volumetric flask to cool down to a constant volume, and use it for the bottom determination of nitrogen. Then re-add 200ml of distilled water to the plastic bottle, cover and seal it, and then put it into a constant temperature box to continue soaking until the cumulative dissolution rate of nutrients reaches 80%. The results are shown in Table 1. The slow-release fertilizer has a good slow-release effect. The theoretical slow-release period is ...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Embodiment 3 Application of this slow-release nitrogen fertilizer improves the biomass and nitrogen use efficiency of Chinese cabbage
[0030] This experiment was carried out from August to November in 2012, and three treatments were designed: treatment 1, no nitrogen fertilizer treatment; treatment 2, common urea treatment; treatment 3, slow-release nitrogen fertilizer treatment in Example 1. Each treatment was repeated 5 times. Each pot is filled with 3kg of soil, and one plant is planted in each pot. The amount of nitrogen used in ordinary urea and slow-release urea is 0.2g / kg soil, N-P 2 o 5 -K 2 The ratio of O application is 1:0.45:2.1 (according to the amount of fertilizer required by cabbage), calcium superphosphate is used for phosphate fertilizer, and potassium sulfate is used for potassium fertilizer. All test fertilizers were applied as base fertilizer to the soil layer 10 cm below the soil surface. After harvesting, the biomass and nitrogen use efficien...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com