Reactor and method for producing hydrogen sulfide
A reactor, hydrogen sulfide technology, used in chemical instruments and methods, hydrogen sulfide, chemical methods for reacting liquids and gaseous media, etc., and can solve a large number of problems.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
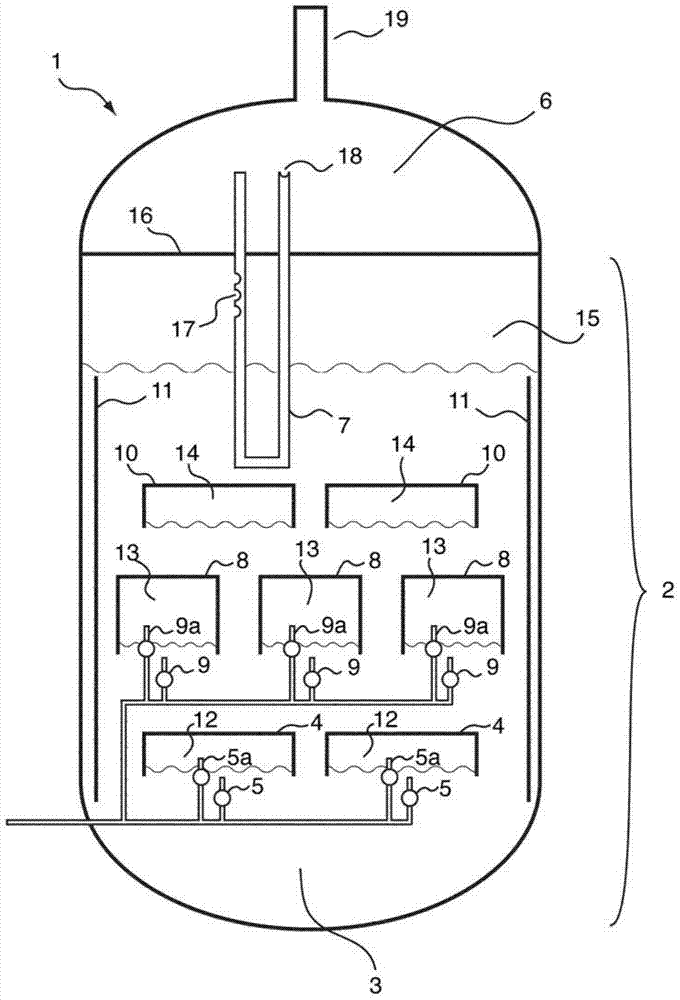
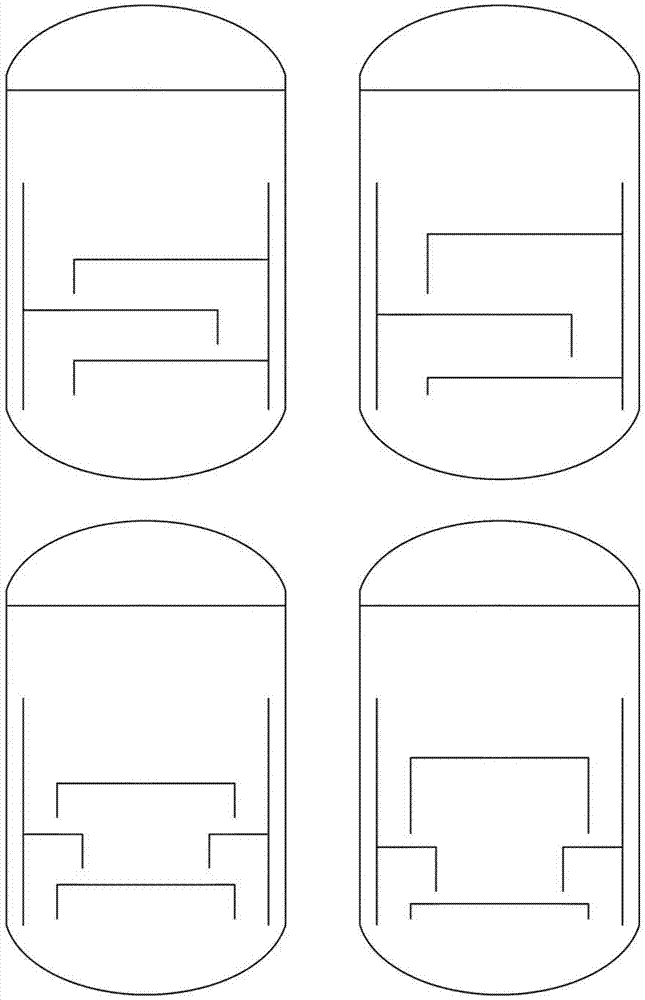
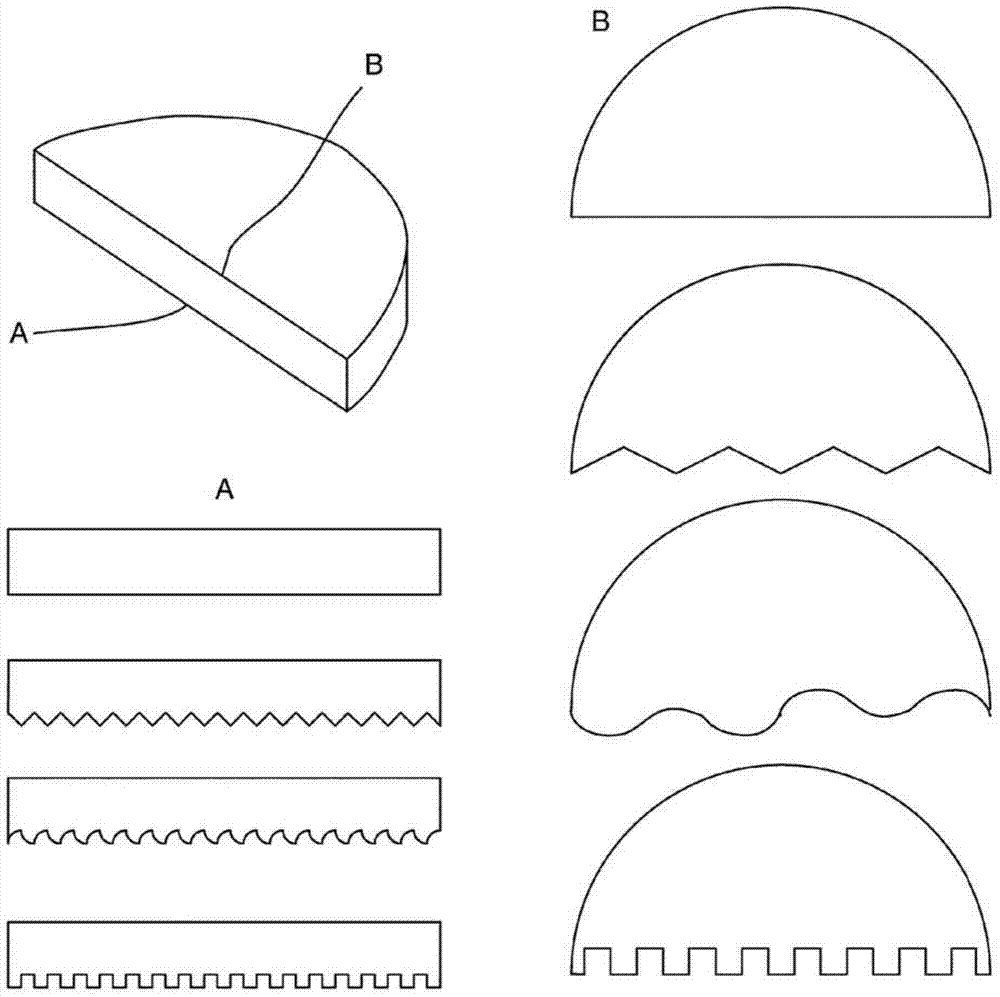
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0110] Embodiment 1 (comparative example)
[0111] 1000 l(STP) / h of hydrogen were introduced continuously via a glass frit at the base into a tube with an inner diameter of 5 cm which had been filled with liquid sulfur up to a height of 1 m. The sulfur consumed is compensated by further metering in liquid sulfur while keeping the filling level constant. Sulfur removed from the product gas stream by condensation is recycled in liquid form into the upper region of the tube. Above the liquid sulfur, sheathed thermocouples for measuring temperature were placed at intervals of 10 cm. When the reactor was electrically heated to 400°C via the outer wall, there was a uniform temperature of about 397°C within the sulfur. However, the thermocouple located above the sulfur showed the highest temperature of 520 °C. In addition, above the liquid sulfur, a sample of the new material made of standard stainless steel (1.4571) was provided at the position of the highest temperature. After ...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Embodiment 2 (comparative example)
[0113] Example 1 was repeated, except that the height of the liquid sulfur was raised to 4m. Maintain the highest temperature value above the liquid sulfur. Severe corrosion phenomena also occurred on material samples.
Embodiment 3
[0114] Embodiment 3 (comparative example)
[0115] Repeat Example 2, except that 15% by weight of powdered Co 3 o 4 MoO 3 / Al 2 o 3 The catalyst is suspended in liquid sulfur. Maintain the highest temperature value above the liquid sulfur. Severe corrosion phenomena also occurred on material samples.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com